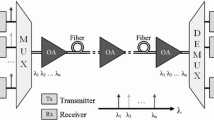
Abstract
Placement of wavelength converters in an arbitrary mesh network is known to be a NP-complete problem. So far, this problem has been solved by heuristic strategies or by the application of optimization tools such as genetic algorithms. In this paper, we introduce a novel evolutionary algorithm: particle swarm optimization (PSO) to find the optimal solution to the converters placement problem. The major advantage of this algorithm is that does not need to build up a search tree or to create auxiliary graphs in find the optimal solutions. In addition, the computed results show that only a few particles are needed to search the optimal solutions of the placement of wavelength converters problem in an arbitrary network. Experiments have been conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed evolutionary algorithm. It was found that the efficiency of PSO can even exceed 90% under certain circumstances. In order to further improve the efficiency in obtaining the optimal solutions, four strategic initialization schemes are investigated and compared with the random initializations of PSO particles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Ramaswami K. N. Sivarajan (1995) ArticleTitleRouting and wavelength assignment in all-optical networks IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 3 IssueID5 489–500 Occurrence Handle10.1109/90.469957
S. Subramaniam, R. A. Barry, Wavelength Assignment in Fixed Routing WDM Networks, vol. 1, Proceedings of IEEE ICC′97 (Montreal, Canada, June 1997), pp. 406–410
J. Jue, G. Xiao, An adaptive routing algorithm for wavelength routed optical networks with a distributed control scheme, Proceedings of Ninth International Conference on Comp. Comm. And Networks, vol. 1 (Las Vegas, NV, USA, Oct. 2000), pp. 192–197
A. Mokhtar M. Azizoglu (1998) ArticleTitleAdaptive wavelength routing in all-optical networks IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 6 IssueID2 197–206 Occurrence Handle10.1109/90.664268
R. A. Barry P. A. Humblet (1996) ArticleTitleModels of blocking probability in all-optical networks with and without wavelength changes IEEE Journal of Selected Areas in Communications 14 IssueID5 858–867 Occurrence Handle10.1109/49.510909
A. Birman (1996) ArticleTitleComputing approximate blocking probabilities for a class of all-optical networks IEEE Journal of Selected Areas in Communications 14 IssueID5 852–857 Occurrence Handle10.1109/49.510908
S. Subramaniam M. Azizoğlu A. K. Samani (1996) ArticleTitleAll-optical networks with sparse wavelength conversion IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 4 IssueID4 544–557 Occurrence Handle10.1109/90.532864
K. R. Venugopal M. ShivaKumar P. Sreenivasa Kumar (2001) ArticleTitleA heuristic for placement of limited range wavelength converters in all-optical networks Computer Networks 35 IssueID2–3 143–163 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1389-1286(00)00145-6
C. Vijayanand M. Shiva Kumar K. R. Venugopal P. Srenivasa Kumar (2000) ArticleTitleConverter placement in all-optical networks using genetic algorithms Computer Communications 23 IssueID13 1223–1234 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0140-3664(00)00196-1
L. Li, S. Thiagarajan, A. Somani, Efficient Algorithms for Wavelength Converter Placement in All-optical Networks, Iowa State University, Ames, IA. [Online] Available:http://shasta.ee.iastate.edu/∼ling/publications/spie99.txt
S. Gao X. Jia C. Huang D. Z. Du (2003) ArticleTitleAn optimisation model for placement of wavelength converters to minimize blocking probability in WDM networks IEEE/OSA Journal of Lightwave Technology 21 IssueID3 684–694 Occurrence Handle10.1109/JLT.2003.809584
S. Thiagarajan A. K. Somani (2003) ArticleTitleOptimal wavelength converter placement in arbitrary topology wavelength-routed networks Computer Communications 26 IssueID9 975–985 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0140-3664(02)00194-9
C. F. Teo, Y. C. Foo, S. F. Chien, Andy L. Y. Low, B. Venkatesh, A. H. You, Optimal Placement of Wavelength Converters in WDM Networks Using Particle Swarm Optimizer, Proc. IEEE ICC′2004, (Paris, France, June 2004), vol. 1, pp. 1669–1673
J. Kennedy, W. M. Spears, Matching algorithms to problems: an experimental test of the particle swarm and some genetic algorithms on the multimodal problem generator, Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence, vol. 1 (Anchorage, AK, USA, May. 1998), pp. 78–83
J. Kennedy, R. C. Eberhart, Particle swarm optimization, Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Neural Networks, vol. 1 (Piscataway, NJ, USA, Dec. 1995), pp. 1942–1948
M. Clerc J. Kennedy (2002) ArticleTitleThe particle swarm: explosion stability and convergence in a multi-dimensional complex space IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computing 6 IssueID1 58–73 Occurrence Handle10.1109/4235.985692
S. Thiagarajan, A. K. Somani, An efficient algorithm for optimal wavelength converter placement on wavelength-routed networks with arbitrary topologies, Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM′99, vol. 2 (New York, NY, USA, March 1999), pp. 916–923
J. Kennedy, R. C. Eberhart, A discrete binary version of the particle swarm algorithm, Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computing, Cybernetics and Simulation, vol. 5 (Orlando, FL, USA, Oct. 1997), pp. 4104–4108
S. Subramaniam, Blocking performance of wavelength-routing networks, in Optical WDM Networks: principles and Practice, K. M. Sivalingam and S. Subramaniam, Eds., (Norwell, MA, Kluwer, 2000)
R. C. Eberhart, Y. Shi, Particle swarm optimization: developments, applications and resources, Proceedings of 2001 Congress on Evol. Comput., vol. 1 (Seoul, Korea, July 2001), pp. 81–86
A. El-Gallad, M. El-Hawary, A. Sallam, A. Kalas, Enhancing the particle swarm optimizer via proper parameters selection, Proceedings of IEEE Canadian Conference on Electrical & Computer Engineering, vol. 2 (Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada, May. 2002), pp. 792–797.
D. E. Golberg (1985) Optimal Initial Population Size for Binary Coded Genetic Algorithms, TGGA report 850001, The Clearing House for Genetic Algorithms University of Alabama Tuscalossa
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teo, C.F., Foo, Y.C., Chien, S.F. et al. Wavelength Converters Placement in All Optical Networks Using Particle Swarm Optimization. Photon Netw Commun 10, 23–37 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-005-1693-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-005-1693-z