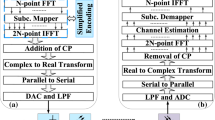
Abstract
In single-carrier wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) systems, the spectral efficiency can be increased by reducing the channel spacing through digital signal processing (DSP). Two major issues with using tight filtering are cross talk between channels and inter-symbol interference (ISI) within a channel. By fulfilling the Nyquist criterion, Nyquist spectral-shaped WDM systems can achieve narrow channel spacings close to the symbol rate \((\hbox {R}_{\mathrm{S}})\) with negligible cross talk and ISI. In principle, DSP can generate any signals with arbitrary waveforms and spectrum shapes. However, the complexity of DSP is limited by its cost and power consumption. It is necessary to optimize the DSP to achieve the required performance at a minimum complexity. In this paper, we first introduced the background of digital signal processing for Nyquist spectral shaping in optical fiber WDM systems. Then, we investigated the use of digital finite impulse response (FIR) filters to generate Nyquist-WDM 16-ary quadrature amplitude modulation (16QAM) signals with the raised-cosine (RC) and root-raised-cosine (RRC) shape spectra. The system performance of both the RC and RRC spectra is also examined. Moreover, we explored the various methods to reduce digital-to-analog converter (DAC) sampling speed, such as using super-Gaussian electrical filters (E-filter) and spectral pre-emphasis. We also discussed receiver-side matched filter design for Nyquist-WDM receiver optimization.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, G.: Recent advances in coherent optical communication. Adv. Opt. Photon. 1, 279–307 (2009)
Tkach, R.W.: Scaling optical communications for the next decade and beyond. Bell Labs Tech. J. 14(4), 3–9 (2010)
Shieh, W., Bao, H., Tang, Y.: Coherent optical OFDM: theory and design. Opt. Express 16(2), 841–859 (2008)
Soto, M.A., Alem, M., Shoaie, M.A., Vedadi, A., Brès, C.-S., Thévenaz, L., Schneider, T.: Optical sinc-shaped Nyquist pulses of exceptional quality. Nat. Commun. 4, 3898–3908 (2013)
Liu, X., Chandrasekhar, S., Zhu, B., Winzer, P.J., Gnauck, A.H., Peckham, D.W.: Transmission of a 448-Gb/s reduced-guard-interval CO-OFDM signal with a 60-GHz optical bandwidth over 2000 km of ULAF and five 80-GHz-Grid ROADMs. In: Proc. OFC/NFOEC, paper PDPC2 (2010)
Proakis, J.G.: Digital Communications, Chap. 9, 4th edn. McGGraw-Hill, New York (2001)
Cartledge, J.C., Downie, J.D., Hurley, J.E., Karar, A.S., Jiang, Y., Roberts, K.: Pulse shaping for 112 Gbit/s polarization multiplexed 16-QAM signals using a 21 Gsa/s DAC. Opt. Express 19(26), B628–B635 (2011)
Cai, J.-X.: 100G transmission over transoceanic distance with high spectral efficiency and large capacity. J. Lightw. Technol. 30(24), 3845–3856 (2012)
Fickers, J., Ghazisaeidi, A., Salsi, M., Charlet, G., Horlin, F., Emplit, P., Bigo, S.: Design Rules for Pulse Shaping in PDM-QPSK and PDM-16QAM Nyquist-WDM Coherent Optical Transmission Systems. In: Proc. ECOC, 2012, paper We.1.C.2 (2012)
Xie, C., Raybon, G., Winzer, P.J.: Hybrid 224-Gb/s and 112-Gb/s PDM-QPSK transmission at 50-GHz channel spacing over 1200-km dispersion-managed LEAF spans and 3 ROADMs. In: Proc. OFC/NFOEC, 2011, paper PDPD2 (2011)
Rafique, D., Napoli, A., Calabro, S., Spinnler, B.: Digital preemphasis in optical communication systems: on the DAC requirements for terabit transmission applications. J. Lightw. Technol. 32(19), 3247–3256 (2014)
Zhou, X., Nelson, L., Issac, R., Magill, P., Zhu, B., Peckham, D.: 1200km Transmission of 50GHz spaced, 5\(\times \)504-Gb/s PDM-32-64 hybrid QAM using Electrical and Optical Spectral Shaping. In: Proc. OFC/NFOEC, 2012, paper OM2A.2 (2012)
Randel, S., Pilori, D., Corteselli, S., Raybon, G., Adamiecki, A., Gnauck, A., Chandrasekhar, S., Winzer, P., Altenhain, L., Bielik, A., Schmid, R.: All-Electronic Flexibly Programmable 864-Gb/s Single-Carrier PMD-64-QAM. In: Proc. OFC/NFOEC, 2014, paper Th5C.8 (2014)
Cai, J.-X., Cai, Y., Davidson, C.R., Foursa, D.G., Lucero, A., Sinkin, O., Patterson, W., Pilipetskii, A., Mohs, G., Bergano, N.S.: Transmission of 96\(\times \)100G pre-filtered PDM-RZ-QPSK channels with 300 % spectral efficiency over 10,608km and 400 % spectral efficiency over 4368 km. In: Proc. OFC/NFOEC, 2010, paper PDPB10 (2010)
Bosco, G.: Spectral shaping in ultra-dense WDM systems: optical versus electrical approaches. In: Proc. OFC/NFOEC, 2012, paper OM3H.1 (2012)
Pan, J., Isautier, P., Ralph, S.E.: Digital pre-shaping for narrowband filtering impairment compensation in superchannel applications. In: Proc. Optical Sensors, 2013, paper JT3A. 1 (2013)
Mazurczyk, M.: Optical spectral shaping and high spectral efficiency in long haul systems. In: Proc. OFC/NFOEC, 2014, paper Tu3J.4 (2014)
Duthel, T., Raabe, C., Hermann, P., Whiteaway, J.E., Geyer, J.C., Fludger, C.R.S., Kupfer, T.: DAC enabled spectrally efficient CP-QPSK at 28Gbaud. In: Proc. ECOC, 2012, paper Tu.4.A.4, (2012)
Wang, J., Xie, C., Pan, Z.: Optimization of DSP to generate spectrally efficient 16QAM Nyquist-WDM signals. Photon. Technol. Lett. 25(8), 772–775 (2013)
Arik, S.O., Ho, K.-P., Kahn, J.M.: Optical network scaling: roles of spectral and spatial aggregation. Opt. Express 22(24), 29868–29887 (2014)
Wang, J., Xie, C., Pan, Z.: Reducing equalizer complexity in coherent receivers for Nyquist spectrally shaped systems with matched filters. In: Proc. OFC/NFOEC, 2013, paper OTu2I.3 (2013)
Gnauck, A.H., Winzer, P.J., Chandrasekhar, S., Liu, X., Zhu, B., Peckham, D.W.: Spectrally efficient long-haul WDM transmission using 224-Gb/s polarization-multiplexed 16-QAM. J. Lightw. Technol. 29(4), 373–377 (2011)
Winzer, P.J.: Optical networking beyond WDM. IEEE Photon. J. 4(2), 647–651 (2012)
Dutta, A.K.: WDM Technologies: Optical Networks. Elsevier Science, New York (2004)
Yu, J., Zhou, X.: Ultra-high-capacity DWDM transmission system for 100G and beyond. IEEE Commun. Mag. 48, S56–S64 (2010)
Cvijetic, N., Cvijetic, M., Huang, M.-F., Ip, E., Huang, Y.-K., Wang, T.: Terabit optical access networks based on WDM-OFDMA-PON. J. Lightw. Technol. 30(4), 493–503 (2012)
Pan, Z., Wang, J., Weng, Y.: Investigation of digital-to-analog converter (DAC) in digital Nyquist-WDM transmission systems. In: Proc. 8th POEM, paper OT2C.1 (2015)
Mazurczyk, M.: Spectral shaping in long haul optical coherent systems with high spectral efficiency. J. Lightw. Technol. 32(16), 2915–2924 (2014)
Dong, Z., Li, X., Yu, J., Chi, N.: 6\(\times \)144-Gb/s Nyquist-WDM PDM-64QAM generation and transmission on a 12-GHz WDM grid equipped with Nyquist-band pre-equalization. J. Lightw. Technol. 30(23), 3687–3692 (2012)
Glover, I., Grant, P.: Digital Communications, Chap. 2. Pearson Education, New York (2004)
Wang, J., Jiang, X., Weng, Y., He, X., Pan, Z.: Non-data-aided chromatic dispersion estimation for Nyquist spectrally shaped fiber transmission systems. In: Proc. 23rd WOCC, paper O1.1 (2014)
Kikuchi, K.: Clock recovering characteristics of adaptive finite-impulse response filters in digital coherent optical receivers. Opt. Express 19(6), 5611–5619 (2011)
Weng, Y., Wang, J., Pan, Z.: Comparison of advanced DSP techniques for spectrally efficient Nyquist-WDM signal generation using digital FIR filters at transmitters based on higher-order modulation formats. In: Proc. SPIE 9773, 977304 (2016)
Winzer, P.J.: High-spectral-efficiency optical modulation formats. J. Lightw. Technol. 30(24), 3824–3835 (2012)
Boyd, K.P.: Optical Communication Systems: Fundamentals, Techniques and Applications, Chap. 3. Nova Science, New York (2015)
Reis, J.D., Shahpari, A., Teixeira, A.L.: Performance optimization of Nyquist signaling for spectrally efficient optical access networks. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 7(2), A200–A208 (2015)
Weng, Y., Wang, J., Pan, Z.: Spectrally Efficient Nyquist-WDM PDM-64QAM Signal Generation using Interleaved DAC with Zero-Order Holding. In: Proc. OFC/NFOEC, paper Th2A.34 (2016)
Rafique, D., Rahman, T., Napoli, A., Spinnler, B.: Digital pre-emphasis in optical communication systems: on the nonlinear performance. J. Lightw. Technol. 33(1), 140–150 (2015)
Winzer, P.J., Pfennigbauer, M., Essiambre, R.-J.: Coherent crosstalk in ultradense WDM systems. J. Lightw. Technol. 23(4), 1734–1744 (2005)
Wang, J., Xie, C., Pan, Z.: Generation of spectrally efficient Nyquist-WDM QPSK signals using digital FIR or FDE filters at transmitters. J. Lightw. Technol. 30(23), 3679–3686 (2012)
Curri, V., Carena, A., Bosco, G., Poggiolini, P., Forghieri, F.: Optimization of DSP-based Nyquist-WDM PM-16QAM transmitter. In: Proc. ECOC, paper Tu.4.A.5 (2012)
Pan, J., Liu, C., Detwiler, T., Stark, A.J., Hsueh, Y.-T., Ralph, S.E.: Inter-channel crosstalk cancellation for Nyquist-WDM superchannel applications. J. Lightw. Technol. 30(24), 3993–3999 (2012)
Rafique, D., Napoli, A., Calabro, S., Spinnler, B.: Digital preemphasis in optical communication systems: on the DAC requirements for terabit transmission applications. J. Lightw. Technol. 32(19), 3247–3256 (2014)
Pan, Z., Wang, J., Weng, Y.: Digital signal processing techniques in Nyquist-WDM transmission system. In: Proc. 14th ICOCN, paper Sa2D.2 (2015)
Xiang, M., Tang, H., Fu, S., Tang, M., Shum, P., Liu, D.: Performance comparison of offset-16QAM and 16QAM for Nyquist WDM superchannel with digital spectral shaping. J. Lightw. Technol. 33(17), 3623–3629 (2015)
Fatadin, I., Ives, D., Savory, S.J.: Blind equalization and carrier phase recovery in a 16-QAM optical coherent system. J. Lightw. Technol. 27(15), 3042–3049 (2009)
Wang, J., Xie, C., Pan, Z.: Matched filter design for RRC spectrally shaped Nyquist-WDM systems. Photon. Technol. Lett. 25(23), 2263–2266 (2013)
Leibrich, J., Rosenkranz, W.: Frequency Domain Equalization with Minimum Complexity in Coherent Optical Transmission Systems. In: Proc. OFC/NFOEC, paper OWV1 (2010)
Zhu, C., Corcoran, B., Tran, A.V., Lowery, A.J.: Nyquist-WDM with low-complexity joint matched filtering and adaptive equalization. Photon. Technol. Lett. 26(23), 2323–2326 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, Z., Wang, J. & Weng, Y. Digital signal processing techniques in Nyquist-WDM transmission systems. Photon Netw Commun 32, 236–245 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-015-0598-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-015-0598-8