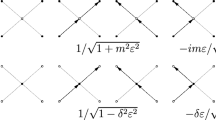
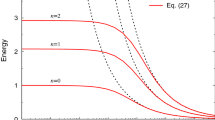
Abstract
We demonstrate the equivalence of two representations of many-body relativistic quantum mechanics: the quantum lattice-gas method and the path integral method. The former serves as an efficient lattice-based quantum algorithm to simulate the space-time dynamics of a system of Dirac particles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. P. Feynman and A. R. Hibbs, Quantum Mechanics and Path Integrals (McGraw-Hill, 1965). Problem 2–6 on page 34
R. P. Feynman, Geometry of dirac equ. in 1 dimension. California Institute of Technology CIT archives, (13.3), February 1946
Jacobson T. and Schulman L.S. (1984). J. Phys. A: Math. Gen 17:375
Jacobson T. (1984). J. Phys. A: Math. Gen 17: 2433
Boghosian B.M. and Taylor IV W. (1998). Phys. Rev E 57:54
Feynman R.P. (1948). Rev. Modern Phys 20(2):367
Schweber S.S. (1986). Rev. Modern Phys 449(2):449
B. Thaller, Visualizing the kinematics of relativistic wave packets. arXiv:quant-ph, (0409079):7, 2004.
Bialynicki-Birula I. (1994). Phys. Rev. D 49(12):6920
Yepez J. (2001). Int. J. Modern Phys. C 12(9):1285
Yepez J. and Boghosian B. (2002). Comput. Phys. Commun 146(3):280
Yepez J. Phys Rev E (046702), 18 (2001).
Shor P.W. (1995). Phys. Rev. A 52:R2493
Knill E., Laflamme R., and Zurek W.H. (1998). Science 279:342
Pravia M., Chen Z., Yepez J., Cory D.G. (2002). Comput. Phys. Commun 146(3):339
Pravia M., Chen Z., Yepez J., Cory D.G. (2003). Quant Informat Process 2:1
Z. Chen, J. Yepez, and D. G. Cory, Phys. Rev. A To appear 2006. arXiv:quant-ph/ 0410198.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jeffrey Yepez: This discrete path integral formalism, included in the beginning of this paper, was presented on August 20, 2004 as an invited talk entitled “Lattice-based quantum algorithms for computational phsyics” at the 13th International Conference on the Discrete Simulation of Fluid Dynamics, hosted by Tufts University in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The quantum algorithm for the Dirac system in 3+1 dimensions, included at the end of this paper, was presented on May 9, 2002 at the Quantum Computation for Physical Modeling Workshop 2002, hosted by the Air Force Research Laboratory in Edgartown, Massachusetts.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yepez, J. Relativistic Path Integral as a Lattice-based Quantum Algorithm. Quantum Inf Process 4, 471–509 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-005-0009-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-005-0009-7
Keywords
- Dirac equation
- quantum computing
- quantum lattice gas
- many-body relativistic quantum mechanics
- path integrals