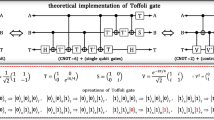
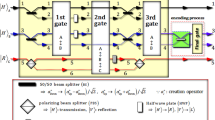
Abstract
Quantum logic operations can be implemented using nonlinear phase shifts (the Kerr effect) or the quantum Zeno effect based on strong two-photon absorption. Both approaches utilize three-level atoms, where the upper level is tuned on resonance for the Zeno gates and off-resonance for the nonlinear phase gates. The performance of nonlinear phase gates and Zeno gates are compared under conditions where the parameters of the resonant cavities and three-level atoms are the same in both cases. It is found that the expected performance is comparable for the two approaches despite the fundamental differences between the Zeno and Kerr effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cirac J.I., Zoller P.: Quantum computations with cold trapped ions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 4091 (1995)
Monroe C., Meekhof D.M., King B.E., Itano W.M., Wineland D.J.: Demonstration of a fundamental quantum logic gate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 4714 (1995)
Monz T., Kim K., Villar A.S., Schindler P., Chwalla M., Riebe M., Roos C.F., Häffner H., Hänsel W., Hennrich M., Blatt R.: Realization of universal ion-trap quantum computation with decoherence-free qubits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 200503 (2009)
Jaksch D., Briegel H.-J., Cirac J.I., Gardiner C.W., Zoller P.: Entanglement of atoms via cold controlled collisions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 1975 (1999)
Isenhower L., Urban E., Zhang X.L., Gill A.T., Henage T., Johnson T.A., Walker T.G., Saffman M.: Demonstration of a neutral atom controlled-NOT quantum gate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 010503 (2010)
DeMille D.: Quantum computation with trapped polar molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 067901 (2002)
André A., DeMille D., Doyle J.M., Lukin M.D., Maxwell S.E., Rabl P., Schoelkopf R.J., Zoller P.: A coherent all-electrical interface between polar molecules and mesoscopic superconducting resonators. Nat. Phys. 2, 636 (2006)
Rabl P., DeMille D., Doyle J.M., Lukin M.D., Schoelkopf R.J., Zoller P.: Hybrid quantum processors: molecular ensembles as quantum memory for solid state circuits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 033003 (2006)
Yelin S.F., Kirby K., Côté R.: Schemes for robust quantum computation with polar molecules. Phys. Rev. A 74, 050301(R) (2006)
Yamamoto T., Pashkin Yu.A., Astafiev O., Nakamura Y., Tsai J.S.: Demonstration of conditional gate operation using superconducting charge qubits. Nature 425, 941 (2003)
Plantenberg J.H., de Groot P.C., Harmans C.J.P.M., Mooij J.E.: Demonstration of controlled-NOT quantum gates on a pair of superconducting quantum bits. Nature 447, 836 (2007)
Niskanen A.O., Harrabi K., Yoshihara F., Nakamura Y., Lloyd S., Tsai J.S.: Quantum coherent tunable coupling of superconducting qubits. Science 316, 723 (2007)
Lucero E., Hofheinz M., Ansmann M., Bialczak R.C., Katz N., Neeley Matthew, O’Connell A.D., Wang H., Cleland A.N., Martinis J.M.: High-fidelity gates in a Josephson qubit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 247001 (2008)
DiCarlo L., Chow J.M., Gambetta J.M., Bishop L.S., Johnson B.R., Schuster D.I., Majer J., Blais A., Frunzio L., Girvin S.M., Schoelkopf R.J.: Demonstration of two-qubit algorithms with a superconducting quantum processor. Nature 460, 240 (2009)
Loss D., DiVincenzo D.P.: Quantum computation with quantum dots. Phys. Rev. A 57, 120 (1998)
Kane B.E.: A silicon-based nuclear spin quantum computer. Nature 393, 133 (1998)
Xu K.J., Huang Y.P., Moore M.G., Piermarocchi C.: Two-qubit conditional phase gate in laser-excited semiconductor quantum dots using the quantum Zeno effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 037401 (2009)
Milburn G.J.: Quantum optical Fredkin gate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 62, 2124 (1989)
Turchette Q.A., Hood C.J., Lange W., Mabuchi H., Kimble H.J.: Measurement of conditional phase shifts for quantum logic. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 4710 (1995)
Knill E., Laflamme R., Milburn G.J.: A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics. Nature 409, 46 (2001)
Pittman T.B., Jacobs B.C., Franson J.D.: Probabilistic quantum logic operations using polarizing beam splitters. Phys. Rev. A 64, 062311 (2001)
Pittman T.B., Jacobs B.C., Franson J.D.: Demonstration of nondeterministic quantum logic operations using linear optical elements. Phys. Rev. Lett 88, 257902 (2002)
Franson J.D., Donegan M.M., Fitch M.J., Jacobs B.C., Pittman T.B.: High-fidelity quantum logic operations using linear optical elements. Phys. Rev. Lett 89, 137901 (2002)
Pittman T.B., Fitch M.J., Jacobs B.C., Franson J.D.: Experimental controlled-NOT logic gate for single photons in the coincidence basis. Phys. Rev. A 68, 032316 (2003)
O’Brein J.L., Pryde G.J., White A.G., Ralph T.C., Branning D.: Demonstration of an all-optical quantum controlled-NOT gate. Nature 426, 264 (2003)
Prevedal R., Walther P., Tiefenbacher F., Bohi P., Kaltenbaek R., Jennewein T., Zeilinger A.: High-speed linear optics quantum computing using active feed-forward. Nature 445, 65 (2007)
Nemoto K., Munro W.J.: Nearly deterministic linear optical controlled-NOT gate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 250502 (2004)
Spiller T.P., Nemoto K., Braunstein S.L., Munro W.J., Van Loock P., Milburn G.J.: Quantum computation by communication. New J. Phys. 8, 30 (2006)
Birnbaum K.M., Boca A., Miller R., Boozer A.D., Northup T.E., Kimble H.J.: Photon blockade in an optical cavity with one trapped atom. Nature 436, 87 (2005)
Lloyd S., Braunstein S.L.: Quantum computation over continuous variables. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 1784 (1999)
Menicucci Nicolas C., van Loock P., Gu M., Weedbrook C., Ralph T.C., Nielsen M.A.: Universal quantum computation with continuous-variable cluster states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 110501 (2006)
Gu M., Weedbrook C., Menicucci N.C., Ralph T.C., van Loock P.: Quantum computing with continuous-variable clusters. Phys. Rev. A 79, 062318 (2009)
Franson J.D., Jacobs B.C., Pittman T.B.: Quantum computing using single photons and the Zeno effect. Phys. Rev. A 70, 062302 (2004)
Franson J.D., Jacobs B.C., Pittman T.B.: Zeno logic gates using microcavities. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 24, 209 (2007)
Leung P.M., Ralph T.C.: Improving the fidelity of optical Zeno gates via distillation. Phys. Rev. A 74, 062325 (2006)
Leung P.M., Ralph T.C.: Optical zeno gate: bounds for fault tolerant operation. New J. Phys. 9, 224 (2007)
Myers C.R., Gilchrist A.: Photon-loss-tolerant Zeno controlled-SIGN gate. Phys. Rev. A 75, 052339 (2007)
Huang Y.P., Moore M.G.: Interaction- and measurement-free quantum Zeno gates for universal computation with single-atom and single-photon qubits. Phys. Rev. A 77, 062332 (2008)
You H., Hendrickson S.M., Franson J.D.: Enhanced two-photon absorption using entangled states and small mode volumes. Phys. Rev. A 80, 043823 (2009)
Armani D.K., Kippenberg T.J., Spillane S.M., Vahala K.J.: Ultra-high-Q toroid microcavity on a chip. Nature 421, 925 (2003)
Vahala K.J.: Optical microcavities. Nature 424, 839 (2003)
Kippenberg T.J., Spillane S.M., Armani D.K., Vahala K.J.: Fabrication and coupling to planar high-Q silica disk microcavities. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83(4), 797 (2003)
Spillane S.M., Kippenberg T.J., Vahala K.J., Goh K.W., Wilcut E., Kimble H.J.: Ultrahigh-Q toroidal microresonators for cavity quantum electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. A 71, 013817 (2005)
Min B., Yang L., Vahala K.: Perturbative analytic theory of an ultrahigh- Q toroidal microcavity. Phys. Rev. A 76, 013823 (2007)
You H., Hendrickson S.M., Franson J.D.: Analysis of enhanced two-photon absorption in tapered optical fibers. Phys. Rev. A 78, 053803 (2008)
Cohen-Tannoudji C.: Optical pumping and interactions of atoms with the electromagnetic field. In: Levy, M. (ed) Cargese Lectures in Physics, vol. 2, pp. 347–393. Gordon and Breach, New York (1968)
Cohen-Tannoudji, C., Dupont-Roc, J., Grynberg, G.: In: Atom-Photon Interactions: Basic Processes and Applications. Wiley, New-York (1992)
Bloembergen N., Levenson M.D.: Doppler-free two-photon absorption spectroscopy. In: Shimoda, K. (eds) Topics in Applied Physics, vol. 13, pp. 329. Springer, Berlin (1976)
Kimble H.J.: Strong interactions of single atoms and photons in cavity QED. Phys. Scr. T 76, 127 (1998)
Nielsen M.A., Chuang I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Jacobs B.C., Franson J.D.: All-optical switching using the quantum Zeno effect and two-photon absorption. Phys. Rev. A 79, 063830 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, H., Franson, J.D. Theoretical comparison of quantum Zeno gates and logic gates based on the cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Quantum Inf Process 11, 1627–1651 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-011-0318-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-011-0318-y