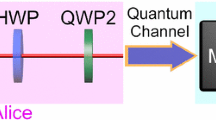
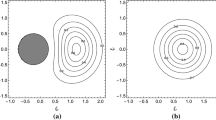
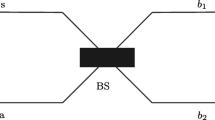
Abstract
We propose an optical scheme for quantum key distribution in which bits are encoded in relative phases of four bipartite weak coherent states\({|\alpha, \alpha\rangle, |-\alpha, -\alpha\rangle, |-\alpha, \alpha\rangle}\) and \({|\alpha, -\alpha \rangle}\), with respect to a strong reference pulse. We discuss security of the scheme against eavesdropping strategies like, photon number splitting, photon beam splitting and intercept-resend attacks. It is found that present scheme is more sensitive against these eavesdropping strategies than the two-dimensional non-orthogonal state based protocol and BB84 protocol. Our scheme is very simple, requires only passive optical elements like beam splitters, phase shifters and photon detectors, hence is at the reach of presently available technology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers Systems and Signal Processing, pp. 175–179. IEEE (1984)
Scarani V., Iblisdir S., Gisin N.: Quantum cloning. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77, 1225–1256 (2005)
Gisin N., Ribordy G., Tittel W., Zbinden H.: Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 145–195 (2002)
Phoenix S.J.D.: Quantum cryptography without conjugate coding. Phys. Rev. A 48, 96 (1993)
Mayers D.: Quantum key distribution and string oblivious transfer in noisy channels. In: Koblitz, N. (ed.) Proceedings of Advances in Cryptology-Crypto ‘96, Lecture Notes in Computer Science Vol 1109., pp. 343. Springer, Berlin (1996)
Biham, E., Boyer, M., Boykin, P. O., Mor, T., Roychowdhury, V.: A Proof of the Security of Quantum Key Distribution. http://www.arxiv.org/abs/quant-ph/9912053
Lo H.K., Chare H.F.: Unconditional security of quantum key distribution over arbitrarily long distances. Science 283, 2050 (1999)
Koashi M., Perskill J.: Secure quantum key distribution with an uncharacterized source. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 057902 (2003)
Christandl, M., Renner, R., Ekert, A.: A generic security proof for quantum key distribution. http://www.arxiv.org/abs/quantph/0402131
Shor P.W., Perskill J.: Simple proof of security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 441 (2000)
Inamori H., Lutkenhaus, N., Mayers, D.: Unconditional security of practical quantum key distribution. http://www.arxiv.org/abs/quant-ph/0107017
Gottesman, D., Lo, H.K., Lutkenhaus, N., Perskill, J.: Security of quantum key distribution with imperfect devices. http://www.arxiv.org/abs/quant-ph/0212066
Huttner B., Imoto N., Gisin N., Mor T.: Quantum cryptography with coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 51, 1863 (1995)
Brassard G., Lütkenhaus N., Mor T., Sanders B.C.: Limitations on practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1330 (2000)
Lütkenhaus N.: Security against individual attacks for realistic quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 61, 052304 (2000)
Hwang W.Y.: Quantum key distribution with high loss: global secure communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 057901 (2003)
Wang X.B.: Beating the photon-number-splitting attack in practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 230503 (2005)
Wang X.B.: Decoy-state protocol for quantum cryptography with four different intensities of coherent light. Phys. Rev. A 72, 012322 (2005)
Ekert A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 661 (1991)
Bennett C.H.: Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 3121 (1992)
Koashi M.: Unconditional security of coherent-state quantum key distribution with a strong phase-reference pulse. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 120501 (2004)
Wu G., Chen J., Li Y., Xu L., Zeng H.: Preventing eavesdropping with bright reference pulses for a practical quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 74, 062323 (2006)
Ralph, T.: Continuous variable quantum cryptography. http://www.arxiv.org/abs/quant-ph/9907073
Hillery M.: Quantum cryptography with squeezed states. Phys. Rev. A 61, 022309 (2000)
Loudan R.: The Quantum Theory of Light. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2000)
Peres A.: Quantum Theory: Concepts and Methods. Kluwer, Dordrecht (1993)
Cover T.M., Thomas J.A.: Elements of Information theory. Wiley, Newyork (1991)
Ash R.B.: Information Theory. Dover, Newyork (1990)
Ekert A.K., Huttner B., Palma G.M., Peres A.: Eavesdropping on quantum-cryptographical systems. Phys. Rev. A 50, 1047 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, M.K., Prakash, H. Bipartite coherent-state quantum key distribution with strong reference pulse. Quantum Inf Process 12, 907–920 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-012-0438-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-012-0438-z