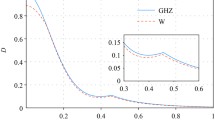
Abstract
Motivated by the space-time diversity transmission technique in wireless communications, a novel probabilistic quantum relay communication scheme in the quantum noisy channel is proposed in order to maximize the correct information transmission and the range of quantum communication, in which quantum signal sequences that carrying two-particle entangled states are transmitted from two senders to two relays and then retransmitted to the receiver after space-time encoded by relays. The quantum signal states can be restored via filtering out the channel noise with two-dimensional Bell measurements by the receiver. Analysis and discussions indicate that our scheme can increase and approximately double the range of quantum communication while not to reduce too much quantum signal-to-noise ratio, and meanwhile the security can be guaranteed under strongest collective attacks and LOCC attacks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hausl C., Hagenauer J.: Relay communication with hierarchical modulation. IEEE Commun. Lett. 11(1), 64–66 (2007)
Tarokh V., Jafarkhani H., Calderbank A.R.: Space-time block codes from orthogonal designs. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theor. 45(5), 1456–1467 (1999)
Gisin N., Thew R.T.: Quantum communication. Nat. Photon. 1, 165–171 (2007)
Briegel H.J., Dür W., Cirac J.I., Zoller P.: Quantum repeaters for communication, arXiv:quant-ph/9803056v1 20 Mar (1998)
Dür W., Briegel H.J., Cirac J.I., Zoller P.: Quantum repeaters based on entanglement purification, arXiv:quant-ph/9808065v1 31 Aug (1998)
Jacobs B.C., Pittman T.B., Franson J.D.: Quantum relays and noise suppression using linear optics. Phys. Rev. A 66(052307), 1–6 (2002)
Zhang A.N., Chen Y.A., Lu C.Y., Qi Zhou X., Zhao Z., Zhang Q., Yang T., Pan J.W.: Quantum-relay-assisted key distribution over high photon loss channels, arXiv:quant-ph/0508062v1, 1–12 (2005)
Guo Y., Chen Z.G., Song W., Lee M.H.: A transmit diversity scheme for quantum communications. Physica Scripta 78(065402), 1–5 (2008)
Shi R.H., Shi J.J., Guo Y., Peng X.Q., Lee M.H.: Quantum MIMO communication scheme based on quantum teleportation with triplet states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50(8), 2334–2346 (2011)
Djordjevic I.B.: Photonic implementation of quantum relay and encoders/decoders for sparse-graph quantum codes based on optical hybrid. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 22(19), 1449–1451 (2010)
Wang C., Ma H.Q., Jiao R.Z., Zhang Y.: An improved quantum repeater protocol using hyperentangled state purification. Eur. Phys. J. D 64, 573–578 (2011)
Alamouti S.M.: A simple transmit diversity technique for wireless communications. IEEE J. Select Areas Commun. 16(8), 1451–1458 (1998)
Li Z., Xia X.G.: A simple Alamouti spaceCTime transmission scheme for asynchronous cooperative systems. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 14(11), 804–807 (2007)
Griffiths R.B.: Quantum Channels, Kraus Operators, POVMs, Version of 4, http://quantum.phys.cmu.edu/QCQI/qitd411.pdf, qitd411, 1–18 (2010)
Li X.X., Li G.F.: Static gain, optical modulation response, and nonlinear phase noise in saturated quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifiers. IEEE J Quantum Elec. 45(5), 499–505 (2009)
Wang C., Shen Y.B., Li X.H., Deng F.G., Zhang W., Long G.L.: Efficient entanglement purification for doubly entangled photon state. Sci. China. Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 52(12), 3464–3467 (2009). doi:10.1007/s11431-009-0307-x
Biham E., Boyer M., Brassard G., Graaf J., Mor T.: Security of quantum key distribution against all collective attacks. Algorithmica 34, 372–388 (2002)
Deng F.G., Li X.H., Li C.Y., Zhou P., Zhou H.Y.: Quantum secure direct communication network with Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pairs. Phys. Lett. A 359, 359–365 (2006)
Dobrzanki R.D., Sen A., Sen U., Lewenstein M.: Entanglement enhances security in quantum communication. Phys. Rev. A. 80, 012311 (2009)
Vandevender A.P., Kwiat P.G.: High efficiency single photon detection via frequency up-conversion. J. Modern Opt. 51(9-10), 1433–1445 (2004)
Grangier P., Levenson J.A., Poizat J.P.: Quantum non-demolition measurements in optics. Nature 396, 537–542 (1998). doi:10.1038/25059
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, J., Shi, R., Guo, Y. et al. Probabilistic quantum relay communication in the noisy channel with analogous space-time code. Quantum Inf Process 12, 1859–1870 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-012-0497-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-012-0497-1