Abstract
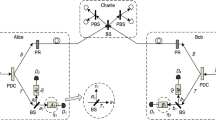
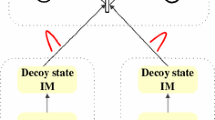
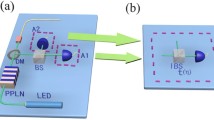
We put forward a new scheme for implementing the measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution (QKD) with weak coherent source, while using only two different intensities. In the new scheme, we insert a beam splitter and a local detector at both Alice’s and Bob’s side, and then all the triggering and non-triggering signals could be employed to process parameter estimations, resulting in very precise estimations for the two-single-photon contributions. Besides, we compare its behavior with two other often used methods, i.e., the conventional standard three-intensity decoy-state measurement-device-independent QKD and the passive measurement-device-independent QKD. Through numerical simulations, we demonstrate that our new approach can exhibit outstanding characteristics not only in the secure transmission distance, but also in the final key generation rate.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lo, H.-K., Chau, H.F.: Unconditional security of quantum key distribution over arbitrarily long distances. Science 283, 2050 (1999)
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 441 (2000)
Mayers, D.: Unconditional security in quantum cryptography. J. ACM 48, 351 (2001)
Brassard, G., Lütkenhaus, N., Mor, T., Sanders, B.C.: Limitations on practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1330 (2000)
Lütkenhaus, N.: Security against individual attacks for realistic quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 61, 052304 (2000)
Lütkenhaus, N., Jahma, M.: Quantum key distribution with realistic states: photon-number statistics in the photon-number splitting attack. New J. Phys. 4, 44.1 (2002)
Makarov, V., Anisimov, A., Skaar, J.: Effects of detector efficiency mismatch on security of quantum cryptosystems. Phys. Rev. A 74, 022313 (2006)
Qi, B., Fung, C.-H.F., Lo, H.-K., et al.: Time-shift attack in practical quantum cryptosystems. Quantum Inf. Comput. 7, 073 (2007)
Fung, C.-H.F., Qi, B., Tamaki, K., Lo, H.-K.: Phase-remapping attack in practical quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 75, 032314 (2007)
Li, H.-W., Wang, S., Huang, J.-Z.: Attacking a practical quantum-key-distribution system with wavelength-dependent beam-splitter and multiwavelength sources. Phys. Rev. A 84, 062308 (2011)
Hwang, W.Y.: Quantum key distribution with high loss: toward global secure communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 057901 (2003)
Wang, X.-B.: Beating the photon-number-splitting attack in practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 230503 (2005)
Lo, H.-K., Ma, X.-F., Chen, K.: Decoy state quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 230504 (2005)
Wang, Q., Wang, X.-B., Guo, G.C.: Practical decoy-state method in quantum key distribution with a heralded single-photon source. Phys. Rev. A 75, 012312 (2007)
Wang, Q., Wang, X.-B.: Improved practical decoy state method in quantum key distribution with parametric down-conversion source. Europhys. Lett. 79, 40001 (2007)
Wang, Q., Chen, W., Xavier, G.: Experimental decoy-state quantum key distribution with a sub-poissionian heralded single-photon source. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 090501 (2008)
Braunstein, S.L., Pirandola, S.: Side-channel-free quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130502 (2012)
Lo, H.K., Curty, M., Qi, B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130503 (2012)
Zhou, Y.-H., Yu, Z.-W., Wang, X.-B.: Tightened estimation can improve the key rate of measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution by more than 100. Phys. Rev. A 89, 052325 (2014)
Wang, X.B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 87, 012320 (2013)
Tamaki, K., Lo, H.-K., Fung, C.-H.F., Qi, B.: Phase encoding schemes for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with basis-dependent flaw. Phys. Rev. A 85, 042307 (2012)
Ma, X., Razavi, M.: Alternative schemes for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 86, 062319 (2012)
Wang, Q., Wang, X.-B.: An efficient implementation of the decoy-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with heralded single-photon sources. Phys. Rev. A 88, 052332 (2013)
Wang, Q., Wang, X.-B.: Simulating of the measurement-device independent quantum key distribution with phase randomized general sources. Sci. Rep. 4, 04612 (2014)
Wang, D., Li, M., Zhu, F., Yin, Z.-Q., Chen, W., Han, Z.-F., Guo, G.-C., Wang, Q.: Quantum key distribution with the single-photon-added coherent source. Phys. Rev. A 90, 062315 (2014)
Curty, M., Ma, X., Qi, B., Moroder, T.: Passive decoy state quantum key distribution with practical light sources. Phys. Rev. A 81, 022310 (2010)
Curty, M., Xu, F., Cui, W., Lim, C.C.W., Tamaki, K., Lo, H.-K.: Finite-key analysis for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Nat. Commun. 5, 3732 (2014)
Tang, Y.L., Yin, H.L., Chen, S.J., Liu, Y., Zhang, W.J., Jiang, X., Zhang, L., Wang, J., You, L.X., Guan, J.Y., Yang, D.X., Wang, Z., Liang, H., Zhang, Z., Zhou, N., Ma, X., Chen, T.Y., Zhang, Q., Pan, J.W.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution over 200 km. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 069901 (2015)
Comandar, L.C., Lucamarini, M., Frohlich, B.: Quantum key distribution without detector vulnerabilities using optically seeded lasers. Nat. Photonics 10, 312C315 (2016)
Wang, S., Yin, Z.-Q., Chen, W.: Experimental demonstration of quantum key distribution without monitoring of the signal disturbance. Nat. Photonics 9, 832C836 (2015)
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China through Grants Nos. 11274178, 61475197 and 61590932, the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions through Grant No. 15KJA120002, the Outstanding Youth Project of Jiangsu Province through Grant No. BK20150039 and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions through Grant No. YX002001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, JR., Zhu, F., Zhou, XY. et al. The enhanced measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with two-intensity decoy states. Quantum Inf Process 15, 3799–3813 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1371-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1371-3