Abstract
The multiple-qubit logical basis, originally introduced in the context of fault-tolerant quantum computing in decoherence-free subspace (DFS), has specific applications for resolving a reference frame misalignment problem in quantum information protocols. In this paper, an alignment-free MDI-QKD scheme is proposed with rotational-invariant state, which is immune to the collective noise induced by misalignment between two distant legitimate parties. In our protocol, the initial logical qubit is created in the polarization-orbit angular momentum hybrid space, while the transmission is entirely done in the rotation-invariant DFS under the collective noise associated with misalignment. The partial Bell state measurement is performed on the logical qubits to sort the logical Bell state. Compared with the original MDI-QKD protocols, the numerical simulations show that our modified scheme has apparent improvements both in transmission distance and key generation rate. Furthermore, only ordinary optical elements are required in our protocol.




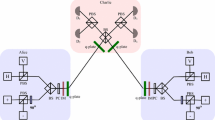
Source: 632-nm CW laser. PolM: polarization modulator; IM: optical intensity modulator; BS: 50:50 beam splitter; SPD: Si single-photon detectors; PBS: polarization beam splitter
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, pp. 175–179. IEEE, New York (1984)
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 441–444 (2000)
Mayers, D.: Unconditional security in quantum cryptography. J. ACM 48, 351–406 (2001)
Gottesman, D., Lo, H.K., Lutkenhaus, N., Preskill, J.: Security of quantum key distribution with imperfect devices. Quantum. Inf. Comput. 4, 325–360 (2004)
Braunstein, S.L., Pirandola, S.: Side-channel-free quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130502 (2012)
Brassard, G., Lutkenhaus, N., Mor, T., Sanders, B.C.: Limitations on practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1330–1333 (2000)
Sun, S.H., Liang, L.M.: Experimental demonstration of an active phase randomization and monitor module for quantum key distribution. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 071107 (2012)
Makarov, V., Skaar, J.: Faked states attack using detector efficiency mismatch on SARG04, phase-time, DPSK, and Ekert protocols. Quantum. Inf. Comput. 86, 0622–0635 (2008)
Zhao, Y., Fung, C.H.F., Qi, B., Chen, C., Lo, H.K.: Quantum hacking: Experimental demonstration of time-shift attack against practical quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 78, 042333 (2008)
Lo, H.K., Curty, M., Qi, B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130503 (2012)
Rubenok, A., Slater, J.A., Chan, P., Lucio, I., Tittel, M.W.: Real-world two-photon interference and proof-of-principle quantum key distribution immune to detector attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 130501 (2014)
Ferreira da Silva, T., Vitoreti, D., Xavier, G.B., do Amaral, G.C., Temporao, G.P., vonder Weid, J.P.: Proof-of-principle demonstration of measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution using polarization qubits. Phys. Rev. A 88, 052303 (2013)
Liu, Y., Chen, T.Y., Wang, L.J., Liang, H., Shentu, G.L., Wang, J., Cui, K., Yin, H.L., Liu, N.L., Li, L., et al.: Experimental measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 130502 (2013)
Tang, Z., Liao, Z., Xu, F., Qi, B., Qian, L., Lo, H.K.: Experimental demonstration of polarization encoding measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 190503 (2013)
Yin, H.L., et al.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution over a 404 km optical fiber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 190501 (2016)
Peres, A., Scudo, P.F.: Entangled quantum states as direction indicators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 4160 (2001)
Peres, A., Scudo, P.F.: Transmission of a Cartesian frame by a quantum system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 167901 (2001)
Laing, A., Scarani, V., Rarity, J.G., O’Brien, J.L.: Reference-frame-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A. 82, 012304 (2010)
Liang, W.Y., Wang, S., Li, H.W., Yin, Z.Q., Chen, W., Yao, Y., Huang, J.Z., Guo, G.C., Han, Z.F.: Proof of principle experiment of reference-frame-independent quantum key distribution with phase coding. Sci. Rep. 4, 3617 (2014)
Chen, T.-Y., et al.: Experimental quantum communication without a shared reference frame. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 150504 (2006)
Aolita, L., Walborn, S.: Quantum communication without alignment using multiple-qubit single-photon states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 100501 (2007)
Vallone, G., Ambrosio, V.D., Sponselli, A., Slussarenko, S., Marrucci, L., Sciarrino, F., Villoresi, P.: Free-space quantum key distribution by rotation-invariant twisted photons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 060503 (2013)
Ambrosio, V.D., Nagali, E., Walborn, S.P., Aolita, L., Slussarenko, S., Marrucci, L., Sciarrino, F.: Complete experimental toolbox for alignment-free quantum communication. Nat. Commun. 3, 961 (2012)
Sasada, Hiroyuki: Megumi Okamoto transverse-mode beam splitter of a light beam and its application to quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. A 68, 012323 (2003)
Xu, F.H., Curty, M., Qi, B., Lo, H.K.: Practical aspects of measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. N. J. Phys. 15, 113007 (2013)
Krenn, M., Fickler, R., Fink, M., Handsteiner, J., Malik, M., Scheidl, T., Ursin, R., Zeilinger, A.: Twisted photon entanglement through turbulent air across Vienna. PNAS 112(46), 14197–14201 (2015)
Bozinovic, N., et al.: Terabit-scale orbital angular momentum mode division multiplexing in fibers. Science 340(6140), 1545–1548 (2013)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank L.M. Liang and Y.Y. Tu for many helpful advices. C. Dong is supported by the fund of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11704412) and the Research Fund of National University of Defense and Technology (Grant No. ZK17-02-09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D., Wei, L., YaLiang, C. et al. Reference-frame-independent measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution using hybrid logical basis. Quantum Inf Process 17, 256 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-018-2030-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-018-2030-7