Abstract
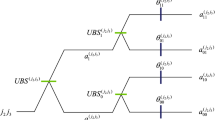
It is well known that transmitting quantum states remotely is one of central tasks in quantum information processing. Until now, there are some important works in remote state preparation, the efficient method to transmit quantum states remotely. However, most of them are focused on remote state preparation via one degree of freedom (DOF) of quantum systems. In this article, we investigate the possibility of performing parallel quantum remote state preparation based on two DOFs of photons. We proposed a protocol for parallel remote preparation of arbitrary single-qubit states via hyperentangled photons which are entangled in both spatial-mode DOF and polarization DOF simultaneously. The sender performs unitary operations on his hyperentangled photon according to his knowledge of prepared states; the receiver can reconstruct the original states on his hyperentangled photon if he cooperates with the sender. The scheme has the advantage of having less quantum entanglement cost and classical communication. Moreover, we also discuss the scheme for recursive remote preparation of arbitrary single-qubit states via partially hyperentangled Bell states.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassad, G.: Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India. IEEE, New York, pp. 175–179. IEEE Press, New York (1984)
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67(6), 661–663 (1991)
Leverrier, A.: Security of continuous-variable quantum key distribution via a Gaussian de Finetti reduction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118(20), 200501 (2017)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65(3), 032302 (2002)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68(4), 042317 (2003)
Hu, J. Y., Yu, B., Jing, M. Y., Xiao, L. T., Jia, S. T., Qin, G. Q., Long, G. L.: Experimental quantum secure direct communication with single photons. Light: Sci. Appl. 5(9), e16144 (2016)
Zhang, W., Ding, D.S., Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L., Shi, B.S., Guo, G.C.: Quantum secure direct communication with quantum memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118(22), 220501 (2017)
Bennett, C.H., Wiesner, S.J.: Communication via one-and two-particle operators on Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69(20), 2881 (1992)
Liu, X.S., Long, G.L., Tong, D.M., Li, F.: General scheme for superdense coding between multiparties. Phys. Rev. A 65(2), 022304 (2002)
Barreiro, J.T., Wei, T.C., Kwiat, P.G.: Beating the channel capacity limit for linear photonic superdense coding. Nat. Phys. 4(4), 282 (2008)
Pati, A.K.: Minimum classical bit for remote preparation and measurement of a qubit. Phys. Rev. A 63(1), 014302 (2000)
Lo, H.K.: Classical-communication cost in distributed quantum-information processing: a generalization of quantum-communication complexity. Phys. Rev. A 62(1), 012313 (2000)
Bennett, C.H., DiVincenzo, D.P., Shor, P.W., Smolin, J.A., Terhal, B.M., Wootters, W.K.: Remote state preparation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87(7), 077902 (2001)
Leung, D.W., Shor, P.W.: Oblivious remote state preparation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90(12), 127905 (2003)
Berry, D.W., Sanders, B.C.: Optimal remote state preparation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90(5), 057901 (2003)
Ye, M.Y., Zhang, Y.S., Guo, G.C.: Faithful remote state preparation using finite classical bits and a nonmaximally entangled state. Phys. Rev. A 69(2), 022310 (2004)
Dai, H.Y., Chen, P.X., Liang, L.M., Li, C.Z.: Classical communication cost and remote preparation of the four-particle GHZ class state. Phys. Lett. A 355, 285–288 (2006)
Dai, H.Y., Chen, P.X., Zhang, M., Li, C.Z.: Remote preparation of an entangled two-qubit state with three parties. Chin. Phys. B 17(1), 27–33 (2008)
Wei, J.H., Dai, H.Y., Zhang, M.: Two efficient schemes for probabilistic remote state preparation and the combination of both schemes. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(9), 2115–2125 (2014)
Wei, J.H., Shi, L., Ma, L.H., Xue, Y., Zhuang, X.C., Kang, Q.Y., Li, X.S.: Remote preparation of an arbitrary multi-qubit state via two-qubit entangled states. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(10), 260 (2017)
Dakić, B., Lipp, Y.O., Ma, X.S., Ringbauer, M., Kropatschek, S., Barz, S., Paterek, T., Vedral, V., Zeilinger, A., Brukner, \(\breve{C}\)., Walther, P.: Quantum discord as resource for remote state preparation. Nat. Phys. 8(9), 666 (2012)
Erhard, M., Qassim, H., Mand, H., Karimi, E., Boyd, R.W.: Real-time imaging of spin-to-orbital angular momentum hybrid remote state preparation. Phys. Rev. A 95(2), 022321 (2015)
Qu, Z.G., Wu, S.Y., Wang, M.M., Sun, L., Wang, X.J.: Effect of quantum noise on deterministic remote state preparation of an arbitrary two-particle state via various quantum entangled channels. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(12), 306 (2017)
Liu, W.T., Wu, W., Ou, B.Q., Chen, P.X., Li, C.Z., Yuan, J.M.: Experimental remote preparation of arbitrary photon polarization states. Phys. Rev. A 76(2), 022308 (2007)
Wu, W., Liu, W.T., Chen, P.X., Li, C.Z.: Deterministic remote preparation of pure and mixed polarization states. Phys. Rev. A 81(4), 042301 (2010)
Lu, Q.C., Liu, D.P., He, Y.H., Liao, Y.M., Qin, X.C., Qin, J.S., Zhou, P.: Linear-optics-based bidirectional controlled remote state preparation via five-photon cluster-type states for quantum communication network. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(1), 535 (2016)
Yu, R.F., Liu, Y.J., Zhou, P.: Joint remote preparation of arbitrary two- and three-photon state with linear-optical elements. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(11), 4785 (2016)
Barreiro, J.T., Wei, T.C., Kwiat, P.G.: Remote preparation of single-photon hybrid entangled and vector-polarization states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105(3), 030407 (2010)
Yang, T., Zhang, Q., Zhang, J., Yin, J., Zhao, Z., Zukowski, M.: All-versus-nothing violation of local realism by two-photon, four-dimensional entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(24), 240406 (2005)
Barreiro, J.T., Langford, N.K., Peters, N.A., Kwiat, P.G.: Generation of hyperentangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(26), 260501 (2005)
Vallone, G., Donati, G., Ceccarelli, R., Mataloni, P.: Six-qubit two-photon hyperentangled cluster states: Characterization and application to quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 81(5), 052301 (2010)
Gao, W.B., Lu, C.Y., Yao, X.C., Xu, P., G\(\ddot{u}\)hne, O., Goebel, A., Chen, Y. A., Peng, C. Z., Chen, Z. B., Pan, J. W.: Experimental demonstration of a hyper-entangled ten-qubit Schr\(\ddot{o}\)inger cat state. Nat. Phys. 6(5), 331 (2010)
Kang, D.P., Helt, L.G., Zhukovsky, S.V., Torres, J.P., Sipe, J.E., Helmy, A.S.: Hyperentangled photon sources in semiconductor waveguides. Phys. Rev. A 89(2), 023833 (2014)
Ren, B.C., Deng, F.G.: Hyper-parallel photonic quantum computing with coupled quantum dots. Sci. Rep. 4, 4623 (2014)
Li, T., Long, G.L.: Hyperparallel optical quantum computation assisted by atomic ensembles embedded in double-sided optical cavities. Phys. Rev. A 94(2), 022343 (2016)
Wei, H.R., Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Hyper-parallel Toffoli gate on three-photon system with two degrees of freedom assisted by single-sided optical microcavities. Opt. Express 24(16), 18619 (2016)
Wei, T.C., Barreiro, J.T., Kwiat, P.G.: Hyperentangled bell-state analysis. Phys. Rev. A 75(6), 060305(R) (2007)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Complete hyperentangled-Bell-state analysis for quantum communication. Phys. Rev. A 82(3), 032318 (2010)
Xia, Y., Chen, Q.Q., Song, J., Song, H.S.: Efficient hyperentangled GreenbergerCHorneCZeilinger states analysis with cross-Kerr nonlinearity. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 29(5), 1029 (2012)
Liu, Q., Wang, G.Y., Ai, Q., Zhang, M., Deng, F.G.: Complete nondestructive analysis of two-photon six-qubit hyperentangled Bell states assisted by cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Sci. Rep. 6, 22016 (2016)
Li, X.H., Ghose, S.: Self-assisted complete maximally hyperentangled state analysis via the cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Phys. Rev. A 93(2), 022302 (2016)
Wang, T.J., Song, S.Y., Long, G.L.: Quantum repeater based on spatial entanglement of photons and quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities. Phys. Rev. A 85(6), 062311 (2012)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G.: Deterministic entanglement purification and complete nonlocal Bell-state analysis with hyperentanglement. Phys. Rev. A 82(3), 032307 (2010)
Li, X.H.: Deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 82(4), 044304 (2010)
Deng, F.G.: One-step error correction for multipartite polarization entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 83(6), 062316 (2011)
Ren, B.C., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement purification and concentration assisted by diamond NV centers inside photonic crystal cavities. Laser Phys. Lett. 10(11), 115201 (2013)
Du, F.F., Li, T., Long, G.L.: Refined hyperentanglement purification of two-photon systems for high-capacity quantum communication with cavity-assisted interaction. Ann. Phys. 375, 105 (2016)
Ren, B.C., Du, F.F., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement concentration for two-photon four-qubit systems with linear optics. Phys. Rev. A 88(1), 012302 (2013)
Li, X.H., Ghose, S.: Hyperconcentration for multipartite entanglement via linear optics. Laser phys. Lett. 11(12), 125201 (2014)
Ren, B.C., Wang, H., Alzahrani, F., Hobiny, A., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement concentration of nonlocal two-photon six-qubit systems with linear optics. Ann. Phys. 385, 86 (2017)
Wang, Z.H., Wu, X.Y., Yu, W.X., Alzahrani, F., Hobiny, A., Deng, F.G.: Practical entanglement concentration of nonlocal polarization-spatial hyperentangled states with linear optics. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(5), 141 (2017)
Wu, F.Z., Yang, G.J., Wang, H.B., Xiong, J., Alzahrani, F., Hobiny, A., Deng, F.G.: High-capacity quantum secure direct communication with two-photon six-qubit hyperentangled states. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 60(12), 120313 (2017)
Nawaz, M., Ikram, M.: Remote state preparation through hyperentangled atomic states. J. Phys. B 51(7), 075501 (2018)
Wang, X.L., Cai, X.D., Su, Z.E., Chen, M.C., Wu, D., Li, L., Liu, N.L., Lu, C.Y., Pan, J.W.: Quantum teleportation of multiple degrees of freedom of a single photon. Nature 518(7540), 516 (2015)
Deng, F.G., Ren, B.C., Li, X.H.: Quantum hyperentanglement and its applications in quantum information processing. Sci. Bull. 62(1), 46 (2017)
Jiang, M., Dong, D.: A recursive two-phase general protocol on deterministic remote preparation of a class of multi-qubit states. J. Phys. B 45(20), 205506 (2012)
Li, X.H., Deng, F.G., Li, C.Y., Liang, Y.J., Zhou, P., Zhou, H.Y.: Deterministic secure quantum communication without maximally entangled states. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 49(4), 1354–1359 (2006)
Yuan, H., Deng, L., Zhang, Y.M., Zhang, W., Zhan, Z.: Optimizing resource consumption, operation complexity and efficiency in quantum-state sharing. J. Phys. B 41(14), 145506 (2008)
Choudhury, B.S., Samanta, S.: Simultaneous perfect teleportation of three 2-qubit states. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(9), 230 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 61501129 and 11564004, Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi under Grant Nos. 2014GXNSFAA118008, Special Funds of Guangxi Distinguished Experts Construction Engineering and Xiangsihu Young Scholars and Innovative Research Team of GXUN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, P., Jiao, XF. & Lv, SX. Parallel remote state preparation of arbitrary single-qubit states via linear-optical elements by using hyperentangled Bell states as the quantum channel. Quantum Inf Process 17, 298 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-018-2067-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-018-2067-7