Abstract
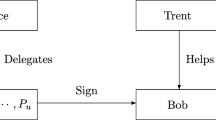
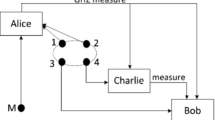
Different from traditional digital signatures, quantum blind signatures can implement a signature without knowing the specific content, and their security is guaranteed by the basic principles of quantum mechanics with unconditional security. Based on the blind signature, multi-proxy signature can avoid internal attacks efficiently by dispersing the authority of proxy signers. In this paper, we propose a new quantum multi-proxy blind signature scheme based on cluster states. We apply the quantum teleportation to transmit data using the four-particle cluster state as a channel. Then, a quantum multi-proxy blind signature scheme is designed. According to the security analysis, blindness, undeniability and unforgeability are all equipped in our scheme. Meanwhile, compared with existing schemes, four-particle cluster states are required as quantum channels in our scheme which uses fewer resources to transmit data and has higher efficiency of signatures.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Li, X., Chen, K., Sun, L.: Certificateless signature and proxy signature schemes from bilinear pairings. Lith. Math. J. 45(1), 76–83 (2005)
Zhang, J., Bai, W., Wang, Y.: Non-interactive ID-based proxy re-signature scheme for IoT based on mobile edge computing. IEEE Access 7, 37865–37875 (2019)
Patonico, S. et al. : Elliptic curve-based proxy re-signcryption scheme for secure data storage on the cloud. Concurr Comput Pract Exp 3 (2020)
Shor, P. W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithm and factoring. In: Proceedings of the 35th Annual Symposium on the Foundations of Computer Science, IEEE Computer Society Press, pp. 124–134 (1994)
Shor, P.W.: Polynomialtime algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM J. Comput. 26(5), 1484–1509 (1997)
Heisenberg, W.: The actual content of quantum theoretical kinematics and mechanic. zhurnal physik (1984)
Wootters, W.K., Zurek, W.H.: A single quantum cannot be cloned. Nature 299, 802–803 (1982)
Chaum, D.: Blind signatures for untraceable payments. In: Advances in Cryptology Proc. Crypto 82 (1983)
Xu, G.B.: Novel quantum proxy signature without entanglement. Int. J. Theor. Phys. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-014-2491-0
Mambo, M.M., Usuda, K., Okamoto, E.: Proxy signatures: delegation of the power to sign messages. IEEE Trans. Fundam. A 79(9), 1338–1354 (1996)
Tan, R., Yang, Q.: Comments on the "Efficient quantum multi-proxy signature. Quantum Inf. Process. 19(9), 1–13 (2020)
Gottesman, D., Chuang, I.: Quantum digital signatures. arXiv preprint quant-ph/0105032 (2001)
Wen, X.J., Liu, Y., Sun, Y.: Quantum multi-signature protocol based on teleportation. Zeitschrift Für Naturforschung A 62(3–4), 147–151 (2007)
Yang, Y.G.: Multi-proxy quantum group signature scheme with threshold shared verification. Chin. Phys. B 17(2), 415 (2008)
Shi, J., et al.: A multiparty quantum proxy group signature scheme for the entangled-state message with quantum Fourier transform. Quantum Inf. Process. 10(5), 653–670 (2011)
Cao, H.J., et al.: A quantum proxy weak blind signature scheme based on controlled quantum teleportation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54(4), 1325–1333 (2015)
Niu, X.F., et al.: A practical e-payment protocol based on quantum multi-proxy blind signature. Commun. Theor. Phys. 70(11), 23–27 (2018)
Tian, J.H., Zhang, J.Z., Li, Y.P.: A quantum multi-proxy blind signature scheme based on genuine four-qubit entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55, 809–816 (2016)
Cao, H.J., Yu, Y.F., Song, Q., et al.: A quantum proxy weak blind signature scheme based on controlled quantum teleportation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54, 1325–1333 (2015)
Zeng, C., Zhang, J.Z., Xie, S.C.: A blind signature scheme for quantum agents based on three-particle GHZ states with Bell states. Small Microcomput. Syst. 38(07), 1485–1489 (2017)
Cao, H.J., et al.: A quantum proxy weak blind signature scheme. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53(2), 419–425 (2014)
Tiliwalidi, Kalibinuer, et al.: A proxy blind signature scheme of quantum information transmission in two-particle state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04095-7
Shao, A.X., Zhang, J.Z., Xie, S.C.: A quantum multi-proxy multi-blind-signature scheme based on genuine six-qubit entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55, 5216–5224 (2016)
Ge, L., et al.: A novel quantum group proxy blind signature scheme based on five-qubit entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04093-9
Zhou, B.M., Lin, L.D., Wang, W., et al.: Security analysis of particular quantum proxy blind signature against the forgery attack. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59, 465–473 (2020)
Guo, W., Zhang, J.Z., Li, Y.P., et al.: Multi-proxy strong blind quantum signature scheme. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55, 3524–3536 (2016)
Yan, L., Chang, Y., Zhang, S., et al.: A quantum multi-proxy weak blind signature scheme based on entanglement swapping. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56, 634–642 (2017)
Wang, G.Y., Fang, X.M., Tan, X.H.: Quantum secure direct communication with cluster state. Chin. Phys. Lett. 23(10), 2658–2661 (2006)
Yuan, H., Song, J.: An efficient deterministic secure quantum communication scheme with Cluster state. Int. J. Quantum Inform. 7(3), 689–696 (2009)
Cao, W.F., Yang, Y.G., Wen, Q.Y.: Quantum secure direct communication with cluster states. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 07, 1271–1275 (2010)
Shen, D., Ma, W., Wang, L.: Two-party quantum key agreement with four-qubit cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(10), 2313–2324 (2014)
Li, Y.H., et al.: Quantum teleportation of a four-qubit state by using six-qubit cluster state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(8), 3547–3550 (2016)
Yang, Y.G., et al.: Arbitrated quantum signature scheme based on cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(6), 2487–2497 (2016)
Fan, L.: A novel quantum blind signature scheme with four-particle cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(3), 1558–1567 (2016)
Fatahi, N., et al.: High-efficient arbitrated quantum signature scheme based on cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(2), 609–616 (2017)
Liang, X.Q., Wu, Y.L., Zhang, Y.H., Wang, S.S., Xu, G.B.: Quantum multi-proxy blind signature scheme based on four-qubit cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(1), 31–39 (2019)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems, and Signal Processing, Bangalore. pp. 175–179 (1984)
Bennett, C.H.: Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 3121–3124 (1992)
Bostrom, K., Felbinger, T.: Deterministic secure direct communication using entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 157901 (2002)
Acknowledgements
Project was supported by Joint Funding Project of Beijing Municipal Commission of Education and Beijing Natural Science Fund Committee (KZ201710015010), the Scientific Research Common Program of Beijing Municipal Commission of Education (KM202010015009\(\pounds \)©, the Initial Funding for the Doctoral Program of BIGC (27170120003/020), the initial funding for the Doctoral Program of BIGC (27170120003/022), BIGC Project (Eb202004) and BIGC Project (Ec202007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, JJ., You, FC. & Li, ZZ. Quantum multi-proxy blind signature based on cluster state. Quantum Inf Process 21, 104 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03446-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03446-4