Abstract
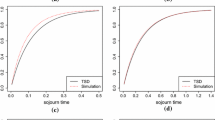
We give in this paper an algorithm to compute the sojourn time distribution in the processor sharing, single server queue with Poisson arrivals and phase type distributed service times. In a first step, we establish the differential system governing the conditional sojourn times probability distributions in this queue, given the number of customers in the different phases of the PH distribution at the arrival instant of a customer. This differential system is then solved by using a uniformization procedure and an exponential of matrix. The proposed algorithm precisely consists of computing this exponential with a controlled accuracy. This algorithm is then used in practical cases to investigate the impact of the variability of service times on sojourn times and the validity of the so-called reduced service rate (RSR) approximation, when service times in the different phases are highly dissymmetrical. For two-stage PH distributions, we give conjectures on the limiting behavior in terms of an M/M/1 PS queue and provide numerical illustrative examples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Abate and W. Whitt, Numerical inversion of Laplace transforms of probability distributions, ORSA J. Comput. 7(1) (1995) 36–43.
R. Agrawal, A.M. Makowski, and P. Nain, On a reduced load equivalence for fluid queues under subexponentiality, Queueing Systems. Theory and Applications 33(1–3) (1999) 5–41.
S. Asmussen, Applied Probability and Queues (J. Wiley and Sons, 1987).
C. Barakat, P. Thiran, G. Iannaccone, C. Diot and P. Owezarski, Modeling internet backbone traffic at the flow level, IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing—Special Issue on Signal Processing in Networking 51(8) (2003) 2111–2124.
S. Ben Fredj, T. Bonald, A. Proutiére, G. Régnié and J.W. Roberts, Statistical bandwidth sharing: a study of congestion at flow level, in: Proc. SIGCOMM 2001, (San Diego, CA, USA, Aug. 2001).
S.C. Borst, O.J. Boxma, J.A. Morrison and R. Núñez-Queija, The equivalence between processor sharing and service in random order, Oper. Res. Lett 31 (2003) 254–262.
S.C. Borst, O.J. Boxma, J.A. Morrison and R. Núñez-Queija, The equivalence between processor sharing and service in random order, Oper. Res. Lett 31 (2003) 254–262.
E.G. Coffman, R.R. Muntz and H. Trotter, Waiting time distributions for processor-sharing systems, J. ACM 17 (1970) 123–130.
L. Flatto, The waiting time distribution for the random order service M/M/1 queue, Annals of Applied Probability 7 (1997) 382–409.
F. Guillemin and J. Boyer, Analysis of the M/M/1 queue with processor sharing via spectral theory, Queueing Systems 39 (2001) 377–397.
F. Guillemin, P. Robert and B. Zwart, Tail asymptotics for processor sharing queues, Annals of Applied Probability 36 (2004) 1–19.
P. Jelenković and P. Momçilović, Large deviation analysis of subexponential waiting time in an MG/1 PS queue (2001). http://comet.ctr.columbia.edu/petar/ps.pdf.Submitted.
M. Yu. Kitaev, The M/G/1 processor-sharing model: Transient behavior, Queueing Systems 14 (1993) 239–273.
M. Yu. Kitaev, The M/G/1 processor-sharing model: Transient behavior, Queueing Systems 14 (1993) 239–273.
J. Morrison, Response time for a processor-sharing system, SIAM J. Appl. Math. 45(1) (1985) 152–167.
R. Núñez-Queija, Processor Sharing Models for Integrated Services Networks, PhD thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology (2000).
T. Ott, The sojourn-time distribution in the M/G/1 queue with processor sharing, J. Appl. Prob. 21 (1984) 360–378.
F. Pollaczek, La loi d’attente des appels téléphoniques. C.R. Acad. Sci. 222 (1946) 353–355.
J. Riordan, Stochastic Service Systems (John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York London, 1962).
J. Roberts and L. Massoulié, Bandwidth sharing and admission control for elastic traffic, in Proc. Infocom’99 (1998).
J. Roberts and L. Massoulié, Bandwidth sharing and admission control for elastic traffic, in Proc. Infocom’99 (1998).
D. Starobinski and M. Sidi, Modeling and analysis of heavy-tailed distributions via classical teletraffic methods, Queueing Systems 36(1–3) (2000) 243–267.
J.L. van den Berg and O.J. Boxma, The M/G/1 queue with processor sharing and its relation to a feedback queue, Queueing Systems 9 (1991) 365-402.
S.F. Yashkov, Processor sharing queues: some progress in analysis, Queueing System 2 (1987) 1–17.
A.P. Zwart and O.J. Boxma, Sojourn time asymptotics in the M/G/1 processor sharing queue, Queueing Systems Theory Appl. 35(1–4) (2000) 141–166.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sericola, B., Guillemin, F. & Boyer, J. Sojourn Times in the M/PH/1 Processor Sharing Queue. Queueing Syst 50, 109–130 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11134-005-0372-1
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11134-005-0372-1