Abstract
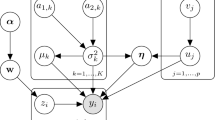
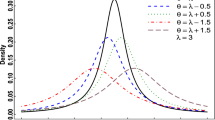
Our article presents a general treatment of the linear regression model, in which the error distribution is modelled nonparametrically and the error variances may be heteroscedastic, thus eliminating the need to transform the dependent variable in many data sets. The mean and variance components of the model may be either parametric or nonparametric, with parsimony achieved through variable selection and model averaging. A Bayesian approach is used for inference with priors that are data-based so that estimation can be carried out automatically with minimal input by the user. A Dirichlet process mixture prior is used to model the error distribution nonparametrically; when there are no regressors in the model, the method reduces to Bayesian density estimation, and we show that in this case the estimator compares favourably with a well-regarded plug-in density estimator. We also consider a method for checking the fit of the full model. The methodology is applied to a number of simulated and real examples and is shown to work well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoniak C.E. 1974. Mixtures of Dirichlet processes with applications to Bayesian nonparametric problems. The Annals of Statistics 2: 1152–1174.
Bartels R., Fiebig D.G., and Plumb M.H. 1996. Gas or electricity, which is cheaper?: An econometric approach with application to Australian expenditure data. The Energy Journal 17: 33–58.
Brooks S.P. and Gelman A. 1998. General methods for monitoring convergence of iterative simulations. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics 7: 434–455.
Carroll R.J. and Ruppert D. 1988. Transformation and Weighting in Regression. Monographs on Statistics and Applied Probability, Chapman and Hall, London.
Chan D., Kohn R., Nott D.J., and Kirby C. 2005. Locally adaptive semiparametric estimation of the mean and variance functions in regression models. Forthcoming in Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics,15: 915–936.
Cripps E., Kohn R., and Nott D. 2006. Bayesian subset selection and model averaging using a centred and dispersed prior for the error variance. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Statistics 48: 237–252.
Dahl D.B. 2003. An improved merge-split sampler for conjugate Dirichlet process mixture models. Technical Report 1086, Department of Statistics, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Escobar M.D. and West M. 1995. Bayesian density estimation and inference using mixtures. Journal of the American Statistical Association 90: 577–588.
Ferguson T.S. 1973. A Bayesian analysis of some nonparametric problems. The Annals of Statistics 1: 209–230.
Gamerman D. 1997. Sampling from the posterior distribution in generalized linear mixed models. Statistics and Computing 7: 57–68.
Green P.J. and Richardson S. 2001. Modelling heterogeneity with and without the Dirichlet process. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics 28: 355–375.
Hanson T. and Johnson W.O. 2002. Modeling regression error with a mixture of Polya trees. Journal of the American Statistical Association 97: 1020–1033.
Hurn M., Justel A., and Robert C.P. 2003. Estimating mixtures of regressions. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics 12: 55–79.
Kohn R., Smith M., and Chan D. 2001. Nonparametric regression using linear combinations of basis functions. Statistics and Computing 11: 313–322.
Kottas A. and Gelfand A.E. 2001. Bayesian semiparametric median regression modeling. Journal of the American Statistical Association 96: 1458–1468.
Kottas A. and Krnjajic M. 2005. Bayesian nonparametric modeling in quantile regression. Technical Report 2005-06, UCSC Department of Applied Math and Statistics.
Bayesian semiparametric inference for the accelerated failure time model. Canadian Journal of Statistics 25: 457–472.
Lo A.Y. 1984. On a class of Bayesian nonparametric estimates: I. Denisty estimates. The Annals of Statistics 12: 351–357.
MacEachern S.N. 1994. Estimating normal means with a conjugate style Dirichlet process prior. Communications in Statistics: Simulation and Computation 7: 727–741.
Marron J.S. and Tsybakov A.B. 1995. Visual error criteria for qualitative smoothing. Journal of the American Statistical Association 90: 499–507.
Marron J.S. and Wand M.P. 1992. Exact mean integrated squared error. Annals of Statistics 20: 712–736.
Marshall E.C. and Spiegelhalter D.J. 2003. Approximate cross-validatory predictive checks in disease mapping models. Statistics in Medicine 22: 1649–1660.
Mukhopadhyay S. and Gelfand A.E. 1997. Dirichlet process mixed generalised linear models. Journal of the American Statistical Association 92: 633–639.
Nott D.J. and Leonte D. 2004. Sampling schemes for Bayesian variable selection in generalized linear models. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics 13: 362–382.
Richardson S. and Green P.J. 1997. On Bayesian analysis of mixtures with an unknown number of components. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, B 59: 731–792.
Ruppert D., Wand M.P., and Carroll R.J. 2003. Semiparametric Regression. Cambridge Series in Statistical and Probabilistic Mathematics. Cambridge University Press.
Sheather S.J. and Jones M.C. 1991) A reliable data-based bandwidth selection method for kernel density estimation. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, B 53: 683–690.
Walker S.G. and Mallick B.K. 1999. Semiparametric accelerated life time model. Biometrics 55: 477–483.
West M. 1992. Hyperparameter estimation in Dirichlet process mixture models. ISDS Discussion paper 92-A03, Duke University.
West M., Müller P., and Escobar M.D. 1994. Hierarchical priors and mixture models, with application in regression and density estimation. In: Smith A. and Freeman P. (Eds.), Aspects of Uncertainty: A tribute to D.V. Lindley, Wiley, New York, pp. 363–386.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leslie, D.S., Kohn, R. & Nott, D.J. A general approach to heteroscedastic linear regression. Stat Comput 17, 131–146 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-006-9013-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-006-9013-8