Abstract
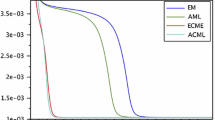
To obtain maximum likelihood (ML) estimation in factor analysis (FA), we propose in this paper a novel and fast conditional maximization (CM) algorithm, which has quadratic and monotone convergence, consisting of a sequence of CM log-likelihood (CML) steps. The main contribution of this algorithm is that the closed form expression for the parameter to be updated in each step can be obtained explicitly, without resorting to any numerical optimization methods. In addition, a new ECME algorithm similar to Liu’s (Biometrika 81, 633–648, 1994) one is obtained as a by-product, which turns out to be very close to the simple iteration algorithm proposed by Lawley (Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. 60, 64–82, 1940) but our algorithm is guaranteed to increase log-likelihood at every iteration and hence to converge. Both algorithms inherit the simplicity and stability of EM but their convergence behaviors are much different as revealed in our extensive simulations: (1) In most situations, ECME and EM perform similarly; (2) CM outperforms EM and ECME substantially in all situations, no matter assessed by the CPU time or the number of iterations. Especially for the case close to the well known Heywood case, it accelerates EM by factors of around 100 or more. Also, CM is much more insensitive to the choice of starting values than EM and ECME.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartholomew, D.J.: Latent Variable Models and Factor Analysis, 1st edn. Oxford University Press, New York (1987)
Chen, R.: An SAS/IML procedure for maximum likelihood factor analysis. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 35(3), 310–317 (2003)
Dempster, A.P., Laird, N.M., Rubin, D.B.: Maximum likelihood from incomplete data using the EM algorithm (with discussion). J. R. Stat. Soc. B 39(1), 1–38 (1977)
Fletcher, R., Powell, M.J.D.: A rapidly convergent descent method for minimization. Comput. J. 2, 163–168 (1963)
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., Friedman, J.: The Elements of Statistical Learning. Springer, New York (2001)
Jennrich, R.I., Bobinson, S.M.: A Newton-Raphson algorithm for maximum likelihood factor analysis. Psychometrika 34(1), 111–123 (1969)
Jöreskog, K.G.: Some contributions to maximum likelihood factor analysis. Psychometrika 32(4), 433–482 (1967)
Lange, K.: Numerical Analysis for Statisticians. Springer, New York (1999)
Lawley, D.N.: The estimation of factor loadings by the method of maximum likelihood. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. A 60, 64–82 (1940)
Lawley, D.N., Maxwell, A.E.: Factor Analysis as a Statistical Method, 2nd edn. Butterworths, London (1971)
Liu, C.: The ECME algorithm: a simple extention of EM and ECM with faster monotone convergence. Biometrika 81, 633–648 (1994)
Liu, C., Rubin, D.B.: Maximum likelihood estimation of factor analysis using the ECME algorithm with complete and incomplete data. Stat. Sinica 8, 729–747 (1998)
Meng, X.-L., Rubin, D.B.: Maximum likelihood estimation via the ECM algorithm: a general framework. Biometrika 80(2), 267–278 (1993)
Meng, X.L., van Dyk, D.A.: The EM algorithm—an old folk-song sung to a fast new tune. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 59(3), 511–567 (1997)
Petersen, K.B., Winther, O., Hansen, L.K.: On the slow convergence of EM and VBEM in low-noise linear models. Neural Comput. 17(9), 1921–1926 (2005)
Rubin, D.B., Thayer, T.T.: EM algorithms for ML factor analysis. Psychometrika 47, 69–76 (1982)
Tipping, M.E., Bishop, C.M.: Probabilistic principal component analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 61, 611–622 (1999)
Wu, C.F.J.: On the convergence properties of the EM algorithm. Ann. Stat. 11(1), 95–103 (1983)
Yu, P.L.H., Lam, K.F., Lo, S.M.: Factor analysis for ranked data with application to a job selection attitude survey. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A 168(3), 583–597 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, JH., Yu, P.L.H. & Jiang, Q. ML estimation for factor analysis: EM or non-EM?. Stat Comput 18, 109–123 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-007-9042-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-007-9042-y