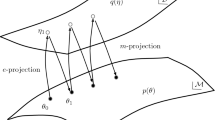
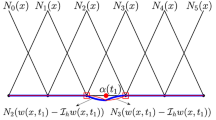
Abstract
A new acceleration scheme for optimization procedures is defined through geometric considerations and applied to the EM algorithm. In many cases it is able to circumvent the problem of stagnation. No modification of the original algorithm is required. It is simply used as a software component. Thus the new scheme can be easily implemented to accelerate a fixed point algorithm maximizing some objective function. Some practical examples and simulations are presented to show its ability to accelerate EM-type algorithms converging slowly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berlinet, A., Roland, Ch.: Acceleration schemes with application to the EM algorithm. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 51, 3689–3702 (2007)
Biernacki, C.: Initializing EM using the properties of its trajectories in Gaussian mixtures. Stat. Comput. 14(3), 267–279 (2004)
Biernacki, C., Celeux, G., Govaert, G.: Choosing starting values for the EM algorithm for getting the highest likelihood in multivariate Gaussian mixture models. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 41, 561–575 (2003)
Brezinski, C., Zaglia, M.R.: Extrapolation Methods: Theory and Practice. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam (1991)
Cappé, O., Moulines, E., Rydén, T.: Inference in Hidden Markov Models. Springer, New York (2005)
Dempster, A.P., Laird, N.M., Rubin, D.B.: Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm (with discussion). J. R. Stat. Soc. B 39, 1–38 (1977)
Hasselblad, V.: Estimation of finite mixtures of distributions from the exponential family. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 64, 1459–1471 (1969)
Jamshidian, M., Jennrich, R.I.: Conjugate gradient acceleration of the EM algorithm. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 88, 221–228 (1993)
Jamshidian, M., Jennrich, R.I.: Acceleration of the EM algorithm by using quasi-Newton methods. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 59(3), 569–587 (1997)
Kent, J.T., Tyler, D.E., Vardi, Y.: A curious likelihood identity for the multivariate t distribution. Commun. Stat. B 23, 441–453 (1994)
Lange, K.: A quasi-Newton acceleration of the EM algorithm. Stat. Sin. 5, 1–18 (1995)
Lee, E.T.Y.: The rational Bézier representation for conics. In: Farin, G.E. (ed.) Geometric Modeling: Algorithms and New Trends. SIAM, Philadelphia (1987)
Liu, C., Rubin, D.B.: The ECME algorithm: a simple extension of EM and ECM with faster monotone convergence. Biometrika 81, 633–648 (1994)
Liu, C., Rubin, D.B., Wu, Y.N.: Parameter expansion to accelerate EM: The PX-EM algorithm. Biometrika 85, 755–770 (1998)
Markatou, M., Basu, A., Lindsay, B.G.: Weighted likelihood equations with boostrap root search. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 93(442), 740–750 (1998)
McLachlan, G., Krishnan, T.: The EM Algorithm and Extensions, 1st edn. Wiley, New York (1997)
McLachlan, G., Krishnan, T.: The EM Algorithm and Extensions, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (2008)
McLachlan, G., Peel, D.: Finite Mixture Models. Wiley, New York (2000)
Meng, X.L., Rubin, D.: Maximum likelihood estimation via the ECM algorithm: A general framework. Biometrika 80, 267–278 (1993)
Meng, X.L., van Dyk, D.: The EM algorithm—an old folk-song sung to a fast new tune. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 59, 511–567 (1997)
Snedecor, G.W., Cochran, W.C.: Statistical Methods. Iowa State University Press, Ames (1967)
Titterington, D.M., Smith, A.F.M., Makov, U.E.: Statistical Analysis of Finite Mixture Distributions’ pp. 89–90. Wiley, New York (1985)
Varadhan, R., Roland, Ch.: Squared extrapolation methods (SQUAREM): A new class of simple and efficient numerical schemes for accelerating the convergence of the EM algorithm. Department of Biostatistics Working Paper, Johns Hopkins University (2004). http://www.bepress.com/jhubiostat/paper63
Wolfe, J.H.: Pattern clustering by multivariate mixture analysis. Multivar. Behav. Res. 5, 329–350 (1970)
Wu, C.F.J.: On the convergence properties of the EM algorithm. Ann. Stat. 11, 95–103 (1983)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berlinet, A., Roland, C. Parabolic acceleration of the EM algorithm. Stat Comput 19, 35–47 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-008-9067-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-008-9067-x