Abstract
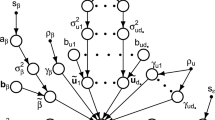
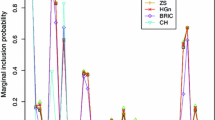
This paper surveys various shrinkage, smoothing and selection priors from a unifying perspective and shows how to combine them for Bayesian regularisation in the general class of structured additive regression models. As a common feature, all regularisation priors are conditionally Gaussian, given further parameters regularising model complexity. Hyperpriors for these parameters encourage shrinkage, smoothness or selection. It is shown that these regularisation (log-) priors can be interpreted as Bayesian analogues of several well-known frequentist penalty terms. Inference can be carried out with unified and computationally efficient MCMC schemes, estimating regularised regression coefficients and basis function coefficients simultaneously with complexity parameters and measuring uncertainty via corresponding marginal posteriors. For variable and function selection we discuss several variants of spike and slab priors which can also be cast into the framework of conditionally Gaussian priors. The performance of the Bayesian regularisation approaches is demonstrated in a hazard regression model and a high-dimensional geoadditive regression model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baladandayuthapani, V., Mallick, B.K., Carroll, R.J.: Spatially adaptive Bayesian penalized regression splines (P-splines). J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 14, 378–394 (2005)
Besag, J., York, J., Mollié, A.: Bayesian image restoration with two applications in spatial statistics. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 43, 1–59 (1991)
Bigelow, J.L., Dunson, D.B.: Bayesian adaptive regression splines for hierarchical data. Biometrics 63, 724–732 (2007)
Bondell, H.D., Reich, B.J.: Simultaneous regression shrinkage, variable selection, and supervised clustering of predictors with OSCAR. Biometrics 64, 115–123 (2008)
Brezger, A., Lang, S.: Generalized additive regression based on Bayesian P-splines. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 50, 967–991 (2006)
Cai, B., Dunson, D.: Bayesian covariance selection in generalized linear mixed models. Biometrics 62, 446–457 (2006)
Casella, G., Moreno, E.: Objective Bayesian variable selection. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 101, 157–167 (2006)
Chen, Z., Dunson, D.: Random effects selection in linear mixed models. Biometrics 59, 762–769 (2003)
Chib, S., Jeliazkov, I.: Inference in semiparametric dynamic models for binary longitudinal data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 101, 685–700 (2006)
Eilers, P.H.C., Marx, B.D.: Flexible smoothing using B-splines and penalties (with comments and rejoinder). Stat. Sci. 11, 89–121 (1996)
Fahrmeir, L., Kneib, T.: On the identification of trend and correlation in temporal and spatial regression. In: Shalab, Heumann, C. (eds.) Recent Advances in Linear Models and Related Areas. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Fahrmeir, L., Kneib, T.: Propriety of posteriors in structured additive regression models: Theory and empirical evidence. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 139, 843–859 (2009)
Fahrmeir, L., Kneib, T., Lang, S.: Penalized structured additive regression: A Bayesian perspective. Stat. Sin. 14, 731–761 (2004)
Fan, J., Li, R.: Variable selection via nonconcave penalized likelihood and its oracle properties. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 96, 1348–1360 (2001)
Fernandez, C., Ley, E., Steel, M.: Benchmark priors for Bayesian model averaging. J. Econom. 100, 381–427 (2001)
Frühwirth-Schnatter, S., Tüchler, R.: Bayesian parsimonious covariance estimation for hierarchical linear mixed models. Stat. Comput. 139, 1–13 (2008)
Frühwirth-Schnatter, S., Wagner, H.: Auxiliary mixture sampling for parameter-driven models of time series of small counts with applications to state space modelling. Biometrika 93, 827–841 (2006)
Frühwirth-Schnatter, S., Frühwirth, R., Held, L., Rue, H.: Improved auxiliary mixture sampling for hierarchical models of non-Gaussian data. Stat. Comput. (2009, to appear)
Fu, W.J.: Penalized regression: The bridge versus the LASSO. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 7, 397–416 (1998)
George, E.I., McCulloch, R.E.: Variable selection via Gibbs sampling. J. Am. Stat. Soc. 88, 881–889 (1993)
George, E.I., McCulloch, R.E.: Stochastic search variable selection. In: Spiegelhalter, et al. (eds.) Markov Chain Monte Carlo in Practice. Chapman & Hall, London (1995)
George, E.I., McCulloch, R.E.: Approaches for Bayesian variable selection. Stat. Sin. 7, 339–374 (1997)
Geweke, J.: Variable selection an model comparison in regression. In: Berger, et al. (eds.) Bayesian Statistics 5, pp. 609–620. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1996)
Goeman, J.J.: An Efficient Algorithm for L1-penalized Estimation. University Medical Center, Leiden (2007)
Griffin, J.E., Brown, P.J.: Alternative prior distributions for variable selection with very many more variables than observations. University of Warwick, Department of Statistics, Technical report (2005)
Griffin, J.E., Brown, P.J.: Bayesian adaptive lassos with non-convex penalization. University of Warwick, Department of Statistics, Technical report (2007)
Hennerfeind, A., Brezger, A., Fahrmeir, L.: Geoadditive survival models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 101, 1065–1075 (2006)
Ishwaran, H., Rao, S.J.: Detecting differentially expressed genes in microarrays using Bayesian model selection. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 462, 438–455 (2003)
Ishwaran, H., Rao, S.J.: Spike and slab variable selection: frequentist and Bayesian strategies. Ann. Stat. 33, 730–773 (2005)
Jullion, A., Lambert, P.: Robust specification of the roughness penalty prior distribution in spatially adaptive Bayesian P-splines models. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 51, 2542–2558 (2007)
Kammann, E.E., Wand, M.P.: Geoadditive models. Appl. Stat. 52, 1–18 (2003)
Kinney, S.K., Dunson, D.B.: Fixed and random effects selection in linear and logistic models. Biometrics 63, 690–698 (2007)
Kneib, T., Fahrmeir, L.: Structured additive regression for categorical space-time data: A mixed model approach. Biometrics 62, 109–118 (2006)
Kneib, T., Fahrmeir, L.: A mixed model approach for geoadditive hazard regression. Scand. J. Stat. 34, 207–228 (2007)
Kneib, T., Konrath, S., Fahrmeir, L.: High-dimensional structured additive regression models: Bayesian regularisation, smoothing and predictive performance. Technical Report No. 46, Department of Statistics, Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich (2009)
Kohn, R., Smith, M., Chan, D.: Nonparametric regression using linear combinations of basis functions. Stat. Comput. 11, 313–322 (2001)
Konrath, S., Kneib, T., Fahrmeir, L.: Bayesian regularization and smoothing for hazard regression. Technical Report No. 35, Department of Statistics, Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich (2008)
Lang, S., Brezger, A.: Bayesian P-Splines. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 13, 183–212 (2004)
Ley, E., Steel, M.: On the effect of prior assumptions in Bayesian model averaging with applications to growth regression. J. Appl. Econom. 24, 651–674 (2009)
Li, Y., Lin, X., Müller, P.: Bayesian inference in semiparametric mixed models for longitudinal data. Biometrics (2009, to appear)
Liang, F., Paulo, R., Molina, G., Clyde, M.A., Berger, J.O.: Mixtures of g priors for Bayesian variable selection. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 103, 410–423 (2008)
Müller, P., Quintana, F.A.: Nonparametric Bayesian data analysis. Stat. Sci. 19, 95–110 (2004)
Nychka, D.: Spatial-process estimates as smoothers. In: Schimek, M. (ed.) Smoothing and Regression: Approaches, Computation and Application. Wiley, New York (2000)
Panagiotelis, A., Smith, M.: Bayesian identification, selection and estimation of semiparametric functions in high-dimensional additive models. J. Econom. 143, 291–316 (2008)
Park, T., Casella, G.: The Bayesian lasso. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 103, 681–686 (2008)
Rue, H., Held, L.: Gaussian Markov Random Fields. Theory and Applications. CRC/Chapman & Hall, London (2005)
Rue, H., Martino, S., Chopin, N.: Approximate Bayesian inference for latent Gaussian models by using integrated nested Laplace approximations. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 71, 1–35 (2009)
Ruppert, D., Wand, M.P., Carroll, R.J.: Semiparametric Regression. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2003)
Scheipl, F., Kneib, T.: Locally adaptive Bayesian P-splines with a normal-exponential-gamma prior. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 53, 3533–3552 (2009)
Smith, M., Kohn, R.: Nonparametric regression using Bayesian variable selection. J. Econom. 75, 317–343 (1996)
Smith, M., Kohn, R.: Parsimonious covariance matrix estimation for longitudinal data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 97, 1141–1153 (2002)
Therneau, T.M., Grambsch, P.M.: Modeling Survival Data: Extending the Cox Model. Springer, New York (2000)
Tibshirani, R.: The LASSO method for variable selection in the Cox model. Stat. Med. 16, 385–395 (1997)
Tüchler, R.: Bayesian variable selection for logistic models using auxiliary mixture sampling. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 17, 76–94 (2008)
Wand, M.P.: Smoothing and mixed models. Comput. Stat. 18, 223–249 (2003)
Wang, X., George, E.I.: Adaptive Bayesian criteria in variable selection for generalized linear models. Stat. Sin. 17, 667–690 (2007)
Zhao, Y., Staudenmayer, J., Coull, B.A., Wand, M.P.: General design Bayesian generalized linear mixed models. Stat. Sci. 21, 35–51 (2006)
Zou, H., Hastie, T.: Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 67, 301–320 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fahrmeir, L., Kneib, T. & Konrath, S. Bayesian regularisation in structured additive regression: a unifying perspective on shrinkage, smoothing and predictor selection. Stat Comput 20, 203–219 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-009-9158-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-009-9158-3