Abstract
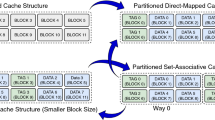
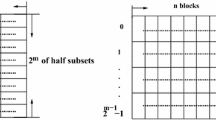
Traditional set associative caches are seriously prone to conflict misses. We propose an adapted new skewed associative architecture as an attempt to alleviate this problem. It has already been shown that skewed associative caches can reduce the rate of conflict misses by using different hash functions to index different banks. Building on this observation, we propose yet another approach to further reduce the rate of conflict misses, nicknamed YAARC (Yet Another Approach to Reducing Conflicts) that uses different hash functions to index into a single bank. Mathematical modeling and simulation results are exploited to evaluate the impact of YAARC on the rate of conflict misses. Mathematical analysis show the superiority of YAARC caches over set and skewed associative caches from the conflict miss point of view. Simulations, using some benchmarks from SPEC CPU2000 benchmark suit that former researchers have reported them as the best candidates for cache performance evaluation, also show nearly 43% conflict miss rate improvement for the skewed associative cache over the set associative cache, and nearly 31% improvement for the YAARC cache over the skewed associative cache. This implies that YAARC caches considerably outperform set and skewed associative caches from the conflict miss point of view. Since production of YAARC caches require a dispensable amount of hardware overhead, they can be considered as a cost effective approach to minimize the rate of conflict misses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Zolfaghari B, Sharifi M (2006) The impact of skewed associativity on the replacement traffic in coma multiprocessors. Int J Comput Syst Sci Eng 21(5):405–411
Zhang C (2006) Balanced cache: reducing conflict misses of direct-mapped caches through programmable decoders. In: 33rd international symposium on computer architecture (ISCA 2006), Boston, MA, USA, 17–21 June 2006
Ding X, Nikolopoulos D, Jiang S, Zhang X (2006) MESA: reducing cache conflicts by integrating static and run-time methods. In: IEEE international symposium on performance analysis of systems and software (ISPASS’06), Austin, TX, March 2006
Qureshi MK, Thompson D, Patt YN (2005) The V-way cache: demand based associativity via global replacement. In: Proceedings of international symposium on computer architecture (ISCA 2005), Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 4–8 June 2005, pp 544–555
Kharbutli M, Solihin Y, Lee J (2005) Eliminating conflict misses using prime number based cache indexing. IEEE Trans Comput 54(5):573–586
Zhang C (2005) Balanced instruction cache: reducing conflict misses of direct mapped caches through balanced sub-array accesses. IEEE Comput Arch Lett 5(1):2–5
Spjuth M, Karlsson M, Hagersten E (2005) Skewed caches from a low-power perspective. In: Proceedings of computing frontiers, Ischia, Italy, May 2005
Kulkarni C, Ghez C, Miranda M, Catthoor F, De Man H (2005) Cache conscious data layout organization for conflict miss reduction in embedded multimedia applications. IEEE Trans Comput Syst 54(1):76–81
Selen T (2004) Reorganization in the skewed-associative TLB. Master’s thesis, Department of Information Technology, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden, September 2004
Seznec A (2004) Concurrent support of multiple page sizes on a skewed associative TLB. IEEE Trans Comput 53(7):924–927
Spjuth M, Karlsson M, Hagersten E (2004) Low power and conflict tolerant cache design. Technical Report #2004-024, Department of Information Technology, Uppsala University, May 2004
Kharbutli M, Irwin K, Solihin Y, Lee J (2004) Using prime numbers for cache indexing to eliminate conflict misses. In: 10th international symposium on high performance computer architecture (HPCA-10), Madrid, Spain, 14–18 February 2004
Jung-Wook P, Cheong-Ghil K, Jung-Hoon L, Shin-Dug K (2004) An energy efficient cache memory architecture for embedded systems. In: Proceedings of the 2004 ACM symposium on applied computing, Nicosia, Cyprus, 14–17 March 2004, pp 884–890
Spjuth M, Karlsson M, Hagersten E (2003) The elbow cache: a power-efficient alternative to highly associative caches. Technical Report #2003-046, Department of Information Technology, Uppsala University, September 2003
Michaud P (2003) A statistical model of skewed associativity. In: International symposium on performance analysis of systems and software, Austin, March 2003
Sharifi M, Zolfaghari B (2002) An approach to exploiting skewed associative memories in avionics systems. In: International conference on parallel and distributed systems, National Central University, Taiwan, ROC, December 2002
Vandierendonck, De Bosschere (2003) Trade-offs for skewed-associative caches. In: International conference on parallel computing (Parco2003), Dresden, Germany, 2–5 September 2003
Djordjalian A (2002) Minimally skewed associative caches. In: Proceedings of 14th symposium on computer architecture and high performance computing (SCAB-PAD’02), Vitria, ES, Brazil, 28–30 October 2002, pp 100–107
Bartolini S, Prete CA (2001) A software strategy to improve cache performance. In: IEEE TCCA Newsletter, pp 24–32
Chu Y, Ito MR (2000) A 2-way thrashing avoidance cache (TAC): an efficient instruction cache scheme for object-oriented languages. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on computer design: VLSI in computers & processors (ICCD 2000), Austin, TX, 17–20 September 2000, pp 329–336
Dahlgren F, Torellas J (1999) Cache only memory architectures. IEEE Comput Mag 32(6):72–79
Kalamatianos J, Khalafi A, Kaeli D, Meleis W (1999) Analysis of temporal based program behavior for improved instruction cache performance. IEEE Trans Comput 48(2):168–175
Lee G, Quattlebaum B, Cho S, Kinney L (1999) Design of a bus based COMA multiprocessor DICE In: Microprocessors and microsystems, vol 22, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 403–411
Seznec A (1997) A new case for skewed associativity. IRISA Report No 1114, July 1997
Bodin F, Seznec A (1997) Skewed associativity improves program performance and enhances predictability. IEEE Trans Comput 46(5):530–544
Channon D, Lai R, Koch D (1997) Associativity revisited: a study of set, column and skewed TLBs using SPEC95. In: ACAC’97, pp 81–96
Gonzalez A, Valero M, Topham N, Parcerisa JM (1997) Eliminating cache conflict misses through XOR based placement functions. In: Proceedings of the international conference on supercomputing, pp 76–83
Torellas J, Padua D (1996) The Illinois aggressive COMA multiprocessor project (I_A COMA). In: Proceedings of the 6th symposium on the frontiers of massively parallel computing, October 1996
Bodin F, Seznec A (1995) Skewed associativity enhances performance predictability. In: Proceedings of the 22nd international symposium on computer architecture (IEEE-ACM), Santa-Margharita, June 1995
Muller HL, Stallard PWA, D Warren DH (1995) The application of skewed associative memories to cache only memory architectures. In: Proceedings of the international conference on parallel processing, ICPP’95, Oconomowoc, Wisconsin, vol 1, 14–18 August 1995, pp 150–154
Srivastava A, Esutace A (1994) ATOM: a system for building customized program analysis tools. Technical Report 94-2, Western Research Laboratory Digital
Seznec A (1993) About set and skewed associativity on second level caches. In: International conference on computer design, Boston, October 1993
Seznec A, Bodin F (1993) Skewed associative caches. In: Proceedings of PARLE ’93—parallel architectures and languages Europe. Lecture notes in computer science, Munich, Germany, 14–17 June 1993
Seznec A (1993) A case for 2-way set associative caches. In: Proceedings of the 20th ISCA (International symposium on computer architecture), San Diego, CA, May 1993, pp 169–178
Joe T, Hennessy L (1992) Comparative performance evaluation of cache coherent NUMA and COMA architectures. In: Proceedings of the 19th annual international symposium on computer architecture, May 1992, pp 80–91
Gupta A et al (1992) Performance limitations of cache coherent NUMA and hierarchical COMA multiprocessors and the flat-COMA solution. Stanford University Technical Report #CSL-TR-92-524, May 1992
Burkhardt III H et al (1992) Overview of the KSR-1 computer system. Technical Report KSR-TR-9202001, Kendall Square Research Corporation
Hagersten E, Haridi S, Landin A (1992) DDM: a cache-only memory architecture. IEEE Comput 25(9):44–54
Cantin JF, Hill MD (2000) Cache performance of the SPEC CPU2000 benchmarks. http://www.cs.wisc.edu/multifacet/misc/spec2000cachedata/
Henning JL (2000) SPEC CPU2000: measuring CPU performance in the new millennium. IEEE Comput 33(7):28–35, http://www.spec.org/osg/cpu2000/papers/COMPUTER_200007-abstract.JLH.html
Burger D, Austin T (1997) The SimpleScalar tool set, version 2.0., Technical Report #1342 University of Wisconsin-Madison
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharifi, M., Zolfaghari, B. YAARC: yet another approach to further reducing the rate of conflict misses. J Supercomput 44, 24–40 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-007-0147-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-007-0147-z