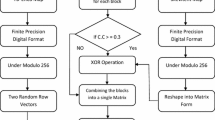
Abstract
With the development of digital imaging technology and the prevalence of mobile devices with camera, internet privacy has been a growing concern for public. Especially in some private chat groups in social network, for example, Facebook, WeChat, and MySpace, some people want to share their personal images by internet service provider without leaking this information while the internet service provider can also take some additional measures on these images, for example, reducing the network bandwidth. How to provide technologies or software with such functionalities, usually conflicting goals, becomes increasingly urgent in both academia and industry. Image encryption is a choice; however, it does not provide the additional function needed by internet service providers. Recently, game theory is widely used in network security to solve such problem with conflicting goals. In fact, there is a game theory between users and service providers. This paper proposes a block-based image compression method in encrypted domain which provides not only the privacy protection capability but also the additional operation capability needed by internet service providers. This block-based method can be formulated as a game theoretical problem and can be optimized by game theory. First, the image to be shared will be encrypted in block-by-block way by owner with simple encryption operation. Second, the service providers can send the part or full of the encrypted image stream according to the available bandwidth with an adaptive parameter sets. Finally, the intended receivers can decrypt the received encrypted stream to recover the image. Extensive experiments show that the proposed algorithm improves the compression performance compared with the-state-of algorithms.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Molina B (2014) Personal Apple: iCloud not breached in celebrity photo leak. Sep. 2014. online available: http://www.usatoday.com/story/tech/personal/2014/09/02/apple-icloud-leak/14979323/
Nie XS, Liu J, Sun JD, Wang LQ, Yang XH (2013) Robust video hashing based on representative-dispersive frames. Sci China Inform Sci 56(6):1–11
Squicciarini AC, Lin D, Sundareswaran S, Wede J (2014) Privacy policy inference of user-uploaded images on content sharing sites. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. doi:10.1109/TKDE.2014.2320729
Mitchell J (2010) Making photo tagging easier. Online Available: http://blog.facebook.com/blog.php?post=467145887130
Gao W, Tian YH, Huang TJ, Yang Q (2010) Vlogging: a survey of videoblogging technology on the web. ACM Comput Surv 42(4): Article No.15
Zhu, H, Dusit N, Walid S, Tamer B (2012) Game theory in wireless and communication networks-theory, models and applications. Cambridge Uinversity Press, Cambridge
Roy S, Ellis C, Shiva S, Dasgupta D, Shandilya V, Wu QS (2010) A survey of game theory as applied to network security. In: Proceedings of the 43rd Hawaii international conference on system sciences, Honolulu, HI, pp 1–10
Mohammad H, Zhu QY, Tansu A, Tamer B, Hubaux JP (2013) Game theory meets network security and privacy. ACM Comput Surv 45(3): Article 24
Lye KW, Wing JM (2005) Game strategies in network security. Int J Inf Secur 4:71–86
Cheng H, Li XB (2000) Partial encryption of compressed images and videos. IEEE Trans Signal Process 48(8):2439–2451
Signal Guest editors: Piva A, Katzenbeisser S (2007) Processing in the encrypted domain. EURASIP J Inform Secur 2007
Johnson M, Ishwar P, Prabhakaran VM, Schonberg D, Ramchandran K (2004) On compressing encrypted data. IEEE Trans Signal Process 52(10): 2992–3006
Zhang GC, Liu SH, Jiang F, Zhao DB, Gao W (2013) An improved image compression scheme with an adaptive parameters set in encrypted domain. VCIP 2013:1–6
Hassinen M, Mussalo P (2005) Client controlled security for web applications. In: The 30th anniversary on local computer networks, IEEE Computer Society, pp 810–816
Poller A, Steinebach M, Liu H (2012) Robust image obfuscation for privacy protection in Web 2.0 applications. IS&T SPIE Electronic Imaging. In: International society for optics and photonics, SPIE, 830304-830304-15
Zhou Y, Panetta K, Agaian S (2009) Image encryption using discrete parametric cosine transform. In: Proceedings of the 43rd asilomar conference on signals, systems and computers, ser. Asilomar’09. Piscataway, NJ, USA. IEEE Press, pp 395–399
Podesser M, Schmidt HP, Uhl A (2002) Selective bitplane encryption for secure transmission of image data in mobile environments. In: The 5th nordic signal processing symposium, pp 10–37
Yekkala A, Madhavan CEV (2007) Bit plane encoding and encryption. In: Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on pattern recognition and machine intelligence, ser. PReMI’07. Springer, Berlin, pp 103–110
Xiong ZX, Liveris AD, Cheng S (2004) Distributed source coding for sensor networks. IEEE Signal Process Mag 21(5):80–94
Schonberg D, Draper SC, Ramchandran K (2005) On blind compression of encrypted correlated data approaching the source entropy rate. In: Proceedings of the 43rd Annual Allerton Conference, Allerton, IL
Schonberg D, Draper SC, Yeo CH, Ramchandran K (2008) Toward compression of encrypted images and video sequences. IEEE Trans Inform Forensics Secur 3(4):749–762
Lazzeretti R, Barni M (2008) Lossless compression of encrypted greylevel and color images. In: Proceedings of the 16th EUSIPCO, Lausanne, Switzerland
Kumar AA, Makur A (2009) Lossy compression of encrypted image by compressive sensing technique. TENCON 2009–2009 IEEE Region 10 Conference, pp 1–5
Liu W, Zeng W, Dong L, Yao Q (2010) Efficient compression of encrypted grayscale images. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(4):1097–1102
Kang XG, Xu XY, Peng AJ, Zeng WJ (2012) Scalable lossy compression for pixel-value encrypted images. In: IEEE data compression conference 2012, Snowbird, Utah, USA April 10–12
Kang XG, Peng AJ, Xu XY, Cao XC (2013) Performing scalable lossy compression on pixel encrypted images. EURASIP J Image Video Process 32:1–6
Zhang XP (2011) Lossy compression and iterative reconstruction for encrypted image. IEEE Trans Inform Forensics Secur 6(1):53–58
Zhang J, Xiong RQ, Ma SW, Zhao DB (2011) High-quality image restoration from partial random samples in spatial domain. In: IEEE visual communications and image processing (VCIP), pp 1–4
Ahmad I, Luo JC (2006) On using game theory to optimize the rate control in video coding. IEEE Trans CSVT 16(2):209–219
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):600–612
Lagendijk RL, Erkin Z, Barni M (2013) Encrypted signal processing for privacy protection: conveying the utility of homomorphic encryption and multiparty computation. IEEE Signal Process Mag 30(1):82–105
Yao Q, Zeng W, Liu W (2009) Multi-resolution based hybrid spatiotemporal compression of encrypted videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on acoustics speech and signal processing, Taipei, Taiwan, ROC, 725–728
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China under Grant 2015CB351804, a scholarship from the China Scholarship Council of the Republic of China under Grant No. 201203070360 and the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No.60803147. The authors would like to thank the authors of [29, 30] for kindly providing their source codes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Paul, A., Zhang, G. et al. A game theory-based block image compression method in encryption domain. J Supercomput 71, 3353–3372 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-015-1413-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-015-1413-0