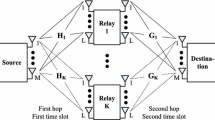
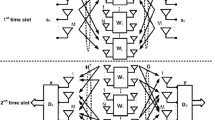
Abstract
In this paper, we consider a multi-source multicasting two-hop multi-input multi-output amplify-forward (AF) relay system, where multiple source nodes multicast their own messages to a group of receivers with the cooperation of an AF relay node. In particular, we aim at minimizing the transmission power consumption and the mean-squared error (MSE) of the receiver estimated signal simultaneously. However, the two objectives are coupled and even conflicting. In view of this, a multi-objective optimization (MOO) framework is adopted to achieve the trade-off between the two objectives. The formulated MOO problem (MOOP) takes into account the constraints of the MSE upper bound and the maximum transmission power budget. Since the MOOP is non-convex and hard to tackle, we propose a resource allocation algorithm by exploiting the weighted Tchebycheff approach and the optimal structure of the relay precoding matrix. Simulation results not only demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, but also unveil an important trade-off between the total power consumption and the MSE at receivers.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vishwannath S, Jindal N, Goldsmith A (2003) Duality, achievable rates, and sum-rate capacity of Gaussian MIMO broadcast channels. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 49:2658–2668
Laneman JN, Tse DNC, Wornell GW (2004) Cooperative diversity in wireless network: efficient protocols and outage behavior. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 50(12):3062–3080
Tang X, Hua Y (2007) Optimal design of non-regenerative MIMO wireless relays. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 6(4):1398–1407
Khandaker MRA, Rong Y (2013) Precoding design for MIMO relay multicasting. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 12(7):3544–3555
Singh VP, Chaturvedi AK (2015) Min-max mean squared error-based linear transceiver design for multiple-input-multiple-output interference relay channel. IET Commun 9(6):853–861
Rong Y (2010) Simplified algorithms for optimizing multiuser multi-hop MIMO relay system. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 59(10):2896–2904
Zhao C, Champagne B (2015) A unified approach to optimal transceiver design for nonregenerative MIMO relaying. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 64(7):2938–2951
He Z, Lang Z, Rong Y, Qu S (2014) Joint transceiver optimization for two-way MIMO relay system with MSE constraint. IEEE Wirel Commun Lett 3(6):613–616
Abu Sayed M, Mostafizur Rahaman M, Islam I, Amin MR (2015) Selection of the best two-hop AF wireless link under multiple antenna schemes over a fading channel. J Inf Process Syst 11(1):57–75
Sun Y, Ng DWK, Schober R (2015) Multi-objective optimization for power efficient full-duplex wireless communication systems. In: Proceedings of IEEE Globecom, pp 1–6
Ng DWK, Lo ES, Schober R (2015) Multi-objective resource allocation for secure communication in cognitive radio networks with wireless information and power transfer. IEEE Trans Veh Technol. 65:3166–3184
Bjornson E, Jorswieck E, Debbah M, Ottersten B (2014) Multiobjective signal processing optimization: the way to balance conflicting metrics in 5G systems. IEEE Signal Process Mag 31(6):14–23
Wu W, Wang B (2015) Robust secrecy beamforming for wireless information and power transfer in multiuser MISO communication system. EURASIP J Wirel Commun Netw 2015:161
Zhang J, Tang J, Wang T, Chen F (2017) Energy-efficient data-gathering rendezvous algorithms with mobile sinks for wireless sensor networks. Int J Sens Netw 23(4):248–257
Wu W, Wu S, Wang B (2017) Robust multi-objective beamforming design for power efficient and secure communication in MU-MISO networks. IEEE Access 5:13277–13285
Marler RT, Arora JS (2004) Survey of multi-objective optimization methods for engineering. Struct Multidiscip Optim 26(6):369–395
Benhabib W, Fizazi H (2017) A multi-objective TRIBES/OC-SVM approach for the extraction of areas of interest from satellite images. J Inf Process Syst 13(2):321–339
Leng S, Ng DWK, Zlatanov N, Schober R (2016) Multi-objective beamforming for energy-efficient SWIPT systems. In: 2016 International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), Kauai, HI, pp 1–7
Kay SM (1993) Fundamentals of statistical signal processing: estimation theory. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cilffs
Wang B, Xiaodu G, Ma L, Yan S (2017) Temperature error correction based on BP neural network in meteorological WSN. Int J Sens Netw 23(4):265–278
Zhou M-Y, Zhao X-H (2017) A power allocation algorithm based on variational inequality problem for cognitive radio networks. J Inf Process Syst 13(2):417–427
Song C, Lee K, Lee I (2010) MMSE based transceiver designs in closed-loop non-regenerative MIMO relaying systems. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 9(7):2310–2319
Boyd S, Vandenberghe L (2004) Convex optimization. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Grant M, Boyd S (2010) CVX: Matlab software for disciplined convex programming (web page and software). http://cvxr.com/cvx/
Zhangjie F, Huang F, Ren K, Weng J, Wang C (2017) Privacy-preserving smart semantic search based on conceptual graphs over encrypted outsourced data. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 12(8):1874–1884
Palomar DP, Cioffi JM, Lagunas MA (2003) Joint Tx–Rx beamforming design for multicarrier MIMO channels: a unified framework for convex optimization. IEEE Trans Signal Process 51(9):2381–2401
Acknowledgements
The work was partially supported by Swedish Research Links (348-2008-6212), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61571241), Industry-university research Prospective joint project of Jiangsu Province (BY2014014), Major projects of Jiangsu Province university natural science research (15KJA510002) and Graduate Innovation Project of Jiangsu (KYLX15_0840).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix A
Appendix A
MSE matrix (12) can be reformulated as:
where \( {\mathbf{U}} = {\mathbf{HFF}}^{H} {\mathbf{H}}^{H} + {\mathbf{I}}_{{N_{r} }} \).
In the above transformations, the inversion lemma is applied to obtain formula (30b) and (30c), while the matrix equality \( {\mathbf{B}}^{H} ({\mathbf{BCB}}^{H} + {\mathbf{I}})^{ - 1} {\mathbf{B}} = {\mathbf{C}}^{ - 1} - ({\mathbf{CB}}^{H} {\mathbf{BC}} + {\mathbf{C}})^{ - 1} \) is used to obtain formula (30d).
The first term in the right side of (30e) can be transformed by utilizing the matrix inversion lemma as:
Applying the relay structure in (16), the matrix inversion lemma and the matrix equality \( {\mathbf{B}}^{H} ({\mathbf{BCB}}^{H} + {\mathbf{I}})^{ - 1} {\mathbf{B}} = {\mathbf{C}}^{ - 1} - ({\mathbf{CB}}^{H} {\mathbf{BC}} + {\mathbf{C}})^{ - 1} \) once again into the second term in the right side of (30e), then we can get the transformation as:
Therefore, we can get MSE formulation (17).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, M., Zhang, D. & Wang, J. Multi-objective optimization design for multi-source multicasting MIMO AF relay systems. J Supercomput 74, 6815–6830 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-018-2275-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-018-2275-z