Abstract
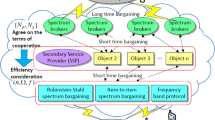
Cognitive radio is becoming an emerging technology that has the potential of dealing with the stringent requirement and scarcity of the radio spectrum resource. In this paper, we focus on the dynamic spectrum access of cognitive radio networks, in which the primary user (PU) and secondary users (SUs) coexist. In property-rights model, the PU has property of the bandwidth and may decide to lease it to secondary network for a fraction of time in exchange for appropriate remuneration. We propose a cooperative communication-aware spectrum leasing framework, in which, PU selects SUs as cooperative relays to help transmit information, while the selected SUs have the right to decide their payment made for PU in order to obtain a proportional access time to the spectrum. Then, the spectrum leasing scheme is cast into a Nash Bargaining Problem, and the Nash Bargaining Solution (NBS) can be used to fairly and efficiently address the resource allocation between PU and secondary network, enhancing both the utility of PU and secondary network. Numerical results show that spectrum leasing based on NBS is an effective method to improve performance for cognitive radio networks.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, D., Yin, S., Zhang, Q., Liu, M., & Li, S. (2009). Mining spectrum usage data: a large-scale spectrum measurement study. In Proc. of ACM the 15th annual international conference on mobile computing and networking. doi:10.1145/1614320.1614323.
Chen, Y. X., Zhao, Q., & Swami, A. (2006). Joint design and separation principle for opportunistic spectrum access. In Proc. of fortieth asilomar conference on signals, systems and computers, Pacific Grove, CA, 29–30 Oct. 2006 (pp. 696–700).
Dasilva, L. A., Bogucka, H., & Mackenzie, A. B. (2011). Game theory in wireless networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 49(8), 110–111.
Debreu, G. (1952). A social equilibrium existence theorem. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, Oct., 886–893.
Devroye, N., Mitran, P., & Tarokh, V. (2006). Achievable rates in cognitive radio. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 52(5), 1813–1827.
Han, Z., Ji, Z., & Ray Liu, K. J. (2005). Fair multiuser channel allocation for OFDMA networks using Nash bargaining solutions and coalitions. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 53(8), 1366–1376.
Hu, Z., Zhang, G. Y., & Zhao, L. L. (2010). A multi-stage dynamic spectrum sharing framework in cognitive radio networks. In Proc. of international conference on computer engineering and technology, Chengdu, 16–18 Apr. 2010 (pp. V2-501–V2-505).
Koltsidas, G., & Pavlidou, F. N. (2010). A game theoretical approach to clustering of ad-hoc and sensor networks. Telecommunication Systems, 47(1), 81–93.
Meng, J., Yin, W. T., Li, H. S., Hossain, E., & Han, Z. (2011). Collaborative spectrum sensing from sparse observations in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 29(2), 327–337.
Muthuramalingam, B., Bhashyam, S., & Thangaraj, A. (2012). A decode and forward protocol for two-stage Gaussian relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 60(1), 68–73.
Owen, G. (1995). Game theory. London: Academic Press.
Peha, J. M. (2005). Approaches to spectrum sharing. IEEE Communications Magazine, 43(2), 10–12.
Peng, M. G., Liu, Y., Wei, D. Y., Wang, W. B., & Chen, H. H. (2011). Hierarchical cooperative relay based heterogeneous networks. IEEE Wireless Communications, 18(3), 48–56.
Qiang, N., & Zarakovitis, C. C. (2012). Nash bargaining game theoretic scheduling for joint channel and power allocation in cognitive radio systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 30(1), 70–81.
Sakran, H., & Shokair, M. (2011). Hard and softened combination for cooperative spectrum sensing over imperfect channels in cognitive radio networks. Telecommunication Systems doi:10.1007/s11235-011-9467-7.
Simeone, O., Stanojev, I., Savazzi, S., Bar-Ness, Y., Spagnolini, U., & Pickholtz, R. (2008). Spectrum leasing via distributed cooperation in cognitive radio. In Proc. of IEEE international conference on communications, Beijing, 19–23 May 2008 (pp. 3427–3431).
Tahir, M., & Mazumder, S. K. (2008). Markov chain model for performance analysis of transmitter power control in contention based wireless MAC protocol. Telecommunication Systems, 38(3), 99–110.
Tang, L., Chen, Q. B., Wang, G. Y., Zeng, X. P., & Wang, H. (2011). Opportunistic power allocation strategies and fair subcarrier allocation in OFDM-based cognitive radio networks. Telecommunication Systems doi:10.1007/s11235-011-9486-4.
Vassaki, S., Panagopoulos, A. D., & Constantinou, P. (2011). Evaluation of channel dependent bandwidth allocation in wireless access networks: centralized and distributed approach. Telecommunication Systems doi:10.1007/s11235-011-9481-9.
Wang, B. B., Wu, Y. L., & Liu, K. J. R. (2010). Game theory for cognitive radio networks: an overview. Computer Networks, 54(14), 2537–2561.
Wang, W., Wu, K. J., Luo, H. Y., Yu, G. D., & Zhang, Z. Y. (2011). Sensing error aware delay-optimal channel allocation scheme for cognitive radio networks. Telecommunication Systems doi:10.1007/s11235-011-9472-x.
Wang, X. B., Li, Z., Xu, P. C., Xu, Y. Y., Gao, X. B., & Chen, H. H. (2010). Spectrum sharing in cognitive radio networks—an auction-based approach. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 40(3), 587–596.
Xu, H., & Li, B. C. (2010). Efficient resource allocation with flexible channel cooperation in OFDMA cognitive radio networks. In Proc. of IEEE INFOCOM, San Diego, CA, 14–19 May 2010 (pp. 1–9).
Yang, B., Feng, G., Shen, Y. Y., Long, C. N., & Guan, X. P. (2009). Channel-aware access for cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 58(7), 3726–3737.
Yang, C. G., & Li, J. D. (2011). Performance analysis of a Stackelberg game-theoretical strategy design in cognitive radio networks. In Proc. of IEEE international conference on signal processing, communications and computing, Xian, 14–16 Sep. 2011 (pp. 1–5).
Zhang, J., & Zhang, Q. (2009). Stackelberg game for utility-based cooperative cognitive radio networks. In Proc. of ACM international symposium on mobile ad hoc networking and computing. doi:10.1145/1530748.1530753.
Zhang, Q., Jia, J. C., & Zhang, J. (2009). Cooperative relay to improve diversity in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 47(2), 111–117.
Zhang, Y. H., & Leung, C. (2009). Cross-layer resource allocation for real-time services in OFDM-based cognitive radio systems. Telecommunication Systems, 42(1–2), 97–108.
Zhu, J., Wang, J., Luo, T., & Li, S. J. (2009). Adaptive transmission scheduling over fading channels for energy-efficient cognitive radio networks by reinforcement learning. Telecommunication Systems, 42(1–2), 123–138.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Programme of China (973 Programme) (no. 2010CB731800), Key Project of National Nature Science Foundation of China (no. 60934003), National Nature Science Foundation of China (no. 61104033; no. 61172095; no. 61203104) and Nature Science Foundation of Hebei Province (no. F2011203226; no. F2012203109; no. F2012203126).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, X., Wang, X., Ma, K. et al. Spectrum leasing based on Nash Bargaining Solution in cognitive radio networks. Telecommun Syst 57, 313–325 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-013-9860-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-013-9860-5