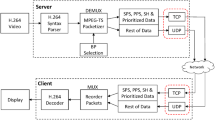
Abstract
There is a significant rise in demand for video transmission over 3G and 4G wireless networks due to the rising popularity of video streaming websites such as YouTube. The market for video streaming over wireless networks is expected to increase sharply in the future. Both of the two basic transport layer protocols without modifications are not suited for video transmission over wireless networks. UDP (user datagram protocol) suffers from inherent unreliability, resulting in corrupted video due to frequent corruption of packets. Inherent features of wireless networks such as noise, interference, etc. result in packet corruption. On the other hand, the performance of TCP (transmission control protocol) is worse than UDP (Thangaraj et al. in Telecommun Syst 45(4):303–312, 2010) because of frequently corrupted packets. Due to its reliable data transfer feature, TCP continuously retransmits the corrupted packet until successful reception at the receiver. This leads to jitter in video playback and poor end user quality of experience. Multiple TCP connections with appropriate optimization can lead to an increased efficiency of bandwidth utilization in comparison to single TCP based video transmission over wireless networks. It has been shown that multiple TCP connections enhance the video transmission and playback experience by providing reliable communication. The parallel TCP scheme proposed in this paper enhances the quality of video transmission and playback experience over MIMO wireless networks employing scalable hierarchical wavelet decomposition based video encoding with multiple TCP connections.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thangaraj, A., Zeng, Q.-A., & Li, X. (2010). Performance analysis of the IEEE 802.11e wireless networks with TCP ACK prioritization. Telecommunication Systems, 45(4), 303–312.
Foschini, Gerard J. (1996). Layered space-time architecture for wireless communication in a fading environment when using multi-element antennas. Bell Labs Technical Journal, 1(2), 41–59.
Tse, D., & Viswanath, P. (2005). Fundamentals of wireless communication. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Chen, M., & Zakhor, A. (2006). Multiple TFRC connections based rate control for wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 8(5), 1045–1062.
Schwarz, H., Marpe, D., & Wiegand, T. (2007). Overview of the scalable video coding extension of the H.264/AVC standard. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 17(9), 1103–1120.
Develder, C., Lambert, P., Lancker, W., Moens, S., Walle, R., Nelis, J., et al. (2012). Delivering scalable video with QoS to the home. Telecommunication Systems, 49(1), 129–148.
Postel, J. (1980). DOD standard transmission control protocol. SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 10(4), 52–132.
Comer, D. (2000). Internetworking with TCP/IP: principles, protocols, and architecture. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall Inc.
Stevens, W. (1997). TCP slow start, congestion avoidance, fast retransmit, and fast recovery algorithms. Washington, DC: RFC Editor.
Paul, S., Ayanoglu, E., La Porta, T.F., Chen, K.-W.H., Sabnani, K.E., & Gitlin, R.D. (1995). An asymmetric protocol for digital cellular communications. In IEEE Computer Society Proceedings of the Fourteenth Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communication Societies (Vol. 3), INFOCOM ’95, pp. 1053–1062, Washington, DC, USA.
Bakre, A., & Badrinath, B.R. (1995). I-TCP: Indirect TCP for mobile hosts. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems, pp. 136–143.
Balakrishnan, H., Seshan, S., Amir, E., & Katz, R.H. (1995). Improving TCP/IP performance over wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 1st annual international conference on Mobile computing and networking, MobiCom ’95, pp. 2–11, New York. ACM.
Papadimitriou, P., Tsaoussidis, V., & Zhang, C. (2010). End-to-end loss differentiation for video streaming with wireless link errors. Telecommunication Systems, 43(3–4), 295–312.
Handley, M., Floyd, S., Padhye, J., & Widmer, J. (2003). TCP friendly rate control (TFRC): Protocol specification. Washington, DC: RFC Editor.
Lochin, E., Dairaine, L., & Jourjon, G. (2006). GTFRC, a TCP friendly QoS-aware rate control for diffserv assured service. Telecommunication Systems, 33(1–3), 3–21.
Martijn Kuipers, B. W., Vaz, R. N., & Nunes, M. S. (2013). Video quality protection for real time video streams over wireless networks. Telecommunication Systems, 52(4), 2259–2270.
Lettieri, P., & Srivastava, M.B. (1998). Adaptive frame length control for improving wireless link throughput, range, and energy efficiency. In INFOCOM ’98. Seventeenth Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies. Proceedings. Vol. 2, pp. 564–571
Wan, H.-H., & Kwok, Y.-K. (2006). High data rate video transmission using parallel TCP connections: Approaches and performance evaluation. Journal of Supercomputing, 35(2), 119–139.
Malliga, G.s., & Varughese, D.K. (2010). TCP - AP and LRED over single and multiple TCP flows in multihop wireless channel. In N. Meghanathan, S. Boumerdassi, N. Chaki & D. Nagamalai (Eds.), Recent trends in networks and communications, vol. 90 of communications in computer and information science, (pp. 400–410). Springer: Berlin Heidelberg.
Lee, J., Gunter, D., Tierney, B., Allcock, B., Bester, J., Bresnahan, J., & Tuecke, S. (2001). Applied techniques for high bandwidth data transfers across wide area networks. url http://escholarship.org/uc/item/6zq8z3cr.
Sivakumar, H., Bailey, S., & Grossman, R.L. (2000). Psockets: The case for application-level network striping for data intensive applications using high speed wide area networks. In IEEE Computer Society Proceedings of the 2000 ACM/IEEE conference on Supercomputing, Supercomputing ’00, Washington, DC.
Jacobson, V. (1988). Congestion avoidance and control. SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 18(4), 314–329.
Mathis, M., Semke, J., Mahdavi, J., & Ott, T. (1997). The macroscopic behavior of the TCP congestion avoidance algorithm. SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 27(3), 67–82.
Margaliot, M. (2008). Pattern recognition (theodoridis, s. and koutroumbas, k.; 2006) [book reviews]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 19(2), 376–376.
Ahmed, N., Natarajan, T., & Rao, K. R. (1974). Discrete cosine transform. IEEE Transactions on Computers, C–23(1), 90–93.
Gray, R. M., & Neuhoff, D. L. (1998). Quantization. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 44(6), 2325–2383.
Lee, J. (1998). Rate-distortion optimization of parametrized quantization matrix for MPEG-2 encoding. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, 1998. ICIP 98, vol. 2, pp. 383–386.
Hassoun, D. (2010). Dynamic streaming in flash media server 3.5, part 1: Overview of the new capabilities. url http://www.adobe.com/devnet/adobe-media-server/articles/dynstream_advanced_pt1.html.
Kohler, E., Handley, M., & Floyd, S. (2006). Datagram congestion control protocol (DCCP). Washington, DC: RFC Editor.
Kohler, E., Handley, M., & Floyd, S. (2006). Profile for datagram congestion control protocol (DCCP) congestion control ID 3: TCP-Friendly Rate Control (TFRC). Washington, DC: RFC Editor.
Kohler, E., & Floyd, S. (2006). Profile for datagram congestion control protocol (DCCP) congestion control ID 2: TCP-like congestion control. Washington, DC: RFC Editor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaurasia, A.K., Jagannatham, A.K. Parallel TCP and scalable video coding for jitter free video transmission over MIMO wireless networks. Telecommun Syst 61, 733–753 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-015-0064-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-015-0064-z