Abstract
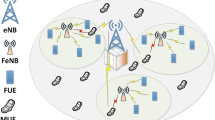
The next generation mobile communication (5G) systems is targeting very high data rate by deploying more number of small cells, but this deployment results in high cross-tier interference because of using the same frequency band. To solve this challenge, an efficient power control scheme is desired specially for the case of uplink scenario. Thus, to solve this challenge, we propose the neighbors’ interference situation-aware uplink power control (IA-ULPC) scheme to reduce the cross-tier interference. In this scheme, we consider the interference situation of the neighbor cells while controlling the power of the users. Moreover, we also derive the target signal-to-interference and noise-ratio (\(P_0\)) equation to dynamically adjust it based on the neighbors’ base station interference situation. We compare the performance of the proposed IA-ULPC with the conventional fractional power control scheme (C-FPC). The extensive system-level simulations are carried out to prove the validity of the proposed IA-ULPC scheme which almost doubles the user average throughput and also decreases the interference around 20% in dense two-tier heterogeneous network environment as compared to C-FPC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Access, E.U.T.R. (2014). 3gpp ts 36.213 v12.1.0.
Ahmad, A., Hassan, N. U., Assaad, M., & Tembine, H. (2016). Joint power control and rate adaptation for video streaming in wireless networks with time-varying interference. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 65(8), 6315–6329.
Ahmad, A., Khan, M. T. R., & Kaleem, Z. (2016). Uplink optimal power allocation for heterogeneous multiuser SIMO SC-FDMA networks. Electronics Letters, 52(24), 1990–1992.
Ahmad, I., Kaleem, Z., & Chang, K. (2013). Uplink power control for interference mitigation based on users priority in two-tier femtocell network. In 2013 international conference on ICT convergence (ICTC) (pp. 474–476). IEEE.
Andrews, J. G., Buzzi, S., Choi, W., Hanly, S. V., Lozano, A., Soong, A. C., et al. (2014). What will 5G be? IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 32(6), 1065–1082.
Assumptions, S. (2009). Parameters for FDD HeNB RF requirements. 3GPP TSG-RAN WG4 R4-092042.
Castellanos, C. U., Villa, D. L., Rosa, C., Pedersen, K. I., Calabrese, F. D., Michaelsen, P. H., & Michel, J. (2008). Performance of uplink fractional power control in utran lte. In Vehicular technology conference, 2008 (pp. 2517–2521). IEEE.
Deb, S., & Monogioudis, P. (2015). Learning-based uplink interference management in 4G LTE cellular systems. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking (TON), 23(2), 398–411.
Equipment, U. (2010). Evolved universal terrestrial radio access (e-utra); radio frequency (rf) system scenarios, 3rd generation partnership project (3GPP). Technical report, TR 36.942 (2010).
Kaleem, Z., Hui, B., & Chang, K. (2014). QoS priority-based dynamic frequency band allocation algorithm for load balancing and interference avoidance in 3GPP LTE HetNet. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2014(1), 1–18.
Kim, W., Kaleem, Z., & Chang, K. (2015). Power headroom report-based uplink power control in 3GPP LTE-A HetNet. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2015(1), 1–13.
Kim, W., Kaleem, Z., & Chang, K. (2015). UE-specific interference-aware open-loop power control in 3GPP LTE-A uplink HetNet. In 2015 seventh international conference on ubiquitous and future networks (pp. 682–684). IEEE.
Morita, M., Nobukiyo, T., & Hamabe, K. (2012). Uplink power control method for lte femtocells based on resource usage aggregation. In IEEE 23rd international symposium on personal indoor and mobile radio communications (PIMRC) (pp. 442–447). IEEE.
Muhammad, B., & Mohammed, A. (2010) Uplink closed loop power control for LTE system. In 2010 6th international conference on emerging technologies (ICET) (pp. 88–93). IEEE.
Network, E.U.T.R.A. (2015) X2 application protocol (x2ap)(3gpp ts 36.423 version 13.3.0 release 13).
Taranetz, M., & Rupp, M. (2012). Performance of femtocell access point deployments in user hot-spot scenarios. In Telecommunication networks and applications conference (ATNAC), Australasian (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported under Start Up Research Grant (SRGP) Project No. 1137 from Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Appendix
Appendix
The transmit power of the FUE/MUE in the serving FeNB/eNB is derived as follows:
By utilizing (4) in (13), we can describe it as:
By substituting (9) in to (14), we can write as:
Suppose \(P_{n\_0}^{\textit{lin}\_{\textit{interf}}}\) is same for all the neighbor cells, then we have
By applying log product rule, that is, \(\log (A \times B)=\log (A)+\log (B)\). Thus we have:
Since, \(P_{n\_0}^{\textit{interf}}=10\log _{10}(P_{n\_0}^{\textit{lin}\_\textit{interf}})\). Thus, we can write (17) as:
Thus, by rearranging (18) the total interference can be calculated as:
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaleem, Z., Ahmad, A. & Rehmani, M.H. Neighbors’ interference situation-aware power control scheme for dense 5G mobile communication system. Telecommun Syst 67, 443–450 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-017-0350-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-017-0350-z