Abstract
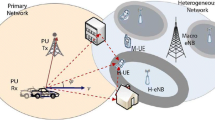
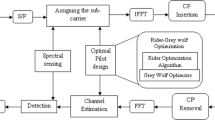
In a cognitive radio system, the goal is to make better use of the radio electric spectrum, allowing non-licensed users access to those currently unused electromagnetic bands assigned to licensed users (LUs). This can be achieved using OFDM, where the non-licensed users must select the temporarily available subcarriers and turn off those subcarriers used by LUs in order to avoid interference. Hence, only a subset of the subcarriers can be used for data or pilot tone transmission. To this end, some pilot allocation algorithms have been proposed for this dynamic scenario, but they are designed in such away that an equispaced pilot placement is respected (as much as possible) while minimizing the mean squared error of the channel estimate. Nevertheless, this equispaced placement can lead to the use of an increased number of pilots in order to achieve a good channel estimation. In this work, a new pilot allocation algorithm based on wavelet transform is presented. The proposed algorithm uses the discrete wavelet transform to analyze the previous channel state information, taking the knowledge of the available subcarriers into account to provide a suboptimal solution for the pilot positions. This solution leads to a non-equispaced pilot placement, which improves the channel estimation and consequently, the system performance. Likewise, the introduced algorithm allows a reduction of the number of necessary pilots, which aids in increasing the data rate. Finally, simulation results corroborate the effectiveness of the algorithm in dynamic channel scenarios.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alsharif, M. H., & Nordin, R. (2017). Evolution towards fifth generation (5G) wireless networks: Current trends and challenges in the deployment of millimetre wave, massive MIMO, and small cells. Telecommunication Systems, 64(4), 617–637. doi:10.1007/s11235-016-0195-x.
Aslam, S., & Lee, K. G. (2012). FOCS: Feedback oriented channel selection scheme for cognitive radios. In 2012 International conference on ICT convergence (ICTC) (pp. 639–641). doi:10.1109/ICTC.2012.6386868.
Baohao, C., Qimei, C., & Fan, Y. (2015). Compressed sensing based channel estimation used in non-sample-spaced multipath channels of OFDM system. The Journal of China Universities of Posts and Telecommunications, 22(2), 31–37. doi:10.1016/S1005-8885(15)60636-7.
Budiarjo, I., Rashad, I., & Nikookar, H. (2007). Efficient pilot pattern for OFDM-based cognitive radio channel estimation—part 2. In 2007 14th IEEE symposium on communications and vehicular technology in the Benelux (pp. 1–5). doi:10.1109/SCVT.2007.4436242.
Cvetkovic, Z., & Vetterli, M. (1995). Discrete-time wavelet extrema representation: Design and consistent reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 43(3), 681–693. doi:10.1109/78.370622.
Dong, L. (2012). MIMO cognitive radio with channel covariance feedback. In 2012 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC) (pp. 1890–1894). doi:10.1109/ICC.2012.6364247.
Gupta, M. K., Shrivastava, S., Raghuvanshi, A. S., & Tiwari, S. (2011). Channel estimation for wavelet based OFDM system. In 2011 International conference on devices and communications (ICDeCom) (pp. 1–4). doi:10.1109/ICDECOM.2011.5738465.
Haykin, S. (2005). Cognitive radio: Brain-empowered wireless communications. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 23(2), 201–220. doi:10.1109/JSAC.2004.839380.
Hosseini, H., Zamani, A. I. A., Yusof, S. K. S., & Fisal, N. (2009). CSI feedback model in the context of adaptive cognitive radio systems. In 2009 Third Asia international conference on modelling simulation (pp. 681–686). doi:10.1109/AMS.2009.30.
Hsia, C., Guo, J., & Chiang, J. (2012). A fast discrete wavelet transform algorithm for visual processing applications. Signal Processing, 92(1), 89–106. doi:10.1016/j.sigpro.2011.06.009.
Hu, D., & He, L. (2010). Pilot design for channel estimation in OFDM-based cognitive radio systems. In 2010 IEEE global telecommunications conference GLOBECOM 2010 (pp. 1–5). doi:10.1109/GLOCOM.2010.5683419.
Hu, D., He, L., & Wang, X. (2011). An efficient pilot design method for OFDM-based cognitive radio systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(4), 1252–1259. doi:10.1109/TWC.2011.012411.100924.
Jindal, S., Dass, D., & Gangopadhyay, R. (2014). Wavelet based spectrum sensing in a multipath Rayleigh fading channel. In 2014 Twentieth national conference on communications (NCC) (pp. 1–6). doi:10.1109/NCC.2014.6811292.
Lakshmanan, M. K., & Nikookar, H. (2006). A review of wavelets for digital wireless communication. Wireless Personal Communications, 37(3), 387–420. doi:10.1007/s11277-006-9077-y.
Lau, K. N. (2003). Optimal partial feedback design for SISO block fading channels. In 2003 IEEE wireless communications and networking, 2003. WCNC 2003 (Vol. 2, pp. 936–940). doi:10.1109/WCNC.2003.1200497.
Liu, J., Feng, S., & Wang, H. (2009). Comb-type pilot aided channel estimation in non-contiguous OFDM systems for cognitive radio. In 2009 5th international conference on wireless communications, networking and mobile computing (pp. 1–4). doi:10.1109/WICOM.2009.5303081.
Longoria-Gandara, O., & Parra-Michel, R. (2011). Estimation of correlated MIMO channels using partial channel state information and DPSS. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(11), 3711–3719. doi:10.1109/TWC.2011.091411.101199.
Ma, X., Giannakis, G. B., & Ohno, S. (2003). Optimal training for block transmissions over doubly selective wireless fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 51(5), 1351–1366. doi:10.1109/TSP.2003.810304.
Mahmoud, H. A., Yucek, T., & Arslan, H. (2009). OFDM for cognitive radio: Merits and challenges. IEEE Wireless Communications, 16(2), 6–15. doi:10.1109/MWC.2009.4907554.
Marques, A. G., Wang, X., & Giannakis, G. B. (2007). Channel-adaptive resource allocation for cognitive OFDMA RADIOS based on limited-rate feedback. In 2007 15th European signal processing conference (pp. 861–865).
Masoumian, S., & Tazehkand, B. (2015). Accurate OFDM sparse channel estimation by optimal deterministic pilot pattern. IETE Journal of Research, 61(3), 230–235. doi:10.1080/03772063.2015.1009402.
Mitola, J., & Maguire, G. Q. (1999). Cognitive radio: Making software radios more personal. IEEE Personal Communications, 6(4), 13–18. doi:10.1109/98.788210.
Munoz, A., Ertle, R., & Unser, M. (2002). Continuous Wavelet transform with arbitrary scales and O(N) complexity. Signal Processing, 82(5), 749–757. doi:10.1016/S0165-1684(02)00140-8.
Negi, R., & Cioffi, J. (1998). Pilot tone selection for channel estimation in a mobile OFDM system. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 44(3), 1122–1128. doi:10.1109/30.713244.
Nocedal, J., & Wright, S. (2006). Numerical optimization. Springer Series in Operations Research and Financial Engineering (2nd ed.). Berlin: Springer.
Pakrooh, P., Amini, A., & Marvasti, F. (2012). OFDM pilot allocation for sparse channel estimation. EURASIP Journal on Advances on Signal Processing, 2012(1), 1–9. doi:10.1186/1687-6180-2012-59.
Pan, W., Shan, Z., Chen, T., Chen, F., & Feng, J. (2016). Optimal pilot design for OFDM systems with non-contiguous subcarriers based on semi-definite programming. Telecommunication Systems, 63(2), 297–305. doi:10.1007/s11235-015-0121-7.
Qi, C., Yue, G., Wu, L., & Nallanathan, A. (2014). Pilot design for sparse channel estimation in OFDM-based cognitive radio systems. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 63(2), 982–987. doi:10.1109/TVT.2013.2280655.
Rashad, I., Budiarjo, I., & Nikookar, H. (2007). Efficient pilot pattern for OFDM-based cognitive radio channel estimation—part 1. In 2007 14th IEEE symposium on communications and vehicular technology in the Benelux (pp. 1–5). doi:10.1109/SCVT.2007.4436228.
So, J., & Srikant, R. (2015). Improving channel utilization via cooperative spectrum sensing with opportunistic feedback in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 19(6), 1065–1068. doi:10.1109/LCOMM.2015.2424957.
Tian, Z., & Giannakis, G. B. (2006). A wavelet approach to wideband spectrum sensing for cognitive radios. In 2006 1st International conference on cognitive radio oriented wireless networks and communications (pp. 1–5). doi:10.1109/CROWNCOM.2006.363459.
Trees, H. L. V., Bell, K. L., & Tian, Z. (2013). Detection estimation and modulation theory, part I: Detection, estimation, and filtering theory (p. 1176). New York: Wiley.
Xie, H., Andrieux, G., Wang, Y., Feng, S., & Yu, Z. (2017). A novel threshold based compressed channel sensing in OFDM system. AEU—International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 77, 149–155. doi:10.1016/j.aeue.2017.05.002.
Zhang, W., & Han, Z. (2010). Opportunistic feedback in collaborative spectrum sensing for cognitive radio. In 2010 IEEE wireless communication and networking conference (pp. 1–6). doi:10.1109/WCNC.2010.5506759.
Zhao, Z., Cheng, X., Wen, M., Jiao, B., & Wang, C. X. (2013). Channel estimation schemes for IEEE 802.11p standard. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 5(4), 38–49. doi:10.1109/MITS.2013.2270032.
Zhu, J., Song, Y., Jiang, D., & Song, H. (2016). Multi-armed bandit channel access scheme with cognitive radio technology in wireless sensor networks for the internet of things. IEEE Access, 4, 4609–4617. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2600633.
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by the Mexican Ministry of Education (SEP-PRODEP -2014) and by the Mexican Council for Science and Technology (CONACYT) through the SEP-CONACYT Basic Research Program #241272.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calderón-Rico, R., Carrasco-Alvarez, R. & Vázquez Castillo, J. Dynamic wavelet-based pilot allocation algorithm for OFDM-based cognitive radio systems. Telecommun Syst 68, 193–200 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-017-0386-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-017-0386-0