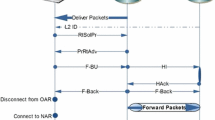
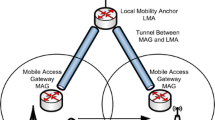
Abstract
In the wireless network and mobile internet, several mobile nodes (MNs) may handover from the same previous network X to the same destination network Y at the same time. However, currently proposed Distributed Mobility Management (DMM)-based protocol mainly focus on the handover processing of a single MN’s handover. It causes many redundant messages’ exchanging when multiple MNs do handover at the same time. In this paper, a Bursty Multi-node Handover scheme for mobile internet using the partially Distributed Mobility Management (BMH–DMM) architecture is proposed to tackle the aforementioned problem. Using the proposed BMH–DMM method, one set of control messages for handover is used instead of n sets of control messages for a group that has n MNs. The performance analysis shown that when the number of MNs that perform handover at the same time and in the same place is increased, the handover overhead is not increased so much, for which the proposed BMH–DMM method can reduce about 30% bandwidth consumption for exchanging handover’s signaling messages. Furthermore, the network utilization, handover delay, packet loss, handover blocking probability of using the proposed BMH–DMM scheme are also smaller than that of using the individual handover approach.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnson, D., Perkins, C., & Arkko, J. (2004). Mobility support in IPv6. RFC 3775.
Koodli, R. Ed. (2009). Mobile IPv6 fast handovers. Network Working Group, RFC 5568.
Devarapalli, V., Chowdhury, K., Gundavelli, S., Patil, B., & Leung, K. (2008). Proxy Mobile IPv6. IETF RFC, 5213.
Chan, A., Liu, D., Seite, P., Yokota, H., & Korhonen, J. (2014). Requirements for distributed mobility management. IETF RFC 7333.
Bernardos, C. J., De la Oliva, A., & Giust, F. (2017). A PMIPv6-based solution for distributed mobility management. Internet-Draft (work in progress), draft-bernardos-dmm-pmip.
Giust, F., Bernardos, C. J., & De La Oliva, A. (2014). Analytic evaluation and experimental validation of a network-based IPv6 distributed mobility management solution. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 13(11), 2484–2497.
Bertin, P., Lee, J. H., & Seite, P. (2015). Distributed mobility anchoring. draft-seite-dmm-dma-06.txt.
Chen, Y. S., Hsu, C. S., & Lee, H. K. (2014). An enhanced group mobility protocol for 6LoWPAN-based wireless body area networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 14(3), 797–807.
Tao, M., Dong, M., Ota, K., & He, Z. (2016). Multiobjective network opportunistic access for group mobility in mobile internet. IEEE Systems Journal, PP(99), 1–10.
Fu, H. L., Lin, P., Yue, H., Huang, G. M., & Lee, C. P. (2014). Group mobility management for large-scale machine-to-machine mobile networking. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 63(3), 1296–1305.
De La Oliva, A., Banchs, A., Soto, I., Melia, T., & Vidal, A. (2008). An overview of IEEE 802.21: Media-independent handover services. IEEE Wireless Communications, 15(4), 96–103.
D’Oro, S., Galluccio, L., Morabito, G., & Palazzo, S. (2015). Exploiting object group localization in the Internet of Things: Performance analysis. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 64(8), 3645–3656.
Chatzikokolakis, K., Kaloxylos, A., Spapis, P., Zhou, C., Bulakci, Ö., & Alonistioti, N. (2016). Context-aware location management of groups of devices in 5G networks. In Proceedings of the 10th IFIP international conference on autonomous infrastructure, management and security, (pp. 155–159).
Chiang, M. S., Huang, C. M., & Tuan, D. D. (2014). Fast handover control scheme for multi-node using the group-based approach. IET Networks, 4(1), 44–53.
Guan, J., You, I., Xu, C., & Zhang, H. (2016). The PMIPv6-based group binding update for IoT devices. Mobile Information Systems, 2016, 1–8. (Article ID 7853219).
Abinader, F., Gundavelli, S., Leung, K., Krishnan, S., & Premec, D. (2012). Bulk binding update support for Proxy Mobile IPv6. RFC 6602.
Chen, L., Shu, Y., Gu, Y., Guo, S., He, T., Zhang, F., et al. (2016). Group-based neighbor discovery in low-duty-cycle mobile sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 15(8), 1996–2009.
Lee, C. H., Huang, C. M., & Tseng, P. H. (2014). Multihomed SIP-based network mobility for the scheduled public transit service. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 14(1), 74–84.
Ernest, P. P., Falowo, O. E., & Chan, H. A. (2016). Design and performance evaluation of distributed mobility management schemes for network mobility. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 61, 46–58.
Ernest, P. P., Chan, H. A., Xie, J., & Falowo, O. E. (2015). Mobility management with distributed mobility routing functions. Telecommunication Systems, 59(2), 229–246.
Sanchez, M. I., Uruena, M., De la Oliva, A., Hernandez, J. A., & Bernardos, C. J. (2013). On providing mobility management in WOBANs: Integration with PMIPv6 and MIH. IEEE Communications Magazine, 51(10), 172–181.
Murtadha, M. K., Noordin, N. K., & Ali, B. M. (2015). Survey and analysis of integrating PMIPv6 and MIH mobility management approaches for heterogeneous wireless networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 82(3), 351–1376.
Ko, H., Lee, G., Pack, S., & Kweon, K. (2016). Timer-based bloom filter aggregation for reducing signaling overhead in distributed mobility management. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 15(2), 516–529.
Yi, L., Zhou, H., Huang, D., & Zhang, H. (2013). D-PMIPv6: A distributed mobility management scheme supported by data and control plane separation. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 58(5), 1415–1426.
Yan, Z., Zeadally, S., Zhang, S., Guo, R., & Park, Y. J. (2016). Distributed mobility management in named data networking. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 16(13), 1773–1783.
Yang, Hua, Wakamiya, Naoki, Murata, Masayuki, Iwai, Takanori, & Yamano, Satoru. (2016). An autonomous and distributed mobility management scheme in mobile core networks. EAI Endorsed Transactions on Creative Technologies, 3(8), 35–42.
Balfaqih, M., Ismail, M., Nordin, R., Rahem, A. A., & Balfaqih, Z. (2017). Fast handover solution for network-based distributed mobility management in intelligent transportation systems. Telecommunication Systems, 64(2), 325–346.
Ghazali, N. E., Ariffin, S. H., Wahab, N. H. A., Ain’Amiruddin, N., & Fisal, N. (2014). Handover threshold analysis using velocity for Proxy Mobile IPv6. In Proceedings of the IEEE Asia Pacific wireless and mobile, (pp. 36–41).
Wang, X., Lei, X., Fan, P., Hu, R. Q., & Horng, S. J. (2014). Cost analysis of movement-based location management in PCS networks: An embedded Markov chain approach. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 63(4), 1886–1902.
Rasem, A., St-Hilaire, M., & Makaya, C. (2016). Efficient handover with optimized localized routing for Proxy Mobile IPv6. Telecommunication Systems, 62(4), 675–693.
Lee, J. H., Bonnin, J. M., You, I., & Chung, T. M. (2013). Comparative handover performance analysis of IPv6 mobility management protocols. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 60(3), 1077–1088.
Gross, D., & Shortle, J. F. (2008). Fundamentals of queueing theory. London: Wiley.
Lee, J. H., & Chung, T. M. (2010). How much do we gain by introducing route optimization in Proxy Mobile Ipv6 networks? Annals of Telecommunications, 65(5–6), bal3-246.
Zubair, M., Kong, X., & Mahfooz, S. (2015). DMAM: Distributed mobility and authentication mechanism in next generation networks. Security and Communication Networks, 8(5), 845–863.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) of the Republic of China, Taiwan, under the Contract Number MOST 105-2221-E-006-063.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, CM., Dao, DT. & Chiang, MS. A Bursty Multi-node Handover scheme for mobile internet using the partially Distributed Mobility Management (BMH–DMM) architecture. Telecommun Syst 69, 113–130 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-018-0435-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-018-0435-3