Abstract
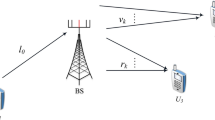
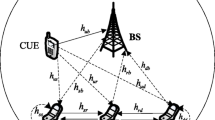
In this paper, we consider an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing based device to device network. The communication between source and destination is facilitated by a dual-hop transmission under amplify and forward relaying protocol. The sum throughput of the system is maximized with joint optimization over power allocation at each transmitting node and sub-carrier pairing over two hops. A dual decomposition based solution is proposed subject to separate transmit power constraint at each node. Simulation results are presented to validate the performance of the proposed algorithm where the results are compared with the existing works in literature as well as with a sub-optimal power optimization solution.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The data received at relay over a particular carrier can be forwarded over the same or a different sub-carrier.
References
Tang, X., Ren, P., Gao, F., & Du, Q. (2017). Interference-aware resource competition toward power-efficient ultra-dense networks. IEEE Transactions on Communication, 65(12), 5415–5428.
Zhang, Q., Zhu, W., & Zhang, Y. (2005). End-to-End QoS for video delivery over wireless internet. Proceedings of the IEEE, 93(1), 123–134.
Hammerstrom, I., & Wittneben, A. (2007). Power allocation schemes for amplify-and-forward MIMO-OFDM relay links. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 6(8), 2798–2802.
Negi, A., & Singh, S. (2005). Power saving approaches in 2-hop relaying cellular networks. In Proceedings of IEEE 16th international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications, Berlin, pp. 1616–1620.
Asadi, A., Wang, Q., & Mancuso, V. (2014). A survey on device-to-device communication in cellular networks. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 16(4), 1801–1819. Fourth quarter.
Peng, T., Lu, Q., Wang, H., Xu, S., & Wang, W. (2009). Interference avoidance mechanisms in the hybrid cellular and device-to-device systems. In Proceedings of IEEE 20th international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications, Tokyo, pp. 617–621.
Yu, C. H., Doppler, K., Ribeiro, C., & Tirkkonen, O. (2009) Performance impact of fading interference to Device-to-Device communication underlaying cellular networks. In Proceedings of IEEE 20th international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications, Tokyo, pp. 858–862.
Xu, C., Song, L., Han, Z., Zhao, Q., Wang, X., Cheng, X., et al. (2013). Efficiency resource allocation for device-to-device underlay communication systems: A reverse iterative combinatorial auction based approach. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 31(9), 348–358.
Xu, S., Wang, H., Chen, T., Huang, Q., & Peng, T. (2010). Effective interference cancellation scheme for device-to-device communication underlaying cellular networks. In Proceedings of IEEE 72nd Vehicular Technology Conference—Fall, Ottawa, ON, pp. 1–5.
Zhang, R., Cheng, X., Yang, L., & Jiao, B. (2013). Interference-aware graph based resource sharing for device-to-device communications underlaying cellular networks. In Proceedings of IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC), pp. 140–145, Shanghai.
Hassan, Y., Hussain, F., Hossen, S., Choudhury, S., & Alam, M. M. (2017). Interference minimization in D2D communication underlaying cellular networks. IEEE Access, 5, 22471–22484.
Doppler, K., Rinne, M., Wijting, C., Ribeiro, C. B., & Hugl, K. (2009). Device-to-device communication as an underlay to LTE-advanced networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 47(12), 42–49.
Jung, M., Hwang, K., & Choi, S. (2012). Joint mode selection and power allocation scheme for power-efficient device-to-device (D2D) communication. In Proceedings of IEEE 75th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Yokohama, pp. 1–5.
Celik, A., Redha, R. M., Qahtan, F. S. A., & Alouini, M. S. (2017). Joint interference management and resource allocation for device-to-device (D2D) communications underlying downlink/uplink decoupled (dude) heterogeneous networks. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on communications (ICC).
He, A., Wang, L., Chen, Y., Wong, K. K., & Elkashlan, M. (2017). Spectral and energy efficiency of uplink D2D underlaid massive MIMO cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 99, 1–1.
Laneman, J., Tse, D., & Wornell, G. (2004). Cooperative diversity in wireless networks: Efficient protocols and outage behavior. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 50(12), 3062–3080.
Fan, L., Zhao, R., Gong, F., Yang, N., & Karagiannidis, G. K. (2017). Secure multiple amplify-and-forward relaying over correlated fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 65(7), 2811–2820.
Janani, M., Hedayat, A., Hunter, T. E., & Nosratinia, A. (2004). Coded cooperation in wireless communications: Space-time transmission and iterative decoding. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 52(2), 362–371.
Kramer, G., Gastpar, M., & Gupta, P. (2005). Cooperative strategies and capacity theorem for relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 51(9), 3037–3063.
Laneman, J. N., Tse, D. N. C., & Wornell, G. W. (2004). Cooperative diversity in wireless networks: Efficient protocols and outage behavior. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 50(12), 3062–3080.
Herdin, M. (2006). A chunk based OFDM amplify-and-forward relaying scheme for 4G mobile radio systems. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on communications (ICC), pp. 4507–4512, Istanbul, Turkey, June 2006.
Waqas, M., Ahmad, M. A., Jabeen, H. T., & Sardar Sidhu, G. A. (2015). An optimization scheme for dual-hop device-to-device (DH-D2D) transmission. In Proceedings of 12th international conference on high-capacity optical networks and enabling/emerging technologies (HONET), pp. 1–5, Islamabad.
Aggelou, G. N., & Tafazolli, R. (2001). On the relaying capability of next-generation GSM cellular networks. IEEE Personal Communications, 8(1), 40–47.
Mingyu, Z., Lihua, L., Haifeng, W., Ping, Z., & Xiaofeng, T. (2007). Sub-carrier coupling for OFDM based AF multi-relay systems. In Proceedings of IEEE 18th international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications, Athens, pp. 1–5.
Han, T., & Ansari, N. (2013). Heuristic relay assignments for green relay assisted device to device communications. In Proceedings of IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Atlanta, GA, pp. 468–473.
Kim, T., & Dong, M. (2014). An iterative Hungarian method to joint relay selection and resource allocation for D2D Communications. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 3(6), 625–628.
Ni, Y., Wang, X., Jin, S., Wong, K. K., Zhu, H., & Zhang, N. (2015). Outage probability of device-to-device communication assisted by one-way amplify-and-forward relaying. IET Communications, 9(2), 271–282.
Tang, R., Zhao, J., Qu, H., Zhu, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2016). Joint mode selection and resource allocation for mobile relay-aided device-to-device communication. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems, 10(3), 950–975.
Zhang, W., & Gao, F. (2016). Blind frequency synchronization for multiuser OFDM uplink with large number of receive antennas. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 64(9), 2255–2268.
Ghosh, A., Ratasuk, R., Mondal, B., Mangalvedhe, N., & Thomas, T. (2010). LTE-advanced: Next-generation wireless broadband technology. IEEE Wireless Communications, 17(3), 10–22.
Singh, K., Gupta, A., Ku, M. L., & Ratnarajah, T. (2016). Joint sub-carrier pairing and power allocation for two-way energy-efficient relay networks. In Proceedings of IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Washington, DC USA, pp. 1–6.
Sidhu, G. A. S., Gao, F., Fan, L., & Nallanathan, A. (2011). A joint resource allocation scheme for relay aided uplink multi-user OFDMA system. In Proceedings of IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference (GLOBECOM), Houston, TX, USA, pp. 1–5.
Sidhu, G. A. S., Gao, F., Wang, W., & Chen, W. (2013). Resource allocation in relay-aided OFDM cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 62(8), 3700–3710.
Luo, L., Li, L., & Su, X. (2017). Optimization of resource allocation in relay assisted multi-user SCMA uplink network. In Proceedings of international conference on computing, networking and communications (ICNC), Silicon Valley, USA, pp. 282–286.
Boyd, S., & Vandenberghe, L. (2004). Convex optimization. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Hammerstrm, I., & Wittneben, A. (2007). Power allocation schemes for amplify-and-forward MIMO-OFDM relay links. IEEE Transactions on wireless communications, 6(8), 2798–2802.
Ahmad, H. M. A., Waqas, M., & Sidhu, G. A. S. (2014). A fast power optimization algorithm for non-regenerative dual hop relay network. In Proceedings of 12th international conference on frontiers of information technology, pp. 46–50, Islamabad.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
and
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, M.A., Waqas, M., Khan, W.A. et al. Resource optimization for dual-hop device to device networks. Telecommun Syst 69, 273–283 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-018-0439-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-018-0439-z