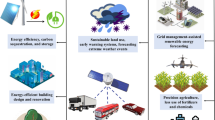
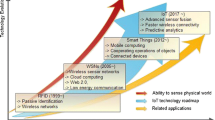
Abstract
Tremendous technological developments in the field of internet of things (IoT) have changed the way we live and work. Although the numerous advantages of IoT are enriching our society, it should be reminded that the IoT also contributes to toxic pollution, consumes energy and generates e-waste. These persistent issues place new stress on the smart world and environments. To enhance the benefits and reduce the harmful effects of IoT, there is an increasingly desired to move towards green IoT. Green IoT is seen as the environmentally friendly future of IoT. Therefore, it is necessary to put different desired measures to conserve environmental resources, reduce carbon footprints and promote efficient techniques for energy usage. It is the reason for moving towards green IoT, where the machines, sensors, communications, clouds, and internet operate in synergy towards the common goal of increased energy efficiency and reduced carbon emissions. This work presents a thorough survey of the current ongoing research and potential technologies of green IoT with an intention to provide some directions for future green IoT research.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atzori, L., Iera, A., & Morabito, G. (2010). The internet of things: A survey. Computer Networks, 54(15), 2787–2805.
Initiative, I. I. (2015). Towards a definition of the Internet of Things (IoT). Revision-1, on-line: http://iot.ieee.org/images/files/pdf/IEEE_IoT_Towards_Definition_Internet_of_Things_Revision1_27MAY15.pdf.. Accessed, (vol. 27, no. 2017, pp. 479–501).
Perera, C., Zaslavsky, A., Christen, P., & Georgakopoulos, D. (2014). Context aware computing for the internet of things: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 16(1), 414–454.
Gubbi, J., Buyya, R., Marusic, S., & Palaniswami, M. (2013). Internet of Things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions. Future generation Computer Systems, 29(7), 1645–1660.
Chen, X., Ma, M., & Liu, A. (2018). Dynamic power management and adaptive packet size selection for IoT in e-Healthcare. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 65, 357–375.
Pavithra, D., & Balakrishnan, R. (2015). IoT based monitoring and control system for home automation. In 2015 global conference on communication technologies (GCCT), (pp. 169–173). IEEE.
Kodali, R. K. Jain, V., Bose, S., & Boppana, L. (2016). IoT based smart security and home automation system. In 2016 international conference on computing, communication and automation (ICCCA) (pp. 1286–1289). IEEE.
Tellez, M., El-Tawab, S., & Heydari, H. M. (2016). Improving the security of wireless sensor networks in an IoT environmental monitoring system. In 2016 IEEE systems and information engineering design symposium (SIEDS) (pp. 72–77). IEEE.
Shah, J., & Mishra, B. (2016). IoT enabled environmental monitoring system for smart cities. In international conference on internet of things and applications (IOTA) (pp. 383–388). IEEE.
Kong, L., Khan, M. K., Wu, F., Chen, G., & Zeng, P. (2017). Millimeter-wave wireless communications for IoT-cloud supported autonomous vehicles: Overview, design, and challenges. IEEE Communications Magazine, 55(1), 62–68.
Popa, D., Popa, D. D., & Codescu, M.-M. (2019). Reliability for a green internet of things. Buletinul AGIR, 1, 45–50.
Prasad, S. S., & Kumar, C. (2013). A green and reliable internet of things. Communications and Network, 5(01), 44.
Botta, A., De Donato, W., Persico, V., & Pescapé, A. (2016). Integration of cloud computing and internet of things: A survey. Future Generation Computer Systems, 56, 684–700.
Gu, M., Li, X., & Cao, Y. (2014). Optical storage arrays: A perspective for future big data storage. Light: Science & Applications, 3(5), e177.
Hashem, I. A. T., Yaqoob, I., Anuar, N. B., Mokhtar, S., Gani, A., & Khan, S. U. (2015). The rise of “big data” on cloud computing: Review and open research issues. Information Systems, 47, 98–115.
Shuja, J., et al. (2017). Greening emerging IT technologies: Techniques and practices. Journal of Internet Services and Applications, 8(1), 9.
Tao, F., Zuo, Y., Da Xu, L., Lv, L., & Zhang, L. (2014). Internet of things and BOM-based life cycle assessment of energy-saving and emission-reduction of products. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 10(2), 1252–1261.
Wang, K., Wang, Y., Sun, Y., Guo, S., & Wu, J. (2016). Green industrial internet of things architecture: An energy-efficient perspective. IEEE Communications Magazine, 54(12), 48–54.
Gelenbe, E., & Caseau, Y. (2015). The impact of information technology on energy consumption and carbon emissions. Ubiquity, 2015, 1.
Arshad, R., Zahoor, S., Shah, M. A., Wahid, A., & Yu, H. (2017). Green IoT: An investigation on energy saving practices for 2020 and beyond. IEEE Access, 5, 15667–15681.
Shaikh, F. K., Zeadally, S., & Exposito, E. (2017). Enabling technologies for green internet of things. IEEE Systems Journal, 11(2), 983–994.
Zhu, C., Leung, V. C., Shu, L., & Ngai, E. C.-H. (2015). Green Internet of Things for smart world. IEEE Access, 3, 2151–2162.
Sala, S. (2009). Information and Communication Technologies for climate change adaptation, with a focus on the agricultural sector. In Thinkpiece for CGIAR Science Forum Workshop on “ICTs transforming agricultural science, research and technology generation,” Wageningen, Netherlands, 2009 (pp. 16–17)
Eakin, H., et al. (2015). Information and communication technologies and climate change adaptation in Latin America and the Caribbean: A framework for action. Climate and Development, 7(3), 208–222.
Upadhyay, A. P., & Bijalwan, A. (2015). Climate change adaptation: Services and role of information communication technology (ICT) in India. American Journal of Environmental Protection, 4(1), 70–74.
Zanamwe, N., & Okunoye, A (2013). Role of information and communication technologies (ICTs) in mitigating, adapting to and monitoring climate change in developing countries. In International conference on ICT for Africa.
Mickoleit, A. (2010). Greener and smarter: ICTs, the environment and climate change. Paris: OECD Publishing.
Reimsbach-Kounatze, C. (2009). Towards green ICT strategies. https://www.oecd.org/sti/ieconomy/towardsgreenictstrategies.htm.
Maksimovic, M. (2018). Greening the future: green internet of things (G-IoT) as a key technological enabler of sustainable development. In Internet of things and big data analytics toward next-generation intelligence (pp. 283–313). Springer.
Pazowski, P. (2015). Green computing: Latest practices and technologies for ICT sustainability. In Joint international conference managing intellectual capital and innovation for sustainable and inclusive society, Bari, Italy (pp. 1853–1860).
Di Salvo, A. L., Agostinho, F., Almeida, C. M., & Giannetti, B. F. (2017). Can cloud computing be labeled as “green”? Insights under an environmental accounting perspective. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 69, 514–526.
Murugesan, S. (2008). Harnessing green IT: Principles and practices. IT Professional, 10(1), 24–33.
Rani, S., Talwar, R., Malhotra, J., Ahmed, S. H., Sarkar, M., & Song, H. (2015). A novel scheme for an energy efficient Internet of Things based on wireless sensor networks. Sensors, 15(11), 28603–28626.
Huang, J., Meng, Y., Gong, X., Liu, Y., & Duan, Q. (2014). A novel deployment scheme for green internet of things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 1(2), 196–205.
Gapchup, A., Wani, A., Wadghule, A., & Jadhav, S. (2017). Emerging trends of green IoT for smart world. International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering, 5(2), 2139–2148.
Lü, Y.-L., Geng, J., & He, G.-Z. (2015). Industrial transformation and green production to reduce environmental emissions: Taking cement industry as a case. Advances in Climate Change Research, 6(3), 202–209.
Khan, R., Khan, S. U., Zaheer, R., & Khan, S. (2012). Future internet: the internet of things architecture, possible applications and key challenges. In 2012 10th international conference on frontiers of information technology (FIT) (pp. 257–260). IEEE.
Liu, X., & Ansari, N. (2019). Toward green IoT: Energy solutions and key challenges. IEEE Communications Magazine, 57(3), 104–110.
Jalali, F., Khodadustan, S., Gray, C., Hinton, K., & Suits, F. (2017). Greening IoT with fog: A survey. In 2017 IEEE international conference on edge computing (EDGE) (pp. 25–31).
Doknić, V. (2014). Internet of things greenhouse monitoring and automation system. http://193.40.244.77/idu0310/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/140605_Internet-of-Things_Vesna-Doknic.pdf.
Wang, H.-I. (2014). Constructing the green campus within the internet of things architecture. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 10(3), 804627.
Prasad, R., Ohmori, S., & Simunic, D. (2010). Towards green ICT. Aalborg: River Publishers.
Uddin, M., & Rahman, A. A. (2012). Energy efficiency and low carbon enabler green IT framework for data centers considering green metrics. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 16(6), 4078–4094.
Shaikh, F. K., Zeadally, S., & Exposito, E. (2015). Enabling technologies for green internet of things. IEEE Systems Journal, 11(2), 983–994.
Xiaojun, C., Xianpeng, L., & Peng, X. (2015). IOT-based air pollution monitoring and forecasting system. In 2015 international conference on computer and computational sciences (ICCCS) (pp. 257–260). IEEE.
Manna, S., Bhunia, S. S., & Mukherjee, N. (2014). Vehicular pollution monitoring using IoT. In Recent advances and innovations in engineering (ICRAIE) (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
Zupancic, T., Westmacott, C., & Bulthuis, M. (2015). The impact of green space on heat and air pollution in urban communities: A meta-narrative systematic review. BC: David Suzuki Foundation Vancouver.
Bandyopadhyay, D., & Sen, J. (2011). Internet of things: Applications and challenges in technology and standardization. Wireless Personal Communications, 58(1), 49–69.
Murugesan, S., & Gangadharan, G. (2012). Harnessing green IT: Principles and practices. New York: Wiley.
Nandyala, C. S., & Kim, H.-K. (2016). Green IoT agriculture and healthcareapplication (GAHA). International Journal of Smart Home, 10(4), 289–300.
Radu, L.-D. (2016). Determinants of Green ICT adoption in organizations: A theoretical perspective. Sustainability, 8(8), 731.
Ozturk, A., et al. (2011). Green ICT (Information and Communication Technologies): A review of academic and practitioner perspectives. International Journal of eBusiness and eGovernment Studies, 3(1), 1–16.
Occhiuzzi, C., Caizzone, S., & Marrocco, G. (2013). Passive UHF RFID antennas for sensing applications: Principles, methods, and classifcations. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 55(6), 14–34.
Amin, Y. (2013). Printable green RFID antennas for embedded sensors. Stockholm: KTH Royal Institute of Technology.
Amin, Y. et al. (2013). Printable RFID antenna with embedded sensor and calibration functions. In Proceedings of the progress in electromagnetics research symposium, Stockholm, Sweden (vol. 1215, p. 567570).
Zelbst, P. J., Sower, V. E., Green, K. W., Jr., & Abshire, R. D. (2011). Radio frequency identification technology utilization and organizational agility. Journal of Computer Information Systems, 52(1), 24–33.
Hubbard, B.,Wang, H., & Leasure, M. (2016). Feasibility study of UAV use for RFID material tracking on construction sites. Presented at the Proceedings of 51st ASC annual international conference proceedings college station, TX, USA.
Allegretti, M., & Bertoldo, S. (2015). Recharging RFID tags for environmental monitoring using UAVs: A feasibility analysis. Wireless Sensor Network, 7(02), 13.
Choi, J. S., Son, B. R., Kang, H. K., & Lee, D. H. (2012). Indoor localization of unmanned aerial vehicle based on passive UHF RFID systems. In 2012 9th international conference on ubiquitous robots and ambient intelligence (URAI) (pp. 188–189). IEEE.
Greco, G., Lucianaz, C., Bertoldo, S., & Allegretti, M. (2015). A solution for monitoring operations in harsh environment: A RFID reader for small UAV. In 2015 international conference on electromagnetics in advanced applications (ICEAA) (pp. 859–862). IEEE.
Namboodiri, V., & Gao, L. (2007). Energy-aware tag anti-collision protocols for RFID systems. In Fifth annual IEEE international conference on pervasive computing and communications, 2007. PerCom’07 (pp. 23–36). IEEE.
Li, T., Wu, S. S., Chen, S., & Yang, M. C. (2012). Generalized energy-efficient algorithms for the RFID estimation problem. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 20(6), 1978–1990.
Prabhu, B., Balakumar, N., & Antony, A. J. (2017). Wireless sensor network based smart environment applications. IJIRT, 3, 1–10.
Lloret, J., Garcia, M., Bri, D., & Sendra, S. (2009). A wireless sensor network deployment for rural and forest fire detection and verification. Sensors, 9(11), 8722–8747.
Aslan, Y. E., Korpeoglu, I., & Ulusoy, Ö. (2012). A framework for use of wireless sensor networks in forest fire detection and monitoring. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 36(6), 614–625.
Bhattacharjee, S., Roy, P., Ghosh, S., Misra, S., & Obaidat, M. S. (2012). Wireless sensor network-based fire detection, alarming, monitoring and prevention system for Bord-and-Pillar coal mines. Journal of Systems and Software, 85(3), 571–581.
Viani, F., Lizzi, L., Rocca, P., Benedetti, M., Donelli, M., & Massa, A. (2008). Object tracking through RSSI measurements in wireless sensor networks. Electronics Letters, 44(10), 653–654.
Han, G., Shen, J., Liu, L., Qian, A., & Shu, L. (2016). TGM-COT: Energy-efficient continuous object tracking scheme with two-layer grid model in wireless sensor networks. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, 20(3), 349–359.
Han, G., Shen, J., Liu, L., & Shu, L. (2017). BRTCO: A novel boundary recognition and tracking algorithm for continuous objects in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Systems Journal, 12(3), 2056–2065.
Wu, F., Rüdiger, C., & Yuce, M. R. (2017). Real-Time performance of a self-powered environmental IoT sensor network system. Sensors, 17(2), 282.
Trasviña-Moreno, C. A., Blasco, R., Marco, Á., Casas, R., & Trasviña-Castro, A. (2017). Unmanned aerial vehicle based wireless sensor network for marine-coastal environment monitoring. Sensors, 17(3), 460.
Sharma, D. (2017). Low cost experimental set up for real time temperature, humidity monitoring through WSN. International Journal of Engineering Science, 4340.
Prabhu, B., Balakumar, N., & Antony, A. (2017). Evolving constraints in military applications using wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer Science & Technology (IJIRCST), 5(1). https://ssrn.com/abstract=2908031.
Ye, W., Heidemann, J., & Estrin, D. (2002). An energy-efficient MAC protocol for wireless sensor networks. In INFOCOM 2002. Twenty-first annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications societies. Proceedings. IEEE (vol. 3, pp. 1567–1576). IEEE.
Anastasi, G., Francesco, M. D., Conti, M., & Passarella, A. (2013). How to prolong the lifetime of WSNs. In Mobile ad hoc and personal communication. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Azevedo, J., & Santos, F. (2012). Energy harvesting from wind and water for autonomous wireless sensor nodes. IET Circuits, Devices and Systems, 6(6), 413–420.
Eu, Z. A., Tan, H.-P., & Seah, W. K. (2011). Design and performance analysis of MAC schemes for wireless sensor networks powered by ambient energy harvesting. Ad Hoc Networks, 9(3), 300–323.
Shaikh, F. K., & Zeadally, S. (2016). Energy harvesting in wireless sensor networks: A comprehensive review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 55, 1041–1054.
Abedin, S. F., Alam, M. G. R., Haw, R., & Hong, C. S. (2015). A system model for energy efficient green-IoT network. In 2015 international conference on information networking (ICOIN) (pp. 177–182). IEEE.
Sun, K.,. & Ryoo, I. (2015). A study on medium access control scheme for energy efficiency in wireless smart sensor networks. In 2015 international conference on information and communication technology convergence (ICTC) (pp. 623–625). IEEE.
Uzoh, P. C., Li, J., Cao, Z., Kim, J., Nadeem, A., & Han, K. (2015). Energy efficient sleep scheduling for wireless sensor networks. In International conference on algorithms and architectures for parallel processing (pp. 430–444). Springer.
Alsamhi, S., Ma, O., & Ansari, M. (2018). Predictive estimation of the optimal signal strength from unmanned aerial vehicle over internet of things using ANN. arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.07614.
Mehmood, A., & Song, H. (2015). Smart energy efficient hierarchical data gathering protocols for wireless sensor networks. SmartCR, 5(5), 425–462.
Naranjo, P. G. V., Shojafar, M., Mostafaei, H., Pooranian, Z., & Baccarelli, E. (2017). P-SEP: A prolong stable election routing algorithm for energy-limited heterogeneous fog-supported wireless sensor networks. The Journal of Supercomputing, 73(2), 733–755.
Yaacoub, E., Kadri, A., & Abu-Dayya, A. (2012). Cooperative wireless sensor networks for green internet of things. In Proceedings of the 8 h ACM symposium on QoS and security for wireless and mobile networks (pp. 79–80). ACM.
Rekha, R. V., & Sekar, J. R. (2016). An unified deployment framework for realization of green internet of things (GIoT). Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research, 24(2), 187–196.
Prabhu, S. B., Dhasharathi, C., Prabhakaran, R., Kumar, M. R., Feroze, S. W., & Sophia, S. (2014). Environmental monitoring and greenhouse control by distributed sensor Network. International Journal of Advanced Networking and Applications, 5(5), 2060.
Morreale, P., Qi, F., & Croft, P. (2011). A green wireless sensor network for environmental monitoring and risk identification. International Journal of Sensor Networks, 10(1–2), 73–82.
Mahapatra, C., Sheng, Z., Kamalinejad, P., Leung, V. C., & Mirabbasi, S. (2017). Optimal power control in green wireless sensor networks with wireless energy harvesting, wake-up radio and transmission control. IEEE Access, 5, 501–518.
Naeem, M., Pareek, U., Lee, D. C., & Anpalagan, A. (2013). Estimation of distribution algorithm for resource allocation in green cooperative cognitive radio sensor networks. Sensors, 13(4), 4884–4905.
Liu, A., Zhang, Q., Li, Z., Choi, Y.-J., Li, J., & Komuro, N. (2017). A green and reliable communication modeling for industrial internet of things. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 58, 364–381.
Rault, T., Bouabdallah, A., & Challal, Y. (2014). Energy efficiency in wireless sensor networks: A top-down survey. Computer Networks, 67, 104–122.
Baccarelli, E., Naranjo, P. G. V., Scarpiniti, M., Shojafar, M., & Abawajy, J. H. (2017). Fog of everything: Energy-efficient networked computing architectures, research challenges, and a case study. IEEE Access, 5, 9882–9910.
Sivakumar, S., Anuratha, V., & Gunasekaran, S. (2017). Survey on integration of cloud computing and internet of things using application perspective. International Journal of Emerging Research in Management & Technology, 6(4), 101–108.
Zhu, C., Leung, V. C., Wang, K., Yang, L. T., & Zhang, Y. (2017). Multi-method data delivery for green sensor-cloud. IEEE Communications Magazine, 55(5), 176–182.
Jain, A., Mishra, M., Peddoju, S. K., & Jain, N. (2013). Energy efficient computing-green cloud computing. In 2013 international conference on energy efficient technologies for sustainability (ICEETS) (pp. 978–982). IEEE.
Baliga, J., Ayre, R. W., Hinton, K., & Tucker, R. S. (2011). Green cloud computing: Balancing energy in processing, storage, and transport. Proceedings of the IEEE, 99(1), 149–167.
Liu, X.-F., Zhan, Z.-H., & Zhang, J. (2017). An energy aware unified ant colony system for dynamic virtual machine placement in cloud computing. Energies, 10(5), 609.
Sarathe, R., Mishra, A., & Sahu, S. K. (2016). Max-min ant system based approach for intelligent VM migration and consolidation for green cloud computing. International Journal of Computer Applications, 136(13), 15–18.
Alsamhi, S. H., Ma, O., & Ansari, M. S. (2019). Survey on artificial intelligence based techniques for emerging robotic communication. Telecommunication Systems. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-019-00561-z.
Alsamhi, S. H., Ma, O., & Ansari, M. S. (2019). Convergence of machine learning and robotics communication in collaboratively assembly: Mobility, connectivity and future prospects. Journal of Intelligent Robotics and Systems (under review).
Wang, C. et al (2018). Method and apparatus for supporting machine-to-machine communications. ed: Google Patents.
Chen, Y., & Wang, W. (2010). Machine-to-machine communication in LTE-A. In 2010 IEEE 72nd vehicular technology conference - fall (pp. 1–4).
Alavikia, Z., & Ghasemi, A. (2018). Collision-aware resource access scheme for LTE-based machine-to-machine communications. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology (pp. 1–1).
Lu, R., Li, X., Liang, X., Shen, X., & Lin, X. (2011). GRS: The green, reliability, and security of emerging machine to machine communications. IEEE Communications Magazine, 49(4), 28–35.
Madakam, S., & Date, H. (2016). Security mechanisms for connectivity of smart devices in the internet of things. In Connectivity frameworks for smart devices (pp. 23–41). Springer.
Valhouli, C. A. (2010). The internet of things: Networked objects and smart devices. The Hammersmith Group Research Report (vol. 20).
Tu, C.-Y., Ho, C.-Y., & Huang, C.-Y. (2011). Energy-efficient algorithms and evaluations for massive access management in cellular based machine to machine communications. In Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Fall), 2011 IEEE, 2011, (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
Andreev, S., Galinina, O., & Koucheryavy, Y. (2011). Energy-efficient client relay scheme for machine-to-machine communication. In Global telecommunications conference (GLOBECOM 2011), 2011 IEEE (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
Bartoli, A., Dohler, M., Hernández-Serrano, J., Kountouris, A., & Barthel, D. (2011). Low-power low-rate goes long-range: The case for secure and cooperative machine-to-machine communications. In International conference on research in networking (pp. 219–230). Springer.
Datsika, E., Antonopoulos, A., Zorba, N., & Verikoukis, C. (2016). Green cooperative device-to-device communication: A social-aware perspective. IEEE Access, 4, 3697–3707.
Dayarathna, M., Wen, Y., & Fan, R. (2016). Data center energy consumption modeling: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 18(1), 732–794.
Himsoon, T., Siriwongpairat, W. P., Han, Z., & Liu, K. R. (2007). Lifetime maximization via cooperative nodes and relay deployment in wireless networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 25(2).
Zhou, M., Cui, Q., Jantti, R., & Tao, X. (2012). Energy-efficient relay selection and power allocation for two-way relay channel with analog network coding. IEEE Communications Letters, 16(6), 816–819.
Niyato, D., Xiao, L., & Wang, P. (2011). Machine-to-machine communications for home energy management system in smart grid. IEEE Communications Magazine, 49(4), 60–65.
Vo, Q. D., Choi, J.-P., Chang, H. M., & Lee, W. C. (2010). Green perspective cognitive radio-based M2M communications for smart meters. In 2010 international conference on information and communication technology convergence (ICTC) (pp. 382–383). IEEE.
Van, D. P., Rimal, B. P., Andreev, S., Tirronen, T., & Maier, M. (2016). Machine-to-machine communications over FiWi enhanced LTE networks: A power-saving framework and end-to-end performance. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 34(4), 1062–1071.
Sun, L., Tian, H., & Xu, L. (2013). A joint energy-saving mechanism for m2m communications in lte-based system. In Wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC), 2013 IEEE (pp. 4706–4711). IEEE.
Ajah, S., Al-Sherbaz, A., Turner, S., & Picton, P. (2015). Machine-to-machine communications energy efficiencies: The implications of different M2M communications specifications. International Journal of Wireless and Mobile Computing, 8(1), 15–26.
Cheng, R. S., Huang, C. M., & Cheng, G. S. (2016). A congestion reduction mechanism using D2D cooperative relay for M2M communication in the LTE-A cellular network. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 16(16), 2477–2494.
Ji, L., Han, B., Liu, M., & Schotten, H. D. (2017). Applying device-to-device communication to enhance IoT services. arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.03734.
Hussain, F., Anpalagan, A., & Naeem, M. (2014). Multi-objective MTC device controller resource optimization in M2M communication. In 2014 27th biennial symposium on communications (QBSC) (pp. 184–188). IEEE.
Alsamhi, S. H., & Rajput, N. (2015). An intelligent HAP for broadband wireless communications: Developments, QoS and applications. International Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering, 3(2), 134–143.
Alsamhi, S., & Rajput, N. (2014). HAP antenna radiation pattern for providing coverage and service characteristics. In 2014 international conference on advances in computing, communications and informatics (ICACCI) (pp. 1434–1439). IEEE.
Alsamhi, S., & Rajput, N. (2014). Performance and analysis of propagation models for efficient handoff in high altitude platform system to sustain QoS. In 2014 IEEE students’ conference on electrical, electronics and computer science (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Alsamhi, S. H., & Rajput, N. (2014). Neural network in intelligent handoff for QoS in HAP and terrestrial systems. International Journal of Materials science and Engineering, 2, 141–146.
Alsamhi, S. H., Ma, O., Ansari, M. S., & Gupta, S. K. (2019). Collaboration of drone and internet of public safety things in smart cities: An overview of QoS and network performance optimization. Drones, 3(1), 13.
Liu, Y., Yang, Z., Yu, R., Xiang, Y., & Xie, S. (2015). An efficient MAC protocol with adaptive energy harvesting for machine-to-machine networks. IEEE access, 3, 358–367.
Abbas, Z., & Yoon, W. (2015). A survey on energy conserving mechanisms for the internet of things: Wireless networking aspects. Sensors, 15(10), 24818–24847.
Cordeschi, N., Shojafar, M., Amendola, D., & Baccarelli, E. (2015). Energy-efficient adaptive networked datacenters for the QoS support of real-time applications. The Journal of Supercomputing, 71(2), 448–478.
Shuja, J., et al. (2016). Survey of techniques and architectures for designing energy-efficient data centers. IEEE Systems Journal, 10(2), 507–519.
Han, N. D., Chung, Y., & Jo, M. (2015). Green data centers for cloud-assisted mobile ad hoc networks in 5G. IEEE Network, 29(2), 70–76.
Roy, A. et al. (2016). Energy-efficient Data Centers and smart temperature control system with IoT sensing. In 2016 IEEE 7th annual information technology, electronics and mobile communication conference (IEMCON) (pp. 1–4). IEEE.
Peoples, C., Parr, G., McClean, S., Scotney, B., & Morrow, P. (2013). Performance evaluation of green data centre management supporting sustainable growth of the internet of things. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 34, 221–242.
Liu, Q., Ma, Y., Alhussein, M., Zhang, Y., & Peng, L. (2016). Green data center with IoT sensing and cloud-assisted smart temperature control system. Computer Networks, 101, 104–112.
Farahnakian, F., et al. (2015). Using ant colony system to consolidate vms for green cloud computing. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 8(2), 187–198.
Ashraf, A., & Porres, I. (2017). Multi-objective dynamic virtual machine consolidation in the cloud using ant colony system. arXiv preprint arXiv:1701.00383.
Matre, P., Silakari, S., & Chourasia, U. (2016). Ant colony optimization (ACO) based dynamic VM consolidation for energy efficient cloud computing. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Security, 14(8), 345.
Baccarelli, E., Amendola, D., & Cordeschi, N. (2015). Minimum-energy bandwidth management for QoS live migration of virtual machines. Computer Networks, 93, 1–22.
Amendola, D., Cordeschi, N., & Baccarelli, E. (2016). Bandwidth management VMs live migration in wireless fog computing for 5G networks. In 2016 5th ieee international conference on cloud networking (Cloudnet) (pp. 21–26). IEEE.
Koutitas, G. (2010). Green network planning of single frequency networks. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 56(4), 541–550.
Chan, C. A., Gygax, A. F., Wong, E., Leckie, C. A., Nirmalathas, A., & Kilper, D. C. (2012). Methodologies for assessing the use-phase power consumption and greenhouse gas emissions of telecommunications network services. Environmental Science and Technology, 47(1), 485–492.
Feng, W., Alshaer, H., & Elmirghani, J. M. (2010). Green information and communication technology: Energy efficiency in a motorway model. IET Communications, 4(7), 850–860.
Chih-Lin, I., Rowell, C., Han, S., Xu, Z., Li, G., & Pan, Z. (2014). Toward green and soft: A 5G perspective. IEEE Communications Magazine, 52(2), 66–73.
Mao, G. (2017). 5G green mobile communication networks. China Communications, 14(2), 183–184.
Abrol, A., & Jha, R. K. (2016). Power optimization in 5G networks: A step towards GrEEn communication. IEEE Access, 4, 1355–1374.
Alsamhi, S. H. A. M. (2015). Quality of service (QoS) enhancement techniques in high altitude platform (HAP) based communication networks. IIT (BHU) Varanasi.
Alsamhi, S., & Rajput, N. (2016). An efficient channel reservation technique for improved QoS for mobile communication deployment using high altitude platform. Wireless Personal Communications, 91(3), 1095–1108.
Alsamhi, S., & Rajput, N. (2015). An intelligent hand-off algorithm to enhance quality of service in high altitude platforms using neural network. Wireless Personal Communications, 82(4), 2059–2073.
Alsamhi, S., & Rajput, N. (2016). Implementation of call admission control technique in HAP for enhanced QoS in wireless network deployment. Telecommunication Systems, 63(2), 141–151.
Alsamhi, S., Ansari, M., Hebah, M., Ahmed, A., Hatem, A., & Alasali, M. (2018). Adaptive handoff prediction and appreciate decision using ANFIS between terrestrial communication and HAP.
Zhao, L., Al-Dubai, A., Li, X., Chen, G., & Min, G. (2017). A new efficient cross-layer relay node selection model for wireless community mesh networks. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 61, 361–372.
Li, J., Liu, Y., Zhang, Z., Ren, J., & Zhao, N. (2017). Towards green IoT networking: Performance optimization of network coding based communication and reliable storage. IEEE Access.
Zhou, L., et al. (2016). Green cell planning and deployment for small cell networks in smart cities. Ad Hoc Networks, 43, 30–42.
Wang, J., Hu, C., & Liu, A. (2017). Comprehensive optimization of energy consumption and delay performance for green communication in internet of things. Mobile Information Systems, vol. 2017.
Wang, X., Vasilakos, A. V., Chen, M., Liu, Y., & Kwon, T. T. (2012). A survey of green mobile networks: Opportunities and challenges. Mobile Networks and Applications, 17(1), 4–20.
Keshav, S., & Rosenberg, C. (2011). How internet concepts and technologies can help green and smarten the electrical grid. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 41(1), 109–114.
Adelin, A., Owezarski, P., & Gayraud, T. (2010). On the impact of monitoring router energy consumption for greening the internet. In 2010 11th IEEE/ACM international conference on grid computing (GRID) (pp. 298–304). IEEE.
Baldi., M., & Ofek, Y. (2009). Time for a” greener” internet”. In IEEE international conference on communications workshops, 2009. ICC Workshops 2009 (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Zhang, J., Wang, X.,& Huang, M. (2014). A Dynamic topology management mechanism in green internet. In 2014 13th international symposium on distributed computing and applications to business, engineering and science (DCABES) (pp. 203–207). IEEE.
Suh, Y., Kim, K., Kim, A., & Shin, Y. (2015). A study on impact of wired access networks for green internet. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 57, 156–168.
Suh, Y., Choi, J., Seo, C., & Shin, Y. (2014). A study on energy savings potential of data network equipment for a green internet. In 2014 16th international conference on advanced communication technology (ICACT) (pp. 1146–1151). IEEE.
Yang, Y.,Wang, D., Xu, M., & Li, S. (2013). Hop-by-hop computing for green Internet routing. In 2013 21st IEEE international conference on network protocols (ICNP) (pp. 1–10). IEEE.
Yang, Y,Wang, D., Pan, D., & Xu, M. (2016). Wind blows, traffic flows: Green internet routing under renewable energy. In IEEE INFOCOM 2016-The 35th annual IEEE international conference on computer communications (pp. 1–9). IEEE.
Hoque, M. A., Siekkinen, M., & Nurminen, J. K. (2014). Energy efficient multimedia streaming to mobile devices—A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 16(1), 579–597.
Zhu, C., Yang, L. T., Shu, L., Rodrigues, J. J., & Hara, T. (2012). A geographic routing oriented sleep scheduling algorithm in duty-cycled sensor networks. In 2012 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC) (pp. 5473–5477). IEEE.
Alvi, S. A, Shah, G. A., & Mahmood, W (2015). Energy efficient green routing protocol for internet of multimedia things. In 2015 IEEE tenth international conference on intelligent sensors, sensor networks and information processing (ISSNIP) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Sample, A. P., Yeager, D. J., Powledge, P. S., & Smith, J. R. (2007). Design of a passively-powered, programmable sensing platform for UHF RFID systems. In IEEE international conference on RFID, 2007 (pp. 149–156). IEEE.
Shu, L., Zhang, Y., Yang, L. T., Wang, Y., Hauswirth, M., & Xiong, N. (2010). TPGF: Geographic routing in wireless multimedia sensor networks. Telecommunication Systems, 44(1–2), 79–95.
Zhu, C., Yang, L. T., Shu, L., Leung, V. C., Rodrigues, J. J., & Wang, L. (2014). Sleep scheduling for geographic routing in duty-cycled mobile sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 61(11), 6346–6355.
Sheng, Z., Fan, J., Liu, C. H., Leung, V. C., Liu, X., & Leung, K. K. (2015). Energy-efficient relay selection for cooperative relaying in wireless multimedia networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 64(3), 1156–1170.
Karakus, C., Gurbuz, A. C., & Tavli, B. (2013). Analysis of energy efficiency of compressive sensing in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 13(5), 1999–2008.
Yoo, S.-J., Park, J.-H., Kim, S.-H., & Shrestha, A. (2016). Flying path optimization in UAV-assisted IoT sensor networks. ICT Express, 2(3), 140–144.
Mozaffari, M., Saad, W., Bennis, M., & Debbah, M. (2015). Drone small cells in the clouds: Design, deployment and performance analysis. In Global communications conference (GLOBECOM), 2015 IEEE (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Alsamhi, S. H., Ma, O., Ansari, M. S., & Almalki, F. (2019). Survey on collaborative smart drones and internet of things for improving smartness of smart cities. IEEE Access.
Cao, H.-R., Yang, Z., Yue, X.-J., & Liu, Y.-X. (2017). An optimization method to improve the performance of unmanned aerial vehicle wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 13(4), 1550147717705614.
Cao, H., Liu, Y., Yue, X., & Zhu, W. (2017). Cloud-assisted UAV data collection for multiple emerging events in distributed WSNs. Sensors, 17(8), 1818.
Dong, M., Ota, K., Lin, M., Tang, Z., Du, S., & Zhu, H. (2014). UAV-assisted data gathering in wireless sensor networks. The Journal of Supercomputing, 70(3), 1142–1155.
Zorbas, D., Razafindralambo, T., & Guerriero, F. (2013). Energy efficient mobile target tracking using flying drones. Procedia Computer Science, 19, 80–87.
Sharma, V., You, I., & Kumar, R. (2016). Energy efficient data dissemination in multi-UAV coordinated wireless sensor networks. Mobile Information Systems, 2016, 8475820. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8475820.
Uragun, B. (2011). Energy efficiency for unmanned aerial vehicles. In 2011 10th international conference on machine learning and applications and workshops (ICMLA) (vol. 2, pp. 316–320). IEEE.
Choi, D. H., Kim, S. H., & Sung, D. K. (2014). Energy-efficient maneuvering and communication of a single UAV-based relay. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 50(3), 2320–2327.
Yu, Y., Lee, S., Lee, J., Cho, K., & Park, S. (2016). Design and implementation of wired drone docking system for cost-effective security system in IoT environment. In 2016 IEEE international conference on consumer electronics (ICCE) (pp. 369–370). IEEE.
Seo, S.-H., Choi, J.-I., & Song, J. (2017). Secure utilization of beacons and UAVs in emergency response systems for building fire hazard. Sensors, 17(10), 2200.
Fujii, K., Higuchi, K, & Rekimoto, J (2013). Endless flyer: a continuous flying drone with automatic battery replacement. In Ubiquitous intelligence and computing, 2013 IEEE 10th international conference on and 10th international conference on autonomic and trusted computing (UIC/ATC) (pp. 216–223). IEEE.
Villa, T. F., Salimi, F., Morton, K., Morawska, L., & Gonzalez, F. (2016). Development and validation of a UAV based system for air pollution measurements. Sensors, 16(12), 2202.
Wang, J., Schluntz, E., Otis, B., & Deyle, T. (2015). A new vision for smart objects and the internet of things: Mobile robots and long-range UHF RFID sensor tags. arXiv preprint arXiv:1507.02373.
Hamilton, A., & Magdalene, A. H. S. (2017). Study of solar powered unmanned aerial vehicle to detect greenhouse gases by using wireless sensor network technology. Journal of Science and Engineering Education, 2, 1–11. ISSN: 2455-5061.
Klimkowska, A., Lee, I., & Choi, K. (2016). Possibilities of UAS for maritime monitoring. In ISPRS-international archives of the photogrammetry, remote sensing and spatial information sciences (pp. 885–891)
Villa, T. F., Gonzalez, F., Miljievic, B., Ristovski, Z. D., & Morawska, L. (2016). An overview of small unmanned aerial vehicles for air quality measurements: Present applications and future prospectives. Sensors, 16(7), 1072.
Telesetsky, A. (2016). Navigating the legal landscape for environmental monitoring by unarmed aerial vehicles. Geo. Wash. J. Energy & Envtl. L, 7, 140.
Alvear, O., Calafate, C. T., Hernández, E., Cano, J.-C., & Manzoni, P. (2015). Mobile pollution data sensing using UAVs. in Proceedings of the 13th international conference on advances in mobile computing and multimedia (pp. 393–397). ACM.
Alvear, O. A., Zema, N. R., Natalizio, E., & Calafate, C. T. (2017). A chemotactic pollution-homing UAV guidance system. In Wireless communications and mobile computing conference (IWCMC), 2017 13th international (pp. 2115–2120). IEEE.
Alvear, O., Zema, N. R., Natalizio, E., & Calafate, C. T. (2017). Using UAV-based systems to monitor air pollution in areas with poor accessibility. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2017, 1–14.
Koo, V. C., et al. (2012). A new unmanned aerial vehicle synthetic aperture radar for environmental monitoring. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 122, 245–268.
Šmídl, V., & Hofman, R. (2013). Tracking of atmospheric release of pollution using unmanned aerial vehicles. Atmospheric Environment, 67, 425–436.
Zang, W., Lin, J., Wang, Y., & Tao, H. (2012). Investigating small-scale water pollution with UAV remote sensing technology. In World automation congress (WAC), 2012 (pp. 1–4). IEEE.
Bronk, C., Lingamneni, A., & Palem, K. (2010). Innovation for sustainability in information and communication technologies (ICT). James A: Baker III Institute for Public Policy, Rice University.
Aslam, S., Hasan, N. U., Shahid, A., Jang, J. W., & Lee, K.-G. (2016). Device centric throughput and QoS optimization for IoTsin a smart building using CRN-techniques. Sensors, 16(10), 1647.
Kulkarni, N., & Abhang, S. (2017). Green industrial automation based on IOT: A survey. International Journal of Emerging Trends in Science and Technology, 4(8), 5805–5810.
Kalarthi, Z. M. (2016). A review paper on smart health care system using Internet of Things. International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology (IJRET), 5, 80–83.
Islam, S. R., Kwak, D., Kabir, M. H., Hossain, M., & Kwak, K.-S. (2015). The internet of things for health care: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Access, 3, 678–708.
Niewolny, D. (2013). How the internet of things is revolutionizing healthcare. White paper (pp. 1–8).
Ullah, F., Habib, M. A., Farhan, M., Khalid, S., Durrani, M. Y., & Jabbar, S. (2017). Semantic interoperability for big-data in heterogeneous IoT infrastructure for healthcare. Sustainable Cities and Society, 34, 90–96.
Sun, F., Yi, C., & Li, Y. J. I. C. (2017). Battery-friendly scheduling policy in MAC layer for WBAN data packets transmission. IET Communication, 11(9), 1423–1430.
Sun, F., & Li, Y. (2015). Power aware topology management and congestion control mechanism in high medical QoS WHMNs. In International conference on biomedical and health informatics (pp. 145–148). Springer.
Zang, W., Miao, F., Gravina, R., et al. (2019). CMDP-based intelligent transmission for wireless body area network in remote health monitoring. Neural Computing and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04034-x.
Yi, C., Wang, L., & Li, Y. (2015). Energy efficient transmission approach for WBAN based on threshold distance. IEEE Sensors Journal, 15(9), 5133–5141.
Sodhro, A. H., Li, Y., & Shah, M. A. J. I. C. (2016). Energy-efficient adaptive transmission power control for wireless body area networks. IET Communications, 10(1), 81–90.
Sodhro, A. H., Li, Y., & Shah, M. A. (2017). Green and friendly media transmission algorithms for wireless body sensor networks. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 76(19), 20001–20025.
Zang, W., Zhang, S., & Li, Y. (2016). An accelerometer-assisted transmission power control solution for energy-efficient communications in WBAN. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 34(12), 3427–3437.
Li, L., et al. (2011). The applications of WiFi-based wireless sensor network in internet of things and smart grid. In 2011 6th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (pp. 789–793).
Yang, X., et al. (2015). Towards a low-cost remote memory attestation for the smart grid. Sensors, 15(8), 20799–20824.
Liu, Y., Weng, X., Wan, J., Yue, X., Song, H., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2017). Exploring data validity in transportation systems for smart cities. IEEE Communications Magazine, 55(5), 26–33.
Karnouskos, S. (2010). The cooperative internet of things enabled smart grid. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE international symposium on consumer electronics (ISCE2010), June (pp. 07–10).
Petrolo, R., Loscrì, V., & Mitton, N. (2015). Towards a smart city based on cloud of things, a survey on the smart city vision and paradigms. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 28, e2931.
Heo, T., et al. (2014). Escaping from ancient Rome! Applications and challenges for designing smart cities. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 25(1), 109–119.
Bibri, S. E., & Krogstie, J. (2017). Smart sustainable cities of the future: An extensive interdisciplinary literature review. Sustainable Cities and Society, 31, 183–212.
Sathyamoorthy, P., Ngai, E. C.-H., Hu, X., & Leung, V. C. (2015). Energy efficiency as an orchestration service for mobile Internet of Things. In Cloud computing technology and science (CloudCom), 2015 IEEE 7th international conference on (pp. 155–162). IEEE.
Ramaswamy, P. (2016) Iot smart parking system for reducing green house gas emission. In Recent trends in information technology (ICRTIT), 2016 international conference on (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Popa, M., & Marcu, A. (2012). A Solution for street lighting in smart cities. Carpathian Journal of Electronic and Computer Engineering, 5, 91.
Vegni, A. M. Biagi, M., & Cusani, R. (2013). Smart vehicles, technologies and main applications in vehicular ad hoc networks. In Vehicular technologies-deployment and applications. InTech.
Su, K., Li, J., & Fu, H. (2011) Smart city and the applications. In Electronics, communications and control (ICECC), 2011 international conference on (pp. 1028–1031). IEEE.
Maksimovic, M. (2017). The role of green internet of things (G-IoT) and big data in making cities smarter, safer and more sustainable,”. International Journal of Computing and Digital Systems, 6(4), 175–184.
Sun, Y., Song, H., Jara, A. J., & Bie, R. (2016). Internet of things and big data analytics for smart and connected communities. IEEE Access, 4, 766–773.
Song, H., Srinivasan, R., Jeschke, S., & Sookoor, T. (2017). Smart cities: Foundations, principles and applications. Hoboken: Wiley.
Jiang, D., Zhang, P., Lv, Z., & Song, H. (2016). Energy-efficient multi-constraint routing algorithm with load balancing for smart city applications. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 3(6), 1437–1447.
Ejaz, W., Naeem, M., Shahid, A., Anpalagan, A., & Jo, M. (2017). Efficient energy management for the internet of things in smart cities. IEEE Communications Magazine, 55(1), 84–91.
Maksiimovici, M., & Omanovic-Miklicanin, E. (2017). Green internet of things and green nanotechnology role in realizing smart and sustainavle agriculture . In Presented at the VIII international scientific agriculture symposium “AGROSYM 2017”, Jahorina, Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Gani, A., Siddiqa, A., Shamshirband, S., & Hanum, F. (2016). A survey on indexing techniques for big data: taxonomy and performance evaluation. Knowledge and Information Systems, 46(2), 241–284.
Caviglione, L., Merlo, A., & Migliardi, M. (2011). What is green security? In 2011 7th international conference on information assurance and security (IAS) (pp. 366–371).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alsamhi, S.H., Ma, O., Ansari, M.S. et al. Greening internet of things for greener and smarter cities: a survey and future prospects. Telecommun Syst 72, 609–632 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-019-00597-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-019-00597-1