Abstract
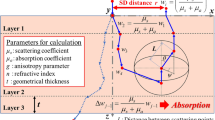
A new model for the scattering of light from layered dielectrics with rough surface boundaries is introduced. The model contains a surface scattering component together with a subsurface scattering component. The former component corresponds to the roughness on the upper surface boundary and is modeled using the modified Beckmann model. The latter component accounts for both refraction due to Fresnel transmission through the layer and rough scattering at the lower layer boundary. One interesting consequence of the model is that the peak radiance is deflected away from the specular direction, a behavior that is also evident in BRDF data from human skin. By allowing independent roughness parameters for each surface boundary and controlling the contributions from the two scattering components in the outgoing radiance using a balance parameter, we can achieve excellent fits of the model to the measured BRDF data. We experiment with BRDF data from skin surface samples (human volunteers) and show that the new model outperforms alternative variants of the Beckmann model and the Lafortune et al. reflectance model. As an application in computer graphics, we also show that realistic images of 3D surfaces can be generated using the new model, by setting the values of its physical parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AIM@SHAPE. (2004). INRIA shape repository. http://www.aim-at-shape.net.
Angelopoulou, E. (2001). Understanding the color of human skin. Proceedings of SPIE, 4299, 243–251.
Beckmann, P. (1967). Scattering of light by rough surfaces. In E. Wolf (Ed.), Progress in optics (Vol. VI, pp. 55–69).
Beckmann, P., & Spizzichino, A. (1963). The scattering of electromagnetic waves from rough surfaces. New York: Pergamon.
Caron, J., Lafait, J., & Andraud, C. (2002). Scalar Kirchhoff’s model for light scattering from dielectric random rough surfaces. Optics Communications, 207, 17–28.
CUReT database. (1996). http://www.cs.columbia.edu/CAVE/curet.
Dana, K. J., Nayar, S. K., van Ginneken, B., & Koenderink, J. J. (1997). Reflectance and texture of real-world surfaces. In Proceedings of IEEE CVPR (pp. 151–157).
Dickens, M. P., Ragheb, H., Smith, W. A. P., & Hancock, E. R. (2007). Analysis of skin reflectance using Beckmann–Kirchhoff scattering and a cyberware 3030 scanner. In ICCV workshop on photometric analysis for computer vision (pp. 35–42).
Donner, C., & Jensen, H. W. (2006). A spectral BSSRDF for shading human skin. In Eurographics symposium on rendering (pp. 409–417).
Hanrahan, P., & Krueger, W. (1993). Reflectance from layered surfaces due to subsurface scattering. In Computer graphics, SIGGRAPH93 proceedings (pp. 165–174).
Harvey, J. E., Vernold, C. L., Krywonos, A., & Thompson, P. L. (1999). Diffracted radiance: a fundamental quantity in a non-paraxial scalar diffraction theory. Applied Optics, 38, 6469–6481.
He, X. D., Torrance, K. E., Sillion, F. X., & Greenberg, D. P. (1991). A comprehensive physical model for light reflection. Computer Graphics, 25, 175–186.
Horn, B. K. H. (1986). Robot vision. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Igarashi, T., Nishino, K., & Nayar, S. K. (2005). The appearance of human skin (Technical Report: CUCS-024-05). Department of Computer Science, Columbia University, USA.
Jensen, H. W., Marschner, S., Levoy, M., & Hanrahan, P. (2001). A practical model for subsurface light transport. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH (pp. 511–518).
Lafortune, E. P. F., Foo, S., Torrance, K. E., & Greenberg, D. P. (1997). Non-linear approximation of reflectance functions. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH (pp. 117–126).
Lu, R., Koenderink, J., & Kappers, A. (1998). Optical properties of velvet. Applied Optics, 37(25), 5974–5984.
Lu, R., Koenderink, J., & Kappers, A. (2000). Optical properties of shot fabric. Applied Optics, 39, 5785–5795.
Matusik, W., Pfister, H., Brand, M., & McMillan, L. (2003). A data-driven reflectance model. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 22(3), 759–769.
Nayar, S. K., Ikeuchi, K., & Kanade, T. (1991). Surface reflection: physical and geometrical perspectives. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 13(7), 611–634.
Nieto-Vesperinas, M., & Garcia, N. (1981). A detailed study of the scattering of scalar waves from random rough surfaces. Optica Acta, 28(12), 1651–1672.
O’Donnell, K. A., & Mendez, E. R. (1987). Experimental study of scattering from characterized random surfaces. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 4(7), 1194–1205.
Ogilvy, J. A. (1991). Theory of wave scattering from random rough surfaces. Bristol: Hilger.
Oren, M., & Nayar, S. K. (1995). Generalization of the Lambertian model and implications for machine vision. International Journal of Computer Vision, 14(3), 227–251.
Oscar & Gollum (2004). In @UCSD magazine (Vol. 1, No. 2), University of California, May 2004. http://alumni.ucsd.edu/magazine.
Phong, B. T. (1975). Illumination for computer generated pictures. Communications of the ACM, 18, 311–317.
Ragheb, H., & Hancock, E. R. (2006). Testing new variants of the Beckmann–Kirchhoff model against radiance data. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 102(2), 145–168.
Ragheb, H., & Hancock, E. R. (2007). The modified Beckmann–Kirchhoff scattering theory for rough surface analysis. Pattern Recognition, 40(7), 2004–2020.
Reflectance data. (1999). Cornell university program of computer graphics. http://www.graphics.cornell.edu/online/measurements.
Stam, J. (1999). Diffraction shaders. In Computer graphics, proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 99 (pp. 101–110). New York: ACM.
Stam, J. (2001). An illumination model for a skin layer bounded by rough surfaces. In Proceedings of Eurographics workshop on rendering (pp. 39–52).
Torrance, K. E., & Sparrow, E. M. (1967). Theory for off-specular reflection from roughened surfaces. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 57(9), 1105–1114.
Vernold, C. L., & Harvey, J. E. (1998). A modified Beckmann–Kirchoff scattering theory for non-paraxial angles. Proceedings of SPIE, 3426, 51–56.
Wolff, L. B. (1994). Diffuse reflectance model for smooth dielectric surfaces. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 11(11), 2956–2968.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ragheb, H., Hancock, E.R. A Light Scattering Model for Layered Dielectrics with Rough Surface Boundaries. Int J Comput Vis 79, 179–207 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-007-0113-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-007-0113-5