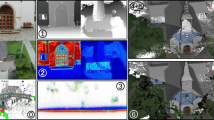
Abstract
Urban environments possess many regularities which can be efficiently exploited for 3D dense reconstruction from multiple widely separated views. We present an approach utilizing properties of piecewise planarity and restricted number of plane orientations to suppress reconstruction and matching ambiguities causing failures of standard dense stereo methods. We formulate the problem of the 3D reconstruction in MRF framework built on an image pre-segmented into superpixels. Using this representation, we propose novel photometric and superpixel boundary consistency terms explicitly derived from superpixels and show that they overcome many difficulties of standard pixel-based formulations and handle favorably problematic scenarios containing many repetitive structures and no or low textured regions. We demonstrate our approach on several wide-baseline scenes demonstrating superior performance compared to previously proposed methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbarzadeh, A., Frahm, J., Mordohai, P., Clipp, B., Engels, C., Gallup, D., Merrell, P., Phelps, M., Sinha, S., Talton, B., Wang, L., Yang, Q., Stewenius, H., Yang, R., Welch, G., Towles, H., Nister, D., & Pollefeys, M. (2006). Towards urban 3D reconstruction from video. In: Proc. of int. symp. on 3d data, processing, visualiz. and transmission (3DPVT).
Brostow, G., Shotton, J., Fauqueur, J., & Cipolla, R. (2008). Segmentation and recognition using structure from motion point clouds. In: Proc. of ECCV.
Cornelius, H., Šára, R., Martinec, D., Pajdla, T., Chum, O., & Matas, J. (2004). Towards complete free-form reconstruction of complex 3D scenes from an unordered set of uncalibrated images. In: Proc. of SMVP Workshop, ECCV, pp. 1–12.
Coughlan, J. M., & Yuille, A. L. (2003). Manhattan world: orientation and outlier detection by bayesian inference. Neural Computation, 15(5), 1063–1088.
Culbertson, B. (2002). A histogram-based color consistency test for voxel coloring. In: Proc. of ICPR.
Debevec, P. E., Taylor, C. J., & Malik, J. (1996). Modeling and rendering architecture from photographs: A hybrid geometry- and image-based approach. In: SIGGRAPH, pp. 11–20.
Dick, A. R., Torr, P. H., & Cipolla, R. (2004). Modelling and interpretation of architecture from several images. International Journal of Computer Vision, 60(2), 111–134.
EosSystems. PhotoModeler. http://www.photomodeler.com.
Felzenszwalb, P., & Huttenlocher, D. (2004). Efficient graph-based image segmentation. International Journal of Computer Vision, 59(2), 167–181.
Furukawa, Y., & Ponce, J. (2007). Accurate, dense, and robust multi-view stereopsis. In: Proc. of CVPR.
Furukawa, Y., Curless, B., Seitz, S., & Szeliski, R. (2009a). Manhattan-world stereo. In: Proc. of CVPR.
Furukawa, Y., Curless, B., Seitz, S., & Szeliski, R. (2009b). Reconstructing building interiors from images. In: Proc. of ICCV.
Gallup, D., Frahm, J. M., Mordohai, P., Yang, Q., & Pollefeys, M. (2007). Real-time plane-sweeping stereo with multiple sweeping directions. In: Proc. of CVPR.
Hartley, R., & Zisserman, A. (2004). Multiple view geometry in computer vision (2nd edn.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Hoiem, D., Efros, A., & Hebert, M. (2007). Recovering surface layout from an image. International Journal of Computer Vision, 75(1)
Irschara, A., Zach, C., & Bischof, H. (2007). Towards wiki-based dense city modeling. In: ICCV workshop on virtual representations and modeling of large-scale environments (VRML).
Kanatani, K., & Sugaya, Y. (2005). Statistical optimization for 3-D reconstruction from a single view. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, E88-D(10), 2260–2268.
Klaus, A., Sormann, M., & Karner, K. (2006). Segment-based stereo matching using belief propagation and a self-adapting dissimilarity measure. In: Proc. of ICPR (pp. 15–18).
Kolmogorov, V. (2006). Convergent tree-reweighted message passing for energy minimization. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 28(10), 1568–1583.
Košecká, J., & Zhang, W. (2002). Video compass. In: Proc. of ECCV (pp. 476–490).
Labatut, P., Pons, J. P., & Keriven, R. (2007). Efficient multi-view reconstruction of large-scale scenes using interest points, delaunay triangulation and graph cuts. In: Proc. of ICCV.
Leibe, B., Cornelis, N., Cornelis, K., & Van Gool, L. (2007). Dynamic 3D scene analysis from a moving vehicle. In: Proc. of CVPR.
Lowe, D. G. (2004). Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. International Journal of Computer Vision, 60(2), 91–110.
Malik, J., Belongie, S., Leung, T. K., & Shi, J. (2001). Contour and texture analysis for image segmentation. International Journal of Computer Vision, 43(1), 7–27.
Mičušík, B., & Košecká, J. (2009). Piecewise planar city 3D modeling from street view panoramic sequences. In: Proc. of CVPR.
Obdržálek, Š., Matas, J. (2006). Object recognition using local affine frames on maximally stable extremal regions. In J. Ponce, M. Hebert, C. Schmid, & A. Zisserman (Eds.), Toward Category-Level Object Recognition (pp. 83–104). Berlin: Springer.
RealViz. ImageModeler. http://imagemodeler.realviz.com.
Ren, X., & Malik, J. (2003). Learning a classification model for segmentation. In: Proc. of ICCV (pp. 10–17).
Rother, C. (2002). A new approach to vanishing point detection in architectural environments. Image Vision Computing, 20(9–10), 647–655.
Russell, B., Efros, A., Sivic, J., Freeman, W. T., & Zisserman, A. (2006). Using multiple segmentations to discover objects and their extent in image collections. In: Proc. of CVPR (pp. II:1605–1614).
Saxena, A., Sun, M., & Ng, A. Y. (2007). 3-D reconstruction from sparse views using monocular vision. In: Proc. of VRML Workshop, ICCV.
Scharstein, D., Szeliski, R., & Zabih, R. (2002). A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms. International Journal of Computer Vision, 47, 7–42.
Seitz, S., Curless, B., Diebel, J., Scharstein, D., & Szeliski, R. (2006). A comparison and evaluation of multi-view stereo reconstruction algorithms. In: Proc. of CVPR (pp. 519–528).
Sinha, S., Steedly, D., & Szeliski, R. (2009). Piecewise planar stereo for image-based rendering. In: Proc. of ICCV.
Sun, J., Li, Y., Kang, S. B., & Shum, H. Y. (2005). Symmetric stereo matching for occlusion handling. In: Proc. of CVPR (pp. II: 399–406).
Tao, H., Sawhney, H. S., & Kumar, R. (2001). A global matching framework for stereo computation. In: Proc. of ICCV (pp. I: 532–539).
Vergauwen, M., & Van Gool, L. (2006). Web-based 3D reconstruction service. Machine Vision Application, 17(6), 411–426 http://www.arc3d.be.
Oxford VGG dataset. http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/data/data-mview.html.
Vogiatzis, G., Esteban, C. H., Torr, P. H., & Cipolla, R. (2007). Multiview stereo via volumetric graph-cuts and occlusion robust photo-consistency. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 29(12), 2241–2246.
Werner, T. (2007). A linear programming approach to Max-sum problem: A review. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 29(7), 1165–1179.
Werner, T., & Zisserman, A. (2002). New techniques for automated reconstruction from photographs. In: Proc. of ECCV (pp. 541–555).
Yoon, K. J., & Kweon, I. S. (2006). Adaptive support-weight approach for correspondence search. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 28(4), 650–656.
Zach, C., Gallup, D., Frahm, J. M., & Niethammer, M. (2008). Fast global labeling for real-time stereo using multiple plane sweeps. In: Proc. of vision, modeling and visualization workshop (VMV).
Zebedin, L., Bauer, J., Karner, K., & Bischof, H. (2008). Fusion of feature- and area-based information for urban buildings modeling from aerial imagery. In: ECCV (pp. 873–886).
Zitnick, C. L., & Kang, S. B. (2007). Stereo for image-based rendering using image over-segmentation. International Journal of Computer Vision, 75(1), 49–65.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The research has received funding from US National Science Foundation Grant No. IIS-0347774 and the Wiener Wissenschafts-, Forschungs- und Technologiefonds-WWTF, Project No. ICT08-030.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mičušík, B., Košecká, J. Multi-view Superpixel Stereo in Urban Environments. Int J Comput Vis 89, 106–119 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-010-0327-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-010-0327-9