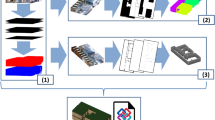
Abstract
In this paper we tackle the problem of 3D modeling for urban environment using a modular, flexible and powerful approach driven from procedural generation. To this end, typologies of architectures are modeled through shape grammars that consist of a set of derivation rules and a set of shape/dictionary elements. Appearance (from statistical point of view with respect to the individual pixel’s properties) of the dictionary elements is then learned using a set of training images. Image classifiers are trained towards recovering image support with respect to the semantics. Then, given a new image and the corresponding footprint, the modeling problem is formulated as a search of the space of shapes, that can be generated on-the-fly by deriving the grammar on the input axiom. Defining an image-based score function for the produced instances using the trained classifiers, the best rules are selected, making sure that we keep exploring the space by allowing some rules to be randomly selected. New rules are then generated by resampling around the selected rules. At the finest level, these rules define the 3D model of the building. Promising results on complex and varying architectural styles demonstrate the potential of the presented method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aichholzer, O., Aurenhammer, F., Alberts, D., & Gärtner, B. (1995). A novel type of skeleton for polygons. Journal of Universal Computer Science, 1(12), 752–761.
Alegre, F. & Dellaert, F. (2004). A probabilistic approach to the semantic interpretation of building facades. International workshop on vision techniques applied to the rehabilitation of city centres.
Bertsekas, D. P. (2006). Neuro-dynamic programming: An overview and recent results. In OR (pp. 71–72).
Bishop, C. (2006). Pattern recognition and machine learning. Berlin: Springer.
Blake, A., Rother, C., Brown, M., Perez, P., & Torr, P. (2004). Interactive image segmentation using an adaptive gmmrf model. In ECCV (pp. 428–441).
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine Learning, 45(1), 5–32.
Cech, J. & Sara, R. (2009). Languages for constrained binary segmentation based on maximum aposteriori probability labeling. International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, 69(2), 69–79.
Delaunoy, A., Prados, E., Gargallo, P., Pons, J.-P., & Sturm, P. (2008). Minimizing the multi-view stereo reprojection error for triangular surface meshes. In British machine vision conference, Leeds, UK, Sep. 2008.
Dick, A. R., Torr, P. H. S., & Cipolla, R. (2004). Modelling and interpretation of architecture from several images. International Journal of Computer Vision, 60(2), 111–134.
Eppstein, D. & Erickson, J. (1999). Raising roofs, crashing cycles, and playing pool: applications of a data structure for finding pairwise interactions. Discrete & Computational Geometry, 22(4), 569–592.
Faugeras, O. D. & Keriven, R. (1998). Variational principles, surface evolution, pdes, level set methods, and the stereo problem. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 7(3), 336–344.
Gargallo, P., Prados, E., & Sturm, P. (2007). Minimizing the reprojection error in surface reconstruction from images. In Proceedings of the international conference on computer vision, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Los Alamitos: IEEE Computer Society.
Gips, J. (1975). Shape grammars and their uses. Basel: Birkhäuser.
Hartley, R. & Zisserman, A. (2003). Multiple view geometry in computer vision (2nd edn.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Karantzalos, K. & Paragios, N. (2009). Variational model-based 3d building extraction from remote sensing data. In International conference on image processing.
Karantzalos, K. & Paragios, N. (2010, in press). Large-scale building reconstruction through information fusion and 3d priors. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing.
Kolmogorov, V. & Zabih, R. (2004). What energy functions can be minimized via graph cuts? IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 26(2), 147–159.
Koutsourakis, P., Simon, L., Teboul, O., & Paragios, N. (2009). Single view reconstruction using shape grammars for urban environments. In International conference on computer vision.
Labatut, P., Pons, J.-P., & Keriven, R. (2007). Efficient multi-view reconstruction of large-scale scenes using interest points, Delaunay triangulation and graph cuts. In IEEE international conference on computer vision, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, Oct. 2007.
Lepetit, V. & Fua, P. (2006). Keypoint recognition using randomized trees. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 28(9), 1465–1479.
Lipp, M., Wonka, P., & Wimmer, M. (2008). Interactive visual editing of grammars for procedural architecture. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 27(3), 1–10. Article No. 102.
Luong, Q.-T. & Faugeras, O. D. (1997). Camera calibration, scene motion and structure recovery from point correspondences and fundamental matrices. International Journal of Computer Vision, 22, 261–289.
Müller, P., Wonka, P., Haegler, S., Ulmer, A., & Gool, L. J. V. (2006). Procedural modeling of buildings. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 25(3), 614–623.
Müller, P., Zeng, G., Wonka, P., & Gool, L. J. V. (2007). Image-based procedural modeling of facades. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 26(3), 85.
Parish, Y. I. H. & Müller, P. (2001). Procedural modeling of cities. In SIGGRAPH (pp. 301–308).
Pons, J.-P., Keriven, R., & Faugeras, O. (2005). Modelling dynamic scenes by registering multi-view image sequences. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 822–827), San Diego, USA, June 2005.
Reznik, S. & Mayer, H. (2007). Implicit shape models, model selection, and plane sweeping for 3d facade interpretation. In PIA07 (p. 173).
Ripperda, N. & Brenner, C. (2006). Reconstruction of façade structures using a formal grammar and rjmcmc. In DAGM-symposium (pp. 750–759).
Ripperda, N. & Brenner, C. (2007). Data driven rule proposal for grammar based facade reconstruction. In PIA07 (p. 1).
Shotton, J., Johnson, M., & Cipolla, R. (2008). Semantic texton forests for image categorization and segmentation. In CVPR.
Snavely, N., Seitz, S. M., & Szeliski, R. (2008). Modeling the world from Internet photo collections. International Journal of Computer Vision, 80(2), 189–210.
Stiny, G. (1975). Pictorial and formal aspects of shape and shape grammars. PhD thesis, Birkhäuser.
Sutton, R. S. & Barto, A. G. (1998). Reinforcement learning: an introduction. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 9(5), 1054–1054.
Vaillant, R. & Faugeras, O. D. (1992). Using extremal boundaries for 3-d object modeling. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 14(2), 157–173.
Viola, P. & Jones, M. (2001). Robust real-time object detection. International Journal of Computer Vision.
Vu, H., Keriven, R., Labatut, P., & Pons, J.-P. (2009). Towards high-resolution large-scale multi-view stereo. In Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Miami, June 2009.
Winn, J. M. & Shotton, J. (2006). The layout consistent random field for recognizing and segmenting partially occluded objects. In CVPR (1) (pp. 37–44).
Wonka, P., Wimmer, M., Sillion, F. X., & Ribarsky, W. (2003). Instant architecture. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 22(3), 669–677.
Zaharescu, A., Boyer, E., & Horaud, R. P. (2007). Transformesh: a topology-adaptive mesh-based approach to surface evolution. In LNCS: Vol. 4844, Proceedings of the eighth Asian conference on computer vision (Vol. II, pp. 166–175), Tokyo, Japan, November 2007. Springer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simon, L., Teboul, O., Koutsourakis, P. et al. Random Exploration of the Procedural Space for Single-View 3D Modeling of Buildings. Int J Comput Vis 93, 253–271 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-010-0370-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-010-0370-6