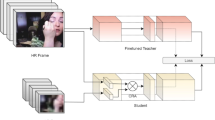
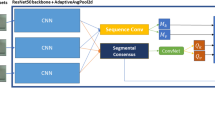
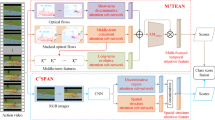
Abstract
Action recognition on extreme low-resolution videos, e.g., a resolution of \(12 \times 16\) pixels, plays a vital role in far-view surveillance and privacy-preserving multimedia analysis. As low-resolution videos often only contain limited information, it is difficult for us to perform action recognition in them. Given the fact that one same action may be represented by videos in both high resolution (HR) and extreme low resolution (eLR), it is worth studying to utilize the relevant HR data to improve the eLR action recognition. In this work, we propose a novel Confident Spatial-Temporal Attention Transfer (CSTAT) for eLR action recognition. CSTAT acquires information from HR data by reducing the attention differences with a transfer-learning strategy. Besides, the confidence of the supervisory signal is also taken into consideration for a more reliable transferring process. Experimental results demonstrate that, the proposed method can effectively improve the accuracy of eLR action recognition and achieve state-of-the-art performances on \(12\times 16\) HMDB51, \(12\times 16\) Kinects-400, and \(12\times 16\) Something-Something v2.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahn, S., Hu, S. X., Damianou, A., Lawrence, N. D., & Dai, Z. (2019). Variational information distillation for knowledge transfer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 9163–9171).
Arnab, A., Dehghani, M., Heigold, G., Sun, C., Lučić, M., & Schmid, C. (2021). Vivit: A video vision transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (pp. 6836–6846).
Baranyi, P. (2021). Rank#2 solutions of TinyAction challenge of CVPR workshop. https://www.crcv.ucf.edu/tiny-actions-challenge-cvpr2021/submissions/ALONG.pdf.
Bertasius, G., Wang, H., & Torresani, L. (2021, July). Is space-time attention all you need for video understanding? In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning(ICML), Vol. 2, No. 3, p. 4.
Beyer, L., Zhai, X., Royer, A., Markeeva, L., Anil, R., & Kolesnikov, A. (2022). Knowledge distillation: A good teacher is patient and consistent. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 10925–10934).
Biswas, S., Bowyer, K. W., & Flynn, P. J. (2010). Multidimensional scaling for matching low-resolution facial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on biometrics: Theory, applications and systems (BTAS) (pp. 1–6).
Boyle, M., Edwards, C., & Greenberg, S. (2000). The effects of filtered video on awareness and privacy. In Proceedings of the ACM conference on computer supported cooperative work (pp. 1–10).
Cao, S., Zou, Q., Mao, X., & Wang, Z. (2021). Metric learning for anti-compression facial forgery detection. In Proceedings of the ACM conference on multimedia (pp. 1–9).
Carreira, J., & Zisserman, A. (2017). Quo vadis, action recognition? a new model and the kinetics dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 6299–6308).
Chen, Y., Kalantidis, Y., Li, J., Yan, S., & Feng, J. (2018). Multi-fiber networks for video recognition. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 364–380).
Chen, J., Wu, J., Konrad, J., & Ishwar, P. (2017). Semi-coupled two-stream fusion convnets for action recognition at extremely low resolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV) (pp. 139–147).
Chen, D., Mei, J.-P., Zhang, Y., Wang, C., Wang, Z., Feng, Y., & Chen, C. (2021). Cross-layer distillation with semantic calibration. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 35, 7028–7036.
Chen, L., Shan, Y., Tian, W., Li, B., & Cao, D. (2018). A fast and efficient double-tree rrt-like sampling-based planner applying on mobile robotic systems. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 23(6), 2568–2578.
Demir, U., Rawat, Y. S., & Shah, M. (2021). Tinyvirat: Low-resolution video action recognition. In 2020 25th international conference on pattern recognition (ICPR) (pp. 7387–7394). IEEE.
Dollar, P., Rabaud, V., Cottrell, G., & Belongie, S. (2005). Behavior recognition via sparse spatio-temporal features. In Proceedings of the IEEE international workshop on visual surveillance and performance evaluation of tracking and surveillance (pp. 65–72).
Donahue, J., Anne Hendricks, L., Guadarrama, S., Rohrbach, M., Venugopalan, S., Saenko, K., & Darrell, T. (2015). Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 2625–2634).
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn, D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer, M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S., & Uszkoreit, J. (2020). An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In International conference on learning representations.
Fan, H., Xiong, B., Mangalam, K., Li, Y., Yan, Z., Malik, J. & Feichtenhofer, C. (2021). Multiscale vision transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (pp. 6824–6835).
Fookes, C., Lin, F., Chandran, V., & Sridharan, S. (2012). Evaluation of image resolution and super-resolution on face recognition performance. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 23(1), 75–93.
Gao, C., Xu, J., Zou, Y., & Huang, J.-B. (2020). Drg: Dual relation graph for human-object interaction detection. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 696–712).
Gunturk, B. K., Batur, A. U., Altunbasak, Y., Hayes, M. H., & Mersereau, R. M. (2003). Eigenface-domain super-resolution for face recognition. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 12(5), 597–606.
Hara, K., Kataoka, H., & Satoh, Y. (2018). Can spatiotemporal 3d cnns retrace the history of 2d CNNs and imagenet. In Proceedings of the conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 6546–6555).
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 770–778).
He, J., Zhang, Z., Xu, Z., & Luo, Z. (2022). Rank#1 solutions of tinyaction challenge of cvpr workshop.
Hinton, G. E., Vinyals, O., & Dean, J. (2015). Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1503.02531.
Huang, Z., & Wang, N. (2017). Like what you like: Knowledge distill via neuron selectivity transfer. arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.01219.
Ji, M., Heo, B., & Park, S. (2021). Show, attend and distill: Knowledge distillation via attention-based feature matching. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 35, 7945–7952.
Jin, L., Shu, X., Li, K., Li, Z., Qi, G.-J., & Tang, J. (2019). Deep ordinal hashing with spatial attention. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 28(5), 2173–2186.
Kay, W., Carreira, J., Simonyan, K., Zhang, B., Hillier, C., Vijayanarasimhan, S., Viola, F., Green, T., Back, T., & Natsev, P. & Suleyman, M. (2017). The kinetics human action video dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.06950.
Kuehne, H., Jhuang, H., Garrote, E., Poggio, T., & Serre, T. (2011). Hmdb: A large video database for human motion recognition. In Proceedings of the international conference on computer vision (ICCV) (pp. 2556–2563).
Laptev, L. (2003). Space-time interest points. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV) (pp. 432–439).
Li, Y., Ji, B., Shi, X., Zhang, J., Kang, B., & Wang, L. (2020). Tea: Temporal excitation and aggregation for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 909–918).
Liu, Z., Zhang, H., Chen, Z., Wang, Z., & Ouyang, W. (2020). Disentangling and unifying graph convolutions for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 143–152).
Neimark, D., Bar, O., Zohar, M., & Asselmann, D. (2021). Video transformer network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (pp. 3163–3172).
Park, W., Kim, D., Lu, Y., & Cho, M. (2019). Relational knowledge distillation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 3967–3976).
Park, D. Y., Cha, M.-H., Kim, D., Han, B., et al. (2021). Learning student-friendly teacher networks for knowledge distillation. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 34, 13292–13303.
Purwanto, D., Renanda Adhi Pramono, R., Chen, Y.-T., & Fang, W.-H. (2019). Extreme low resolution action recognition with spatial-temporal multi-head self-attention and knowledge distillation. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision workshops (ICCVW).
Purwanto, D., Pramono, R. R. A., Chen, Y.-T., & Fang, W.-H. (2019). Three-stream network with bidirectional self-attention for action recognition in extreme low resolution videos. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 26(8), 1187–1191.
Qiu, Z., Yao, T., & Mei, T. (2017). Learning spatio-temporal representation with pseudo-3d residual networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV) (pp. 5533–5541).
Raval, N., Srivastava, A., Lebeck, K., Cox, L., & Machanavajjhala, A. (2014). Markit: Privacy markers for protecting visual secrets. In Proceedings of the ACM international joint conference on pervasive and ubiquitous computing: adjunct publication (pp. 1289–1295).
Ren, C., Dai, D., & Yan, H. (2012). Coupled kernel embedding for low-resolution face image recognition. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 21(8), 3770–3783.
Russo, P., Ticca, S., Alati, E., & Pirri, F. (2021). Learning to See Through a Few Pixels: Multi Streams Network for Extreme Low-Resolution Action Recognition. IEEE Access, 9, 12019–12026
Ryoo, M. S., Kim, K., & Yang, H. J. (2017). Extreme low resolution activity recognition with multi-siamese embedding learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (pp. 7315–7322).
Ryoo, M. S., Rothrock, B., & Matthies, L. (2015). Pooled motion features for first-person videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 896–904).
Ryoo, M. S., Rothrock, B., Fleming, C., & Yang, H. J. (2017). Privacy-preserving human activity recognition from extreme low resolution. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (pp. 4255–4262).
Sadanand, S., & Corso, J. J. (2012). Action bank: A high-level representation of activity in video. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 1234–1241).
Shao, D., Zhao, Y., Dai, B., & Lin, D. (2020). Intra- and inter-action understanding via temporal action parsing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 730–739).
Shekhar, S., Patel, V. M., & Chellappa, R. (2011). Synthesis-based recognition of low resolution faces. In Proceedings of the international joint conference on biometrics (IJCB) (pp. 1–6).
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2014). Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In Proceedings of the advances in neural information processing systems (NIPS) (pp. 568–576).
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2015). Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In Proceedings of the international conference on learning representations (ICLR).
Soomro, K., Zamir, A. R., & Shah, M. (2012). Ucf101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild. arXiv preprint arXiv:1212.0402.
Stanton, S., Izmailov, P., Kirichenko, P., Alemi, A. A., & Wilson, A. G. (2021). Does knowledge distillation really work? Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 34, 6906–6919.
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., & Wojna, Z. (2016). Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 2818–2826).
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., & Paluri, M. (2015). Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV) (pp. 4489–4497).
Tran, D., Wang, H., Torresani, L., Ray, J., LeCun, Y., & Paluri, M. (2018). A closer look at spatiotemporal convolutions for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 6450–6459).
Veeriah, V., Zhuang, N., & Qi, G.-J. (2015). Differential recurrent neural networks for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV) (pp. 4041–4049).
Wang, H., & Schmid, C. (2013). Action recognition with improved trajectories. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV) (pp. 3551–3558).
Wang, X., & Tang, X. (2003). Face hallucination and recognition. In Proceedings of the international conference on audio- and video-based biometric person authentication (pp. 486–494).
Wang, Z., Chang, S., Yang, Y., Liu, D., & Huang, T. S. (2016). Studying very low resolution recognition using deep networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 4792–4800).
Wang, T., Geng, T., Wang, J., & Zheng, F. (2022). Rank#3 solutions of tinyaction challenge of CVPR workshop.
Wang, L., Xiong, Y., Wang, Z., Qiao, Y., Lin, D., Tang, X., & Van Gool, L. (2016). Temporal segment networks: Towards good practices for deep action recognition. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 20–36).
Weinland, D., Özuysal, M., & Fua, P. (2010). Making action recognition robust to occlusions and viewpoint changes. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 635–648).
Xie, S., Sun, C., Huang, J., Tu, Z., & Murphy, K. (2017). Rethinking spatiotemporal feature learning for video understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1712.04851.
Xu, G., Liu, Z., & Loy, C. C. (2020). Computation-efficient knowledge distillation via uncertainty-aware mixup. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.09413.
Xu, M., Sharghi, A., Chen, X., & Crandall, D. J. (2018). Fully-coupled two-stream spatiotemporal networks for extremely low resolution action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV) (pp. 1607–1615).
Yang, C., Xu, Y., Shi, J., Dai, B., & Zhou, B. (2020). Temporal pyramid network for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 591–600).
Yi, P., Wang, Z., Jiang, K., Jiang, J., Lu, T., & Ma, J. (2020). A progressive fusion generative adversarial network for realistic and consistent video super-resolution. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 44(5), 2264–2280.
Zagoruyko, S., & Komodakis, N. (2016). Paying more attention to attention: Improving the performance of convolutional neural networks via attention transfer. In Proceedings of the international conference on learning representations (ICLR).
Zou, W. W. W., & Yuen, P. C. (2012). Very low resolution face recognition problem. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 21(1), 327–340.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Key R &D Program of China under Grant Nos. 2022YFB4703700, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 62171324, the Key Research and Development Program of Hubei Province under Grant No. 2020BAB018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Karteek Alahari.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, Y., Zou, Q., Chen, X. et al. Extreme Low-Resolution Action Recognition with Confident Spatial-Temporal Attention Transfer. Int J Comput Vis 131, 1550–1565 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-023-01771-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-023-01771-4