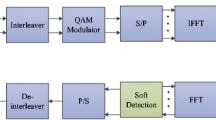
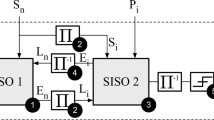
Abstract
Emerging Software Defined Radio (SDR) baseband platforms are based on multiple processors with massive parallelism. Although the computational power of these platforms would theoretically enable SDR solutions with advanced wireless signal processing, existing work implements still rather basic algorithms. For instance, current Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) detector implementations are typically based on simple linear hard-output and not on advanced near-Maximum Likelihood (ML) soft-output detection. However, only the latter enables to exploit the full potential of MIMO technology. In this work, we explore the feasibility of advanced soft-output near-ML MIMO detectors on massive parallel processors. Although such detectors are considered to be very challenging due to their high computational complexity, we combine architecture-friendly algorithm design, application specific instructions and instruction-level/data-level parallelism explorations to make SDR solutions feasible. We show that, by applying the proposed combination of techniques, it is possible to obtain SDR implementations which can deliver data rates that are sufficient for future wireless systems. For example, a 2 × 4 Coarse Grain Array (CGA) processor with 16-way Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD) can deliver 192/368 Mbps throughput for 2 × 2 64/16-QAM transmissions. Finally, we estimate the area and power consumption of the programmable solution and compare it against a traditional Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) approach. This enables us to draw conclusions from the cost perspective.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antikainen, J., Salmela, P., Silveny, O., Juntti, M., Takala, J., & Myllyla, M. (2008). Fine-grained application-specific instruction set processor design for the K-Best list sphere detector algorithm. In International conference on embedded computer systems (IC-SAMOS) (pp. 108–115).
Bolcskei, H., Gesbert, D., Papadias, C. B., & van der Veen, A. (2006). Space-time wireless systems: From array processing to MIMO communications. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Bougard, B., Li, M., Novo, D., Van Der Perre, L., & Catthoor, F. (2008). Bridging the energy gap in size, weight and power constrained software defined radio: Agile baseband processing as a key enabler. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP).
Bougard, B., De Stutter, B., Rabou, S., Novo, D., Allam, O., Dupont, S., et al. (2008). A coarse-grained array based baseband processor for 100 Mbps+ software defined radio. In Design, automation and test in Europe (DATE) (pp. 716–721).
Burg, A., Borgmann, M., Wenk, M., Zellweger, M., Fichtner, W., & Bolcskei, H. (2005). VLSI implementation of MIMO detection using the sphere decoding algorithm. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40(7), 1566–1577.
Chen, S., & Zhang, T. (2007). Low power soft-output signal detector design for wireless MIMO communications systems. In Proceedings of the intern. Symposium on low power electronics and design (pp. 232–237).
Chen, S., Zhang, T., & Xin, Y. (2007). Relaxed K-Best MIMO signal detector design and VLSI implementation. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 15(3), 328–337.
Eberli, S., Burg, A., & Fichtner, W. (2009). Implementation of a 2 × 2 MIMO-OFDM receiver on an application specific processor. Microelectronics Journal, 40(11), 1642–1649.
Fasthuber, R., Li, M., Novo, D., Raghavan, P., Van Der Perre, L., & Catthoor, (2009). Novel energy-efficient scalable soft-output SSFE MIMO detector architectures. In International conference on embedded computer systems (IC-SAMOS).
Garrett, D., Woodward, G. K., Davis, L., & Nicol, C. (2005). A 28.8 Mb/s 4 × 4 MIMO 3G CDMA receiver for frequency selective channels. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), 40(1), 320–330.
Gries, M., Keutzer, K., Meyr, H., & Martin, G. (2005). Building ASIPS: The mescal methodology. Berlin: Springer.
Guo, Z., & Nilsson, P. (2006). Algorithm and implementation of the K-Best sphere decoding for MIMO detection. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 24(3), 491–503.
Hochwald, B. M., & ten Brink, S. (2003). Achieving near-capacity on a multiple-antenna channel. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 51(3), 389–399.
Ienne, P., & Leupers, R. (2006). Customizable embedded processors: Design technologies and applications. San Francisco: Morgan Kauffman.
Jafri, A. R., Karakolah, D., Baghdadi, A., & Jezequel, M. (2009). ASIP-based flexible MMSE-IC linear equalizer for MIMO turbo-equalization applications. In Design, automation and test in Europe (DATE).
Janhunen, J., Silven, O., Juntti, M., & Myllyla, M. (2008). Software defined radio implementation of K-Best list sphere detector algorithm. In International conference on embedded computer systems (IC-SAMOS) (pp. 100–107).
Koike, T., Seki, Y., Murata, H., Yoshida, S., & Araki, K. (2005). FPGA implementation of 1 Gbps real-time 4 × 4 MIMO-MLD. Vehicular Technology Conference, 2, 1110–1114.
Li, M., Bougard, B., Lopez, E., Bourdoux, A., Novo, D., Van Der Perre, L., et al. (2008). Selective spanning with fast enumeration: A near maximum-likelihood MIMO detector designed for parallel programmable baseband architectures. In IEEE intern. conference on communications (ICC) 2008 (pp. 737–741).
Li, M., Bougard, B., Naessens, F., Van Der Perre, L., & Catthoor, F. (2008). An implementation friendly low complexity multiplierless LLR generator for soft MIMO sphere decoders. In IEEE workshop on signal processing systems (SIPS).
Li, M., Bougard, B., Xu, W., Novo, D., Van Der Perre, L., & Catthoor, F. (2008). Optimizing near-ML MIMO detector for SDR baseband on parallel programmable architectures. In Design, automation and test in Europe (DATE) (pp. 444–449).
Lin, Y., Lee, H., Woh, M., Harel, Y., Mahlke, S., Mudge, T., et al. (2007). SODA: A high-performance DSP architecture for software-defined radio. IEEE Micro, 27(1), 114–123.
Mei, B., Lambrechts, A., Mignolet, J. Y., Verkest, D., & Lauwereins, R. (2005). Architecture exploration for a reconfigurable architecture template. IEEE Design and Test of Computers, 22(2), 90–101.
Nilsson, A., Tell, E., & Liu, D. (2008). An 11 mm2 70 mW fully-programmable baseband processor for mobile WiMAX and DVB-T/H in 0.12 um CMOS. In Intern. solid-state circuits conference (ISSCC) (pp. 266–612).
Noll, T. G., Weiss, O., & Gansen, M. (2001). A flexible datapath generator for physical oriented design. In European solid-state circuits conf. (ESSCIRC) (pp. 393–396).
Paulraj, A. J., Gore, D. A., Nabar, R. U., & Bolcskei, H. (2004). An overview of MIMO communications—a key to gigabit wireless. Proceedings of the IEEE, 92(2), 198–218.
Ramacher, U. (2007). Software-defined radio prospects for multistandard mobile phones. Computer, 40(10), 62–69.
Shariat-Yazdi, R., & Kwasniewski, T. (2007). Reconfigurable K-Best MIMO detector architecture and FPGA implementation. In International symposium on intelligent signal processing and communication systems (ISPACS) (pp. 349–352).
Texas Instruments (2005). Datasheet of the TMS320C6416 fixed-point digital signal processor.
van Berkel, K., Heinle, F., Meuwissen, P., Moerman, K., & Weiss, M. (2005). Vector processing as an enabler for software-defined radio in handheld devices. Journal on Applied Signal Proc. (EURASIP), 2005, 2613–2625.
Wang, R., & Giannakis, G. B. (2004). Approaching MIMO channel capacity with reduced-complexity soft sphere decoding. IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), 3, 1620–1625.
Wu, D., Eilert, J., & Liu, D. (2009). Implementation of a high-speed MIMO soft-output symbol detector for software defined radio. Journal of Signal Processing Systems, 1–11. ISSN 1939–8018. doi:10.1007/s11265-009-0369-9.
Wu, M., Gupta, S., Sun, Y., & Cavallaro, J. R. (2009). A GPU implementation of a real-time MIMO detector. In IEEE workshop on signal processing systems (SiPS’09).
Wu, M., Sun, Y., & Cavallaro, J. R. (2009). Reconfigurable real-Time MIMO detector on GPU. In Asilomar conf. on signals, systems and computers (ASILOMAR’09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fasthuber, R., Li, M., Novo, D. et al. Exploration of Soft-Output MIMO Detector Implementations on Massive Parallel Processors. J Sign Process Syst 64, 75–92 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-010-0499-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-010-0499-0