Abstract
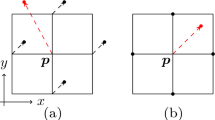
We present a surface denoising method using the vertex-centered finite volume method coupled with the mesh covariance fractional anisotropy. The approach is computationally fast and able to effectively remove undesirable noise while preserving prominent geometric features of a 3D mesh surface such as curved surface regions, sharp edges, and fine details. Extensive experimental results on various 3D models demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed iterative algorithm, which yields satisfactory output results in just one single iteration.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taubin, G. (1995). A signal processing approach to fair surface design. Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH, pp. 351–358.
Ohtake, Y., Belyaev, A.G., Bogaevski, I.A. (2000). Polyhedral surface smoothing with simultaneous mesh regularization. Proc. Geom. Modeling and Processing, pp. 229–237.
Taubin, G. (2001). Linear anisotropic mesh filtering. IBM Research Report, RC2213.
Petitjean, S. (2002). A survey of methods for recovering quadrics in triangle meshes. ACM Computing Surveys, 34(2), 211–262.
Shen, Y., & Barner, K.E. (2004). Fuzzy vector median-based surface smoothing. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 10(3), 252–265.
Yagou, H., Ohtake, Y., Belyaev, A. (2002). Mesh smoothing via mean and median filtering applied to face normals. Proc. Geometric Modeling and Processing Theory and Applications, pp. 124–131.
Fleishman, S., Drori, I., Cohen-Or, D. (2003). Bilateral mesh denoising. Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH, pp. 950–953.
Jones, T., Durand, F., Desbrun, M. (2003). Non-iterative, feature preserving mesh smoothing. Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH, pp. 943–949.
Desbrun, M., Meyer, M., Schröder, P., Barr, A. (1999). Implicit fairing of irregular meshes using diffusion and curvature flow. Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH, pp. 317–324.
Desbrun, M., Meyer, M., Schröder, P., Barr, A. (2000). Anisotropic feature-preserving denoising of height fields and bivariate data. Proc. Graphics Interface, pp. 145–152.
Clarenz, U., Diewald, U., Rumpf, M. (2000). Anisotropic geometric diffusion in surface processing. Proc. IEEE Visualization, pp. 397–405.
Clarenz, U., Diewald, U., Rumpf, M. (2004). Processing textured surfaces via anisotropic geometric diffusion. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 13(2), 248–261.
Bajaj, C.L., & Xu, G. (2003). Anisotropic diffusion of subdivision surfaces and functions on surfaces. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 22(1), 4–32.
Tasdizen, T., Whitaker, R., Burchard, P., Osher, S. (2002). Geometric surface smoothing via anisotropic diffusion of normals. Proc. IEEE Visualization, pp. 125–132.
Tasdizen, T., Whitaker, R., Burchard, P., Osher, S. (2003). Geometric surface processing via normal maps. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 22(4), 1012–1033.
Hildebrandt, K., & Polthier, K. (2004). Anisotropic filtering of non-linear surface features. Computer Graphics Forum, 23(3), 391–400.
LeVeque, R. (2002). Finite volume methods for hyperbolic problems. England: Cambridge University Press.
Hirsch, C. (2007). Numerical computation of internal and external flows, 2nd edn. United Kingdom: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Basser, P.J., & Pierpaoli, C. (1996). Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. Journal of magnetic resonance Series B, 111(3), 209–219.
Rousseeuw, P.J., & Leroy, A.M. (1987). Robust regression and outlier detection. New York: Wiley.
Huang, H., & Ascher, U. (2008). Fast denoising of surface meshes with intrinsic texture. Inverse Problems, 24(3), 034003.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported in part by NSERC Discovery Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kacem, A., Hamza, A.B. A Finite Volume Framework for Geometric Surface Processing. J Sign Process Syst 76, 63–75 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-013-0807-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-013-0807-6