Abstract
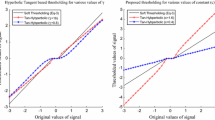
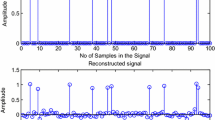
Sparse signal reconstruction methods are used in a wide range of applications such as compressive sensing, denoising, signal separation and general linear inverse problems. The numerical algorithms used for the sparse signal recovery frequently involve finding solutions to the least squares optimization problem with l 1-norm regularization. As the l 1-norm penalty is not differentiable, so it rules out the possibility of using the efficient optimization techniques that call for the derivative of the objective function. This paper presents a hyperbolic tangent based surrogate function to closely approximate the l 1-norm regularization. Simultaneously, we also develop an iterative algorithm for sparse signal reconstruction using the gradient of the proposed smooth function. The algorithm can be used to recover the compressively sampled images from a reduced set of measurements. Various numerical and imaging experiments are used to illustrate the performance of the promising recovery method. It has been shown that the algorithm can be used to reconstruct the compressively sampled images from less number of acquired data, which makes fast imaging possible without compromising high spatial resolutions. The results are validated using phantom as well as original MR and microwave SAR images.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck, A., & Teboulle, M. (2009). A Fast Iterative Shrinkage-Thresholding Algorithm for Linear Inverse Problems. Siam Journal Imaging Science, 2(1), 183–202. doi:10.1137/080716542.
Candes, E. J., Romberg, J. K., & Tao, T. (2006). Stable signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements. Commun Pur. Applications of Mathematics, 59(8), 1207–1223. doi:10.1002/Cpa.20124.
Candès, E. J., Romberg, J., & Tao, T. (2006). Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. Information Theory, IEEE Transactions on, 52(2), 489–509.
Candes, E. J., & Wakin, M. B. (2008). An introduction to compressive sampling. Ieee Signal Processing Magazine, 25(2), 21–30. doi:10.1109/Msp.2007.914731.
Baraniuk, R. G., Candes, E., Nowak, R., & Vetterli, M. (2008). Compressive sampling. Ieee Signal Processing Magazine, 25(2), 12–13. doi:10.1109/Msp.2008.915557.
Yang, A.Y., Sastry, S.S., Ganesh, A., Ma, Y. (2010). Fast ℓ 1-minimization algorithms and an application in robust face recognition: A review. In: Image Processing (ICIP), 2010 17th IEEE International Conference on 2010, pp. 1849–1852. IEEE
Bach, F., Jenatton, R., Mairal, J., & Obozinski, G. (2012). Optimization with sparsity-inducing penalties. Foundations and trends® in. Machine Learning, 4(1), 1–106.
Donoho, D. L. (2006). For most large underdetermined systems of linear equations the minimal Commun Pur. Applications of Mathematics, 59(6), 797–829.
Candes, E. J., & Tao, T. (2006). Near-optimal signal recovery from random projections: universal encoding strategies? Information Theory, IEEE Transactions on, 52(12), 5406–5425.
Candes, E., Romberg, J. (2005). ll-magic: Recovery of sparse signals via convex programming. URL: www. acm. caltech. edu/l1magic/downloads/l1magic. pdf 4 (2005).
Wright, S. J., Nowak, R. D., & Figueiredo, M. A. (2009). Sparse reconstruction by separable approximation. Signal Processing, IEEE Transactions on, 57(7), 2479–2493.
Malioutov, D.M., Cetin, M., Willsky, A.S. (2005). Homotopy continuation for sparse signal representation. In: acoustics, speech, and Signal Processing, (2005). Proceedings.(ICASSP'05). IEEE International Conference on 2005, pp. v/733-v/736 Vol. 735. IEEE
Figueiredo, M. A., Nowak, R. D., & Wright, S. J. (2007). Gradient projection for sparse reconstruction: application to compressed sensing and other inverse problems. Selected topics in signal processing. IEEE Journal of, 1(4), 586–597.
Yang, J., & Zhang, Y. (2011). Alternating direction algorithms for l1-problems in compressive sensing. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 33(1), 250–278.
Becker, S., Bobin, J., & Candès, E. J. (2011). NESTA: a fast and accurate first-order method for sparse recovery. Siam Journal Imaging Science, 4(1), 1–39.
Haykin, S. S. (2008). Adaptive filter theory. Pearson Education India.
Haykin, S.S., Haykin, S.S., Haykin, S.S., Haykin, S.S. (2009). Neural networks and learning machines, vol. 3. Pearson Education Upper Saddle River
Menon, A., Mehrotra, K., Mohan, C. K., & Ranka, S. (1996). Characterization of a class of sigmoid functions with applications to neural networks. Neural Networks, 9(5), 819–835.
Fang, X.-F., Zhang, J.-S., Li, Y.-Q. (2014). Sparse signal reconstruction based on Multiparameter approximation function with smoothed norm. Mathematical Problems in Engineering 9 (2014). doi:10.1155/2014/416542
Wang, W., & Wang, Q. (2014). Approximated Function Based Spectral Gradient Algorithm for Sparse Signal Recovery. Statistics, Optimization & Information Computing, 2(1), 10–20.
Barzilai, J., & Borwein, J. M. (1988). Two-point step size gradient methods. IMA Journal of Numerical Analysis, 8(1), 141–148.
Shah, J., Qureshi, I., Omer, H., & Khaliq, A. (2014). A modified POCS-based reconstruction method for compressively sampled MR imaging. International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, 24(3), 203–207. doi:10.1002/ima.22095.
Wang, Z., Bovik, A. C., Sheikh, H. R., & Simoncelli, E. P. (2004). Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. Image Processing, IEEE Transactions on, 13(4), 600–612.
Donoho, D. L., & Tanner, J. (2010). Precise undersampling theorems. Proceedings of the IEEE, 98(6), 913–924.
Shah, J. A., Qureshi, I. M., Omer, H., Khaliq, A. A., & Deng, Y. (2015). Compressively sampled magnetic resonance image reconstruction using separable surrogate functional method. Concept Magnetics Reson A, 43(5), 157–165.
Tropp, J. A., & Wright, S. J. (2010). Computational methods for sparse solution of linear inverse problems. Proceedings of the IEEE, 98(6), 948–958.
Yang, A. Y., Genesh, A., Zhou, Z., Sastry, S. S., & Ma, Y. (2010). A Review of Fast L (1)-Minimization Algorithms for Robust Face Recognition. In. DTIC Document.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, J., Qureshi, I., Deng, Y. et al. Reconstruction of Sparse Signals and Compressively Sampled Images Based on Smooth l 1-Norm Approximation. J Sign Process Syst 88, 333–344 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-016-1168-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-016-1168-8