Abstract
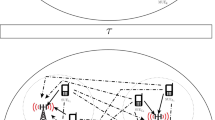
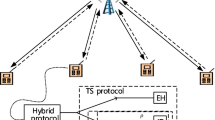
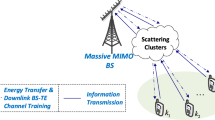
Wireless powered communications have been recently proposed as a variable power solution for the heterogeneous networks (HetNets) with small and flexible deployments of low-power base stations (BSs). In this paper, we consider the wireless powered multi-tier multi-input multi-output (MIMO) HetNets, where the multi-antenna BSs perform downlink transmission. In particular, we consider two cases of interests, i.e., 1) energy harvesting (EH) without energy beamforming (EB) tier and 2) EH with EB tier. Using tools of stochastic geometry, we perform analysis on the throughput and energy efficiency (EE) of the considered network. Closed-form and tractable results are obtained to reveal interesting insights that the proposed wireless-powered MIMO HetNets can achieve higher EE as compared to the conventional HetNets without EH, and the EE performance can be further improved by introducing well-designed EB across tiers.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
It is noted in order to obtain sufficient energy, a rectenna is equipped at each EH BS to harvest ambient RF energy [30].
References
Buzzi, S., Chih-Lin, I., Klein, T.E., Poor, H.V., Yang, C., Zappone, A. (2016). A survey of energy-efficient techniques for 5G networks and challenges ahead. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 34, 697–709.
Ghosh, A., Mangalvedhe, N., Ratasuk, R., Mondal, B., Cudak, M., Visotsky, E., Thomas, T., Andrews, J.G., Xia, P., Jo, H.S., et al. (2012). Heterogeneous cellular networks: from theory to practice. IEEE Communications Magazine, 50, 54–64.
Qing, L., Zhu, Q., Wang, M. (2006). Design of a distributed energy-efficient clustering algorithm for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Computer Communications, 29, 2230–2237.
Huang, Y., Zhang, X., Zhang, J., Tang, J., Su, Z., Wang, W. (2014). Energy-efficient design in heterogeneous cellular networks based on large-scale user behavior constraints. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13, 4746–4757.
Wang, W., & Shen, G. (2010). Energy efficiency of heterogeneous cellular network. In IEEE Vehicular technology conference fall (VTC 2010-Fall) (pp. 1–5). Ottawa.
Arnold, O., Richter, F., Fettweis, G., Blume, O. (2010). Power consumption modeling of different base station types in heterogeneous cellular networks. In Future network and mobile summit (pp. 1–8). Florence.
Xu, W., Zhou, X., Lee, C.H., Feng, Z., Lin, J. (2016). Energy-efficient joint sensing duration, detection threshold, and power allocation optimization in cognitive OFDM systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 15, 8339–8352.
Soh, Y.S., Quek, T.Q., Kountouris, M., Shin, H. (2013). Energy efficient heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 31, 840–850.
Ngo, H.Q., Larsson, E.G., Marzetta, T.L. (2013). Energy and spectral efficiency of very large multiuser MIMO systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 61, 1436–1449.
Bi, S., Ho, C.K., Zhang, R. (2015). Wireless powered communication: opportunities and challenges. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53, 117–125.
Buzzi, S., Chih-Lin, I., Klein, T.E., Poor, H.V. (2016). A survey of energy-efficient tech- niques for 5G networks and challenges ahead. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 34, 697–709.
Bi, S., Ho, C.K., Zhang, R. (2016). Wireless powered communication networks: an overview. IEEE Wireless Communications, 23, 10–18.
Xu, W., Liu, Z., Li, S., Lin, J. (2017). Two-plus-one cognitive cooperation based on energy harvesting and spatial multiplexing. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 66, 7589–7593.
Sun, Q., Zhu, G., Shen, C., Li, X. (2014). Joint beamforming design and time allocation for wireless powered communication networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 18, 1783–1786.
Lindemark, B, & Oberg, G. (2001). Solar power for radio base station (rbs) sites applications including system dimensioning, cell planning and operation. In International telecommunications energy conference (pp. 587–590). Edinburgh.
Piro, G., Miozzo, M., Forte, G., Baldo, N., Grieco, L.A., Boggia, G., Dini, P. (2013). Hetnets powered by renewable energy sources: sustainable next-generation cellular networks. IEEE Internet Computing, 17, 32–39.
Ju, H., & Zhang, R. (2014). User cooperation in wireless powered communication networks. In IEEE Global communications conference (GLOBECOM) (pp. 1430–1435). Austin.
Ng, D.W.K., Lo, E.S., Schober, R. (2013). Wireless information and power transfer: energy efficiency optimization in OFDMA systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12, 6352–6370.
Chen, X., Wang, X., Chen, X. (2013). Energy-efficient optimization for wireless information and power transfer in large-scale MIMO systems employing energy beamforming. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2, 667–670.
Haenggi, M., Andrews, J.G., Baccelli, F., Dousse, O. (2009). Stochastic geometry and random graphs for the analysis and design of wireless networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 27, 1029–1046.
Haenggi, M., & Ganti, R.K. (2009). Interference in large wireless networks (pp. 127–248). Now Publishers Inc.
Andrews, J.G., Gupta, A.K., Dhillon, H. (2016). A primer on cellular network analysis using stochastic geometry.
Dhillon, H.S., Ganti, R.K., Baccelli, F., Andrews, J.G. (2012). Modeling and analysis of K-tier downlink heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 30, 550–560.
Dhillon, H.S., Kountouris, M., Andrews, J.G. (2013). Downlink MIMO hetnets: modeling, ordering results and performance analysis. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12, 5208–5222.
Deng, Y., Wang, L., Elkashlan, M., Renzo, M.D., Yuan, J. (2016). Modeling and analysis of wireless power transfer in heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 64, 5290–5303.
Zhang, T., Zhao, J., An, L., Liu, D. (2016). Energy efficiency of base station deployment in ultra dense hetNets: a stochastic geometry analysis. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 5, 184–187.
Singh, S., Dhillon, H.S., Andrews, J.G. (2012). Offloading in heterogeneous networks: modeling, analysis, and design insights. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12, 2484–2497.
Gupta, A., Dhillon, H., Vishwanath, S., Andrews, J. (2014). Downlink multi-antenna heterogeneous cellular network with load balancing. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 62, 4052–4067.
Li, C., Zhang, J., Letaief, K. (2014). Throughput and energy efficiency analysis of small cell networks with multi-antenna base stations. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13, 2505–2517.
Zhao, Y, Leung, V.C.M., Zhu, C, Gao, H, Chen, Z, Ji, H. (2017). Energy-efficient sub-carrier and power allocation in cloud-based cellular network with ambient RF energy harvesting. IEEE Access, 5, 1340–1352.
Alzer, H. (1997). On some inequalities for the incomplete Gamma function. Mathematics of Computation of the American Mathematical Society, 66, 771–778.
Baccelli, F., & Blaszczyszyn, B. (2009). Stochastic geometry and wireless networks: theory. Now Publishers Inc.
Yu, P.S., Lee, J., Quek, T., Hong, Y.W. (2015). Traffic offloading in heterogeneous networks with energy harvesting personal cells network throughput and energy efficiency. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 15, 1536–1276.
Yu, SM, & Kim, SL. (2013). Downlink capacity and base station density in cellular networks. In International symposium and workshops on modeling and optimization in mobile (pp. 119–124). Tsukuba Science City.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix A
Recalling the definition in (4), the Laplace transformation of E can be derived as
where (a) follows from the independence of tiers, (b) uses the probability generating function (PGFL) of PPP [22], and \(\mathbb {R}^{2}\) is presented as a two-dimensional plane. (c) follows from the Laplace transform of g j (x) ∼Γ(U j ,1), (d) follows from Binomial theorem where \(\left ({\begin {array}{c} U_{j}\\ m \end {array}}\right )\) represents \({C_{U_{j}}^{m}}={\frac {U_{j}!}{m!(U_{j}-m)!}}\), (e) uses the transformation to the polar coordinates where x = (R,𝜃), (f) follows by \((s\beta P_{j})^{\alpha _{j}}R=r\), then \(R=r(s\beta P_{j})^{-\alpha _{j}},dR=(s\beta P_{j})^{-\alpha _{j}}dr\), (g) follows from \(\frac {1}{\text {1}+r^{-\alpha _{j}}}=t\) and then (h) employs the Beta function \(B(x,y)={{\int }_{0}^{1}}u^{x-1}(1-u)^{y-1}du\).
Appendix B
From the viewpoint of a typical EB BS, the PMF of the number of EH BSs \(N_{E}^{\prime }\) in tier K associated with one EB BS in tier i can refer to [34]
From the viewpoint of a typical EH BS, there is a tagged EB BS that the typical EH BS is associated with. Besides, there are other EH BSs associated with the tagged EB BS. With reference to [27], the PMF of the number of the other EH BSs (apart from the typical EH BS that are associated with the tagged EB BS) is the same with Eq. 56. Then, the PMF of the number of EH BSs N E including the typical EH BS that are associated with one tagged EB BS can be written as
Therefore, N E and \(N_{E}^{\prime }\) can be approximated by the mean value \(1 + 1.28\frac {\lambda _{K}}{p\lambda _{i}}\) and \(\frac {\lambda _{K}}{p\lambda _{i}}\) [33]. respectively.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, H., Gao, J., Shi, Z. et al. Throughput and Energy Efficiency of Wireless Powered Multi-tier MIMO HetNets. J Sign Process Syst 90, 857–871 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-018-1354-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-018-1354-y