Abstract
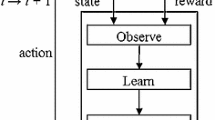
In wireless sensor networks (WSNs), resource-constrained nodes are expected to operate in highly dynamic and often unattended environments. Hence, support for intelligent, autonomous, adaptive and distributed resource management is an essential ingredient of a middleware solution for developing scalable and dynamic WSN applications. In this article, we present a resource management framework based on a two-tier reinforcement learning scheme to enable autonomous self-learning and adaptive applications with inherent support for efficient resource management. Our design goal is to build a system with a bottom-up approach where each sensor node is responsible for its resource allocation and task selection. The first learning tier (micro-learning) allows individual sensor nodes to self-schedule their tasks by using only local information, thus enabling a timely adaptation. The second learning tier (macro-learning) governs the micro-learners by tuning their operating parameters so as to guide the system towards a global application-specific optimization goal (e.g., maximizing the network lifetime). The effectiveness of our framework is exemplified by means of a target tracking application built on top of it. Finally, the performance of our scheme is compared against other existing approaches by simulation. We show that our two-tier reinforcement learning scheme is significantly more efficient than traditional approaches to resource management while fulfilling the application requirements.













Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
In order to reduce the related overhead, we assume that the rewards are piggybacked into the messages.
References
Alex, H., Kumar, M., & Shirazi, B. (2008). Midfusion: An adaptive middleware for information fusion in sensor network applications. Information Fusion, 9(3), 332–343. doi:10.1016/j.inffus.2005.05.007.
Byers, J. W., & Nasser, G. (2000). Utility-based decision-making in wireless sensor networks. In: MobiHoc (pp. 143–144). ACM. doi:10.1145/514151.514178.
Di Francesco, M., Das, S. K., & Anastasi, G. (2011). Data collection in wireless sensor networks with mobile elements: A survey. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks 8(1). doi:10.1145/1993042.1993049.
Frank, C., & Römer, K. (2005). Algorithms for generic role assignment in wireless sensor networks. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.59.8091; http://www.vs.inf.ethz.ch/publ/papers/sensys05.roleassignment.ps.
Hadim, S., & Mohamed, N. (2006). Middleware challenges and approaches for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Distributed Systems Online 7(3), Article no. 0603–o3001.
Heinzelman, W., Murphy, A., Carvalho, H., & Perillo, M. (2004). Middleware to support sensor network applications. IEEE Network 18,(1), 6–14.
Intanagonwiwat, C., Govindan, R., & Estrin, D. (2000). Directed diffusion: A scalable and robust communication paradigm for sensor networks. In MOBICOM (pp. 56–67). doi:10.1145/345910.345920.
J-sim: Component-based, compositional simulation environment. http://sites.google.com/site/jsimofficial/.
Kagan Tumer, D. H. W. (2004). Collectives and the design of complex systems. Berlin: Springer.
Kogekar, S., Neema, S., Eames, B., Koutsoukos, X., Ledeczi, A., & Maroti, M. (2004). Constraint-guided dynamic reconfiguration in sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the 3rd international symposium on information processing in sensor networks (IPSN-04) (pp. 379–387). New York: ACM Press.
Krishnamachari, B., Wicker, S. B., Béjar, R., & Fernández, C. (2003) On the complexity of distributed self-configuration in wireless networks. Telecommunication Systems 22(1–4), 33–59. doi:10.1023/A:1023426501170.
Leen-Kiat Soh Costa Tsatsoulis, H. S. (2003). Distributed sensor networks: A multiagent perspective, chap. In A satisfying, negotiated and learning coalition formation architecture (pp. 109–137). Kluwer.
Liu, T., & Martonosi, M. (2003). Impala: A middleware system for managing autonomic, parallel sensor systems. In: PPoPP’03: Proceedings of the 9th ACM SIGPLAN symposium on principles and practice of parallel programming (pp. 107–118).
Mahadevan, S., & Conell, J. (1992). Automatic programming of behavior-based robots using reinforcement learning. Artificial Intelligence 55(2), 311–365.
Mainland, G., Parkes, D. C., & Welsh, M. (2005). Decentralized, adaptive resource allocation for sensor networks. In NSDI’05: Proceedings of the 2nd symposium on networked systems design & implementation (pp. 315–328).
Marron, P. J., Lachenmann, A., Minder, D., Hahner, J., Sauter, R., & Rothermel, K. (2005). TinyCubus: A flexible and adaptive framework sensor networks. In: EWSN’05: Proceedings of the 2nd European workshop on wireless sensor networks (pp. 278–289).
Modi, P. J., Shen, W., Tambe, M., & Yokoo, M. (2005). Adopt: Asynchronous distributed constraint optimization with quality guarantees. Artificial Intelligence, 161(1–2), 149–180.
Ortiz, C., Rauenbush, T., Hsu, E., & Vincent, R. (2003). Distributed sensor networks: A multiagent perspective. In Dynamic resource-bounded negotiation in non-additive domains (pp. 61–106). Kluwer.
Sadagopan, N., Singh, M., & Krishnamachari, B. (2006). Decentralized utility-based sensor network design. MONET 11(3), 341–350. doi:10.1007/s11036-006-5187-8.
Shah, K., Di Francesco, M., Anastasi, G., & Kumar, M. (2011). A framework for resource-aware data accumulation in sparse wireless sensor networks. Computer Communications 34(17), 2094–2103. doi:10.1016/j.comcom.2011.06.010.
Shah, K., & Kumar, M. (2007). Distributed independent reinforcement learning (DIRL) approach to resource management in wireless sensor networks. In: IEEE internatonal conference on mobile adhoc and sensor systems, 2007 (MASS 2007) (pp. 1–9). doi:10.1109/MOBHOC.2007.4428658.
Shah, K., & Kumar, M. (2008). Resource management in wireless sensor networks using collective intelligence. In: International conference on intelligent sensors, sensor networks and information processing, 2008 (ISSNIP 2008) (pp. 423–428). doi:10.1109/ISSNIP.2008.4762025.
Sutton, R. (1984). Temporal credit assignment in reinforcement learning. Ph.D. thesis, Department of Computer Science, University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA. Published as COINS Technical Report 84-2.
Sutton, R. S., & Barto, A. G. (1998). Reinforcement learning: An introduction. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press. http://www.cs.ualberta.ca/sutton/book/ebook/the-book.html.
Terfloth, K., Wittenburg, G., & Schiller, J. H. (2006). FACTS—a rule-based middleware architecture for wireless sensor networks. In COMSWARE IEEE.
Victor Lesser Charles Ortiz, M. T. (2003). Distributed sensor networks: A multiagent perspective. Kluwer.
Watkins, C. (1989). Learning from delayed rewards. Ph.D. thesis, University of Cambridge, England.
Watkins, C. J., & Dayan, P. (1992). Q-learning. Machine Learning 8(3), 279–292.
Wolpert, D., & Tumer, K. (1999). An introduction to collective intelligence. CoRR cs.LG/9908014. http://arxiv.org/abs/cs.LG/9908014 (Informal publication).
Wolpert, D., & Tumer, K. (2002). Collective intelligence, data routing and braess’ paradox. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research (JAIR), 16, 359–387. doi:10.1613/jair.995.
Yu, Y., Krishnamachari, B., & Prasanna, V. K. (2004). Issues in designing middleware for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Network, 18(1), 15–21.
Acknowledgments
The research work presented in this article was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) under Grants ECCS-0824120 and CNS-0721951.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, K., Di Francesco, M. & Kumar, M. Distributed resource management in wireless sensor networks using reinforcement learning. Wireless Netw 19, 705–724 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-012-0496-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-012-0496-2