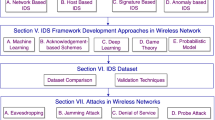
Abstract
In this paper we propose a MAC called “Neighbor Initiated Approach for avoiding Deaf and Hidden node problems in directional MAC protocol for Ad Hoc networks”, which takes advantage of the multi beam smart antennas. Through the antenna, a node can simultaneously transmit/receive a packet to/from all the directions around it. Thus the antenna switches itself in transmission and reception mode. In our scheme all transmission and reception will be directional. We discussed the hidden and deaf node problems with directional MAC and proposed the scheme to overcome those shortcomings. Our scheme has been inspired by the IEEE 802.11, which includes a new scheme to inform its neighbors who was deaf due to other communication. Moreover, the simultaneous transmission of the RTS/CTS through it’s all beams prevent the hidden node problem. In our scheme the idle nodes stay in reception mode for sensing the channel through its M non overlapping beams, as a substitute of omnidirectional antenna. It prevents the hidden node problem due to asymmetry in gain. We have simulated our scheme by OPNET 16.0, and compared our results with CDR MAC, DMAC and IEEE 802.11 protocols. Our results show that NIADH performs better than that of the existing protocols in majority of the scenarios.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACK:
-
Acknowledgement
- CCTS:
-
Circular CTS
- CDR MAC:
-
Circular directional RTS MAC
- CRTS:
-
Circular RTS
- CTS:
-
Clear to send
- DCF:
-
Distributed coordinate function
- DCTS:
-
Directional CTS
- DMAC:
-
Directional MAC
- DNAV:
-
Directional network allocation vector
- DRTS:
-
Directional RTS
- MAC:
-
Medium access control
- MBSA:
-
Multi beam smart antenna
- NIADH:
-
Neighbor initiated approach for avoiding deaf and hidden node problems in directional MAC protocol for Ad Hoc networks
- NIP:
-
Neighbor information packet
- OPNET:
-
Optimized network engineering tools
- RTS:
-
Request to send
- SINR:
-
Signal to interference and noise ratio
- WLAN:
-
Wireless local area network
- WTS:
-
Wait to send
References
Jurdak, R., Lopes, C. V., & Baldi, P. (2004) A survey, classification and comparative analysis of medium access control protocols for ad hoc networks. Communication Surveys & Tutorials, IEEE. 6(1), 2–16 (First Quarter). doi:10.1109/COMST.2004.5342231.
Draft Supplement to Standard [for] Information Technology Telecommunications and information exchange between systems Local and metropolitan area networks Specific requirements Part 11.(2003). Wireless LAN medium access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) specifications: Further higher data rate extension in the 2.4 GHz band (Amendment to IEEE Std 802.11, 1999 Edition), IEEE Std P802.11 g/D8.2.
Choudhury, R. R., Yang, X., Ramanathan, R., & Vaidya, N. (2002). Using directional antennas for medium access control in ad hoc networks. In ACM international conference on mobile computing and networking mobicom. doi:10.1109/WCNC.2000.904804.
Choudhury, R. R., Yang, X., & Vaidya, N. Using directional antennas in ad hoc networks. Final Report submitted from Texas A&M University to BBN.
Chang, C. T, Chang, C. Y., & Lu, Y. J. (2010). Maximizing throughput by exploiting spatial reuse opportunities with smart antenna systems. In: IEEE international conference on Communications (ICC), pp. 1–5, pp. 23–27. doi:10.1109/ICC.2010.5502361.
Hung, L. L., Wu, S. H., & Chang, C. T. (2011). Maximizing throughput for delay-constraint transmissions with smart antenna systems in WLANs, In Innovative mobile and internet services in ubiquitous computing (IMIS). Fifth international conference. (pp. 583–588), June 30, 2011–July 2, 2011. doi:10.1109/IMIS.2011.57.
Ramanathan, R. (2001). On the performance of ad hoc networks with beamforming antennas. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM international symposium on mobile ad hoc networking and computing (pp. 5–105) (MobiHoc ‘01). New York, NY, USA: ACM. doi:10.1145/501426.501430.
Gossain, H., Cordeiro, C., Joshi, T., & Agrawal, D. P. (2006). Cross-layer directional antenna MAC protocol for wireless ad hoc networks: Research Articles. Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing, 6(2), 171–182. doi:10.1002/wcm.v6:2.
Gummalla, V., Chandra, A., & Limb, J. O. (2000). Wireless medium access control protocols. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 3(2 Second Quarter), 2–15. doi:10.1109/COMST.2000.5340799002E.
Horneffer, M., & Plassmann, D. (1996) Directed antennas in the mobile broadband system. In INFOCOM ‘96. Fifteenth annual joint conference of the IEEE computer societies. Networking the next generation. Proceedings IEEE, Vol. 2, pp. 704–712, Vol. 2, 24–28 Mar 1996. doi:10.1109/INFCOM.1996.493367.
Yum, T. S., & Hung, K. W. (1992). Design algorithms for multihop packet radio networks with multiple directional antennas stations. Communications, IEEE Transactions, 40(11), 1716–1724. doi:10.1109/26.179935.
Nasipuri, A., Ye, S., You, J., & Hiromoto, R. E. (2000). A MAC protocol for mobile ad hoc networks using directional antennas. In IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC 2000) (pp. 1214–1219). doi:10.1109/WCNC.2000.904804.
Ko, Y. B., Shankarkumar, V., & Vaidya, N. H. (2000). Medium access control protocols using directional antennas in ad hoc networks. In INFOCOM 2000, 19 annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications societies, Proceedings IEEE. (Vol. 1, pp. 13–21). doi:10.1109/INFCOM.2000.832169.
Takata, M., Bandai, M., & Watanabe, T. (2007) A MAC protocol with directional antennas for deafness avoidance in ad hoc networks. In IEEE GLOBECOM ‘07. (pp. 620–625). doi:10.1109/GLOCOM.2007.121.
Korakis, T., Jakllari, G., & Tassiulas, L. (2003). A MAC protocol for full exploitation of directional antennas in ad-hoc wireless networks. In: MobiHoc ‘03. doi:10.1145/778415.778428.
Jakllari, G., Broustis, I., Korakis, T., Krishnamurthy, S. V., & Tassiulas, L. (2005). Handling asymmetry in gain in directional antenna equipped ad hoc networks. In IEEE 16th international symposium on Personal, indoor and mobile radio communications (PIMRC 2005), vol. 2, pp. 1284–1288, Vol. 2, 11–14. doi:10.1109/PIMRC.2005.1651648.
Takai, M., Martin, J., Bagrodia, R., & Ren, A. (2002). Directional virtual carrier sensing for directional antennas in mobile ad hoc networks. In MobiHoc ‘02 (pp. 183–193). New York, NY, USA: ACM. doi:10.1145/513800.513823.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Korea government (MEST, No.2010-0018116).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alam, M.N., Hussain, M.A. & Kwak, K.S. Neighbor initiated approach for avoiding deaf and hidden node problems in directional MAC protocol for ad-hoc networks. Wireless Netw 19, 933–943 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-012-0510-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-012-0510-8