Abstract
This paper proposes a novel scheme for the slow block fading Gaussian multiple access relay channel inspired by the compute-and-forward (CoF) relaying strategy. The CoF relaying strategy exploits interference to obtain significantly higher rates between users in a network by decoding linear functions of the transmitted messages. Unlike other approaches in the literature, our approach is valid for any number of transmitters and, most importantly, it only requires channel state information at the receiver side, while it still attains similar or higher rates than the other approaches found in the literature.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
where the channel is assumed to be constant over each coherence time interval and the coherence time is considered to be larger than the code block length (see, e.g., [23, pp. 583–584]).
Recall that the transmitted average energy per complex dimension \(E_s\) is equal for all transmitters.
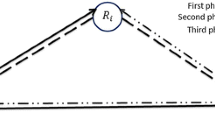
A practical implementation of the CoF relaying strategy relies on decoding a synchronous linear combination of the transmitted messages. Although perfect synchronization is not feasible, different types of asynchronism and their corresponding performance degradation have been studied in the literature (see, e.g., [31,32,33]).
Observe that the relay also needs to let the destination know the chosen coefficient vector \(\widehat{{{\varvec{\alpha }}}_r}\), which is considered negligible in terms of data rate.
See [40] for a review on the complexity of integer coefficient search methods for CoF proposed in literature.
References
Nazer, B., & Gastpar, M. (2007). Computation over multiple-access channels. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 53(10), 3498–3516.
Wannstrom, J. (2013). LTE-advanced. http://www.3gpp.org/technologies/keywords-acronyms/97-lte-advanced.
Ahlswede, R., Cai, Ning, Li, S.-Y. R., & Yeung, R. W. (2000). Network information flow. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 46(4), 1204–1216.
Kim, S. J., Mitran, P., & Tarokh, V. (2008). Performance bounds for bidirectional coded cooperation protocols. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 54(11), 5235–5241.
Avestimehr, A. S., Diggavi, S. N., & Tse, D. N. C. (2011). Wireless network information flow: A deterministic approach. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 57(4), 1872–1905.
Lim, S., Kim, Y.-H., El Gamal, A., & Chung, S.-Y. (2011). Noisy network coding. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 57(5), 3132–3152.
Nazer, B., & Gastpar, M. (2011). Compute-and-forward: Harnessing interference through structured codes. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 57(10), 6463–6486.
Insausti, X., Camaró, F., Crespo, P. M., Beferull-Lozano, B., & Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, J. (2013). Distributed pseudo-gossip algorithm and finite-length computational codes for efficient in-network subspace projection. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 7(2), 163–174.
Song, Y., & Devroye, N. (2013). Lattice codes for the gaussian relay channel: Decode-and-forward and compress-and-forward. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 59(8), 4927–4948.
Hong, S.-N., & Caire, G. (2013). Compute-and-forward strategies for cooperative distributed antenna systems. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 59(9), 5227–5243.
Kramer, G., Gastpar, M., & Gupta, P. (2005). Cooperative strategies and capacity theorems for relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 51(9), 3037–3063.
Sankar, L., Liang, Y., Mandayam, N. B., & Poor, H. V. (2011). Fading multiple access relay channels: Achievable rates and opportunistic scheduling. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 57(4), 1911–1931.
Hernaez, M., Crespo, P. M., & Del Ser, J. (2013). On the design of a novel joint network-channel coding scheme for the multiple access relay channel. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 31(8), 1368–1378.
El Soussi, M., Zaidi, A., & Vandendorpe, L. (2014). Compute-and-forward on a multiaccess relay channel: Coding and symmetric-rate optimization. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13(4), 1932–1947.
Erez, U., Litsyn, S., & Zamir, R. (2005). Lattices which are good for (almost) everything. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 51(10), 3401–3416.
Feng, C., Silva, D., & Kschischang, F. R. (2013). An algebraic approach to physical-layer network coding. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 59(11), 7576–7596.
Hern, B., & Narayanan, K. R. (2013). Multilevel coding schemes for compute-and-forward with flexible decoding. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 59(11), 7613–7631.
Wei, L., & Chen, W. (2012). Compute-and-forward network coding design over multi-source multi-relay channels. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 11(9), 3348–3357.
Ordentlich, O., Zhan, J., Erez, U., Gastpar, M., & Nazer, B. (2011). Practical code design for compute-and-forward. In IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory Proceedings (ISIT), 2011 (pp. 1876–1880).
Vem, A., Huang, Y.-C., Narayanan, K. R., & Pfister, H. D. (2014). Multilevel lattices based on spatially-coupled LDPC codes with applications. In IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), 2014 (pp 2336–2340).
Hong, S.-N., & Caire, G. (2011). Quantized compute and forward: A low-complexity architecture for distributed antenna systems. In IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), 2011 (pp. 420–424).
Tunali, N. E., & Narayanan, K. R. (2011). Concatenated signal codes with applications to compute and forward. In IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference (GLOBECOM 2011), 2011 (pp. 1–5).
El Gamal, A., & Kim, Y.-H. (2012). Network information theory. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Goldsmith, A. (2005). Wireless communications. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Tse, D., & Viswanath, P. (2005). Fundamentals of wireless communication., Wiley series in telecommunications Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Nazer, B. (2012). Successive compute-and-forward. In Proceedings of the international Zurich seminar on communications (pp. 103–106).
Tseng, T. Y., Lee, C. P., Lin, S. C., Su, H. J. (2014). Non-orthogonal compute-and-forward with joint lattice decoding for the multiple-access relay channel. In 2014 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps) (pp. 924–929).
Aguerri, I. E., & Zaidi, A. (2016). Lossy compression for compute-and-forward in limited backhaul uplink multicell processing. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 64(12), 5227–5238.
Wei, S., Li, J., Chen, W., Zheng, L., & Su, H. (2015). Design of generalized analog network coding for a multiple-access relay channel. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 63(1), 170–185.
Hejazi, M., Azimi-Abarghouyi, S. M., Makki, B., Nasiri-Kenari, M., & Svensson, T. (2016). Robust successive compute-and-forward over multiuser multirelay networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 65(10), 8112–8129.
Najafi, H., Damen, M. O., & Hjorungnes, A. (2013). Asynchronous compute-and-forward. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 61(7), 2704–2712.
Zhang, H., Mehta, N. B., Molisch, A. F., Zhang, J., & Dai, S. H. (2008). Asynchronous interference mitigation in cooperative base station systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 7(1), 155–165.
Wei, S. (2007). Diversity multiplexing tradeoff of asynchronous cooperative diversity in wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 53(11), 4150–4172.
Holtzman, J. M., & Zorzi, M. (2006). Advances in wireless communications., The springer international series in engineering and computer science New York: Springer.
Zhang, Y., Chen, H. H., & Guizani, M. (2009). Cooperative wireless communications., Wireless networks and mobile communications Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Song, L., & Shen, J. (2010). Evolved cellular network planning and optimization for UMTS and LTE. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Braithwaite, C., & Scott, M. (2003). UMTS network planning and development: Design and implementation of the 3G CDMA infrastructure. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science.
Lawler, E. L., & Wood, D. E. (1966). Branch-and-bound methods: A survey. Operations Research, 14(4), 699–719.
Wolsey, L. A. (1998). Integer programming. New Jersey: Wiley.
Liu, W., & Ling, C. (2016). Efficient integer coefficient search for compute-and-forward. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 15(12), 8039–8050.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported in part by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness through the RACHEL Project (TEC2013-47141-C4-2-R), the CARMEN Project (TEC2016-75067-C4-3-R) and the COMONSENS network (TEC2015-69648-REDC).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Insausti, X., Sáez, A. & Crespo, P.M. A novel scheme inspired by the compute-and-forward relaying strategy for the multiple access relay channel. Wireless Netw 25, 665–673 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-017-1583-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-017-1583-1