Abstract
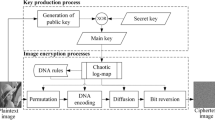
Based on computer generated hologram (CGH) and multiple chaotic systems, a novel image encryption scheme is presented, in which shuffling the positions and changing the values of image pixels are combined to confuse the relationship between the ciphertext and the original image. In the encryption process, the complex distribution is permuted by use of the designed scrambling algorithm which is based on Chen’s chaotic system and logistic maps firstly. Subsequently, the Burch’s coding method is used to fabricate the CGH as the encrypted image. Finally, the pixel values of the encrypted CGH are changed by sine map to withstand statistical analysis attacks. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method has high security level and certain robustness against statistical analysis attacks, data loss, noise disturbance and differential attack.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, F., Song, H., Jiang, D., & Wen, H. (2019). Adaboost-based security level classification of mobile intelligent terminals. The Journal of Supercomputing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-019-02954-y.
Liu, Z. J., Xu, L., Lin, C., et al. (2011). Image encryption scheme by using iterative random phase encoding in gyrator transform domains. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 49(4), 542–546.
Xi, S. X., Wang, X. L., Song, L. P., et al. (2017). Experimental study on optical image encryption with asymmetric double random phase and computer-generated hologram. Optics Express, 25, 8212–8222.
Chen, L., Jiang, D., Song, H., et al. (2018). A lightweight end-side user experience data collection system for quality evaluation of multimedia communications. IEEE Access, 6, 15408–15419.
Zhou, B., Xu, X. T., Liu, J. G., Xu, X. K., & Wang, N. X. (2019). Information interaction model for the mobile communication networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 525, 1170–1176.
Huo, L., & Jiang, D. (2019). Stackelberg game-based energy-efficient resource allocation for 5G cellular networks. Telecommunication System, 23(4), 1–11.
Fekher, K., Abbas, B., Abderrahim, B., Priyanka, R., & Mohamed, A. (2019). A survey of localization systems in internet of things. Mobile Networks and Applications, 24(3), 761–785.
Huo, L., Jiang, D., Zhu, X., et al. (2019). An SDN-based fine-grained measurement and modeling approach to vehicular communication network traffic. International Journal of Communication Systems. https://doi.org/10.1002/dac.4092.
Mouratidis, H., Shei, S., & Delaney, A. (2019). A security requirements modelling language for cloud computing environments. Software & Systems Modeling. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10270-019-00747-8.
Sun, M., Jiang, D., Song, H., et al. (2017). Statistical resolution limit analysis of two closely-spaced signal sources using Rao test. IEEE Access, 5, 22013–22022.
Jiang, D., Zhang, P., Lv, Z., et al. (2016). Energy-efficient multi-constraint routing algorithm with load balancing for smart city applications. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 3(6), 1437–1447.
Kong, L., & Ma, B. (2019). Intelligent manufacturing model of construction industry based on Internet of Things technology. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04369-8.
Jiang, D., Li, W., & Lv, H. (2017). An energy-efficient cooperative multicast routing in multi-hop wireless networks for smart medical applications. Neurocomputing, 220, 160–169.
Huo, L., Jiang, D., & Lv, Z. (2018). Soft frequency reuse-based optimization algorithm for energy efficiency of multi-cell networks. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 66(2), 316–331.
Krichen, M. (2019). Improving formal verification and testing techniques for internet of things and smart Cities. Mobile Networks and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-019-01369-6.
Jiang, D., Huo, L., & Song, H. (2018). Rethinking behaviors and activities of base stations in mobile cellular networks based on big data analysis. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 1(1), 1–12.
Yu, G., & Liu, J. (2019). A hybrid prediction approach for road tunnel traffic based on spatial-temporary data fusion. Applied Intelligence, 49(4), 1421–1436.
Jiang, D., Wang, Y., Lv, Z., et al. (2019). Big data analysis-based network behavior insight of cellular networks for industry 4.0 applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics. https://doi.org/10.1109/tii.2019.2930226.
Wang, F., Jiang, D., & Qi, S. (2019). An adaptive routing algorithm for integrated information networks. China Communications, 7(1), 196–207.
Riisa, S., & Gadouleaub, M. (2019). Max-flow min-cut theorems on dispersion and entropy measures for communication networks. Information and Computation, 267, 49–73.
Jiang, D., Huo, L., Lv, Z., et al. (2018). A joint multi-criteria utility-based network selection approach for vehicle-to-infrastructure networking. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 19(10), 3305–3319.
Ranjith Kumar, A., & Sivagami, A. (2019). Security aware multipath routing protocol for WMSNs for minimizing effect of compromising attacks. Journal of Network and Systems Management, 27(3), 573–599.
Jiang, D., Huo, L., & Li, Y. (2018). Fine-granularity inference and estimations to network traffic for SDN. PLoS ONE, 13(5), 1–23.
Zhu, J., Song, Y., Jiang, D., et al. (2018). A new deep-Q-learning-based transmission scheduling mechanism for the cognitive Internet of things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 5(4), 2375–2385.
Tian, R., & Zhu, H. (2019). Complex application identification and private network mining algorithm based on traffic-aware model in large-scale networks. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-019-00803-6.
Jiang, D., Wang, W., Shi, L., et al. (2018). A compressive sensing-based approach to end-to-end network traffic reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 5(3), 1–12.
Refregier, P., & Javidi, B. (1995). Optical image encryption based on input plane and Fourier plane random encoding. Optics Letters, 20, 767–769.
Li, X. W., Kim, S. T., & Wang, Q. H. (2017). Copyright protection for elemental image array by hypercomplex Fourier transform and an adaptive texturized holographic algorithm. Optics Express, 25, 17076–17091.
Nischal, N. K., Joseph, J., & Singh, K. (2004). Securing information using fractional Fourier transform in digital holography. Optics Communications, 235, 253–259.
Lee, I. H., & Cho, M. J. (2014). Double random phase encryption using orthogonal encoding for multiple-image transmission. Journal of the Optical Society of Korea, 18, 201–206.
Li, X. X., & Zhao, D. M. (2010). Optical color image encryption with redefined fractional Hartley transform. Optik, 121(7), 673–677.
Alfalou, A., & Brosseau, C. (2013). Implementing compression and encryption of phase shifting digital holograms for three-dimensional object reconstruction. Optics Communications, 307, 67–72.
Guo, Y., Huang, Q., Du, J., & Zhan, Y. (2018). Decomposition storage of information based on computer-generated hologram interference and its application in optical image encryption. Applied Optics, 40, 2860–2863.
Xi, S. X., Wang, X. L., Sun, X., et al. (2013). Three random phase encryption technology in the Fresnel diffraction system based on computer-generated hologram. Optical Engineering, 53(1), 011004.
Pan, W., Wun, W. W., & Zhang, X. L. (2009). Encryption algorithm of virtual optical based on computer-generated hologram and double random phase. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 36(s2), 312–317.
Wang, Y. Y., Wang, Y. R., Wang, Y., et al. (2007). Optical image encryption based on binary Fourier transform computer-generated hologram and pixel scrambling technology. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 45(7), 761–765.
Liu, J., Jin, H. Z., Ma, L. H., Li, Y., & Jin, W. M. (2013). Optical color image encryption based on computer generated hologram and chaotic theory. Optics Communications, 307, 76–79.
Wu, J. H., Luo, X. Z., Zhou, N. R., et al. (2013). Four-image encryption method based on spectrum truncation, chaos and the MODFrFT. Optics & Laser Technology, 45, 571–577.
Tricoles, G. (1987). Computer generated holograms: An historical review. Applied Optics, 26, 4351–4357.
Guan, Z. H., Huang, F. J., Guan, W. J., et al. (2005). Chaos-based image encryption algorithm. Physics Letters A, 346(1), 153–157.
Belazi, A., & Ellatif, A. A. (2017). A simple yet efficient S-box method based on chaotic sine map. Optik, 130, 1438–1444.
He, M. Z., Tan, Q. F., Cao, L. C., He, Q. S., & Jin, G. F. (2009). Security enhanced optical encryption system by random phase key and permutation key. Optics Express, 17, 22462–22473.
Smila, M., & Sankar, S. (2014). Novel algorithms for finding an optimal scanning path for JPEG image compression. IJETCSE, 8, 230–236.
Shen, J. J., & Ren, J. M. (2010). A robust associative watermarking technique based on vector quantization. Digital Signal Process, 20, 1408–1423.
Zhang, Y., & Xiao, D. (2013). Double optical image encryption using discrete Chirikov standard map and chaos-based fractional random transform. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 51, 472–480.
Akhshani, A., Behnia, S., Akhavan, A., et al. (2010). A novel scheme for image encryption based on 2D piecewise chaotic maps. Optics Communications, 283(17), 3259–3266.
Gonzalez, R. C., & Woods, R. E. (2007). Digital Image Processing (3rd ed.). New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Guo, C. L., Liu, S., & Sheridan, J. T. (2014). Optical double image encryption employing a pseudo image technique in the Fourier domain. Optics Communications, 321, 61–72.
Ping, P., Xu, F., Mao, Y. C., & Zj, Wang. (2018). Designing permutation–substitution image encryption networks with Henon map. Neurocomputing, 283, 53–63.
Zhang, J., Fang, D. X., & Ren, H. E. (2014). Image encryption algorithm based on DNA encoding and chaotic maps. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 917147, 1–10.
Acknowledgements
This work is partly supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No.2018A0303070009 and No. 2014A030310038), the Educational Commission of Guangdong Province (No. 2018KTSCX143 and No. 2015KTSCX089).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, C., Li, X., Xu, S. et al. Computer generated hologram-based image cryptosystem with multiple chaotic systems. Wireless Netw 27, 3507–3521 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-019-02223-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-019-02223-z