Abstract
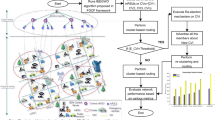
Vehicular ad-hoc networks (VANETs) suffer from dis-connectivity due to very high mobility, node sparseness, and lossy link. Thus, the broadcasting algorithms in the vehicular multi-hop scenario have to operate in all extreme scenarios as dense, sparse, and disconnected topologies that are changeable dynamically due to different traffic conditions. The store-and-carry-forward scheme for disconnected topologies with dynamic nodes can be model as a Steiner-tree problem due to link weight change dynamically. The Steiner tree has to be recomputed to obtain the new Steiner tree, making it more difficult for broadcasting algorithms in VANETs. We show that broadcasting in VANETs (i.e., given graph \(G(V_1, E_1)\) with the terminal set, \(T_1 \subseteq V1\)), modeled as to find as many (maximum) disjoint Steiner trees as possible that are disjoint on the non-terminal nodes and the edges are APX-hard even for small \(T_1\). If all the nodes in G are terminal nodes, i.e., \(T_1=V_1\), the trouble is finding a maximum cardinality set of edge-disjoint spanning trees and encountering a considerable lot of edge-disjoint spanning tree. We then propose an \(O(\log n)\)-Approximation Algorithm for Broadcasting in VANETs via bipartite graph (\(G=((T_1,V_1/T_1),E_1)\)) and using projection. We compared the performance of the proposed scheme (i.e., EASBVN) with existing state-of-the-scheme and found it to be better than the state-of-the-art schemes (i.e., DV-CAST, UVCAST, DPPEMB, MoZo, and MobiVNDN) in terms of end-to-end delay and re-healing time.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wisitpongphan, N., Bai, F., Mudalige, P., Sadekar, V., & Tonguz, O. K. (2007). Routing in sparse vehicular ad hoc wireless networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 25(8), 0733–8716.
Skordylis, A., & Trigoni, N. (2008). Delay-bounded routing in vehicular ad-hoc networks. In 9th ACM international symposium on mobile ad hoc networking and computing (pp. 341–350).
Jeong, J., Guo, S., Gu, Y., He, T., & Du, D. H. C. (2011). Trajectory-based data forwarding for light-traffic vehicular ad hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 22, 743–757.
Lin, Dan, Kang, Jian, Squicciarini, Anna, Yingjie, Wu, Gurung, Sashi, & Tonguz, Ozan. (2017). MoZo: A moving zone based routing protocol using pure V2V communication in VANETs. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 16(5), 1357–1370.
Daxin, T., Liu, C., Duan, X., Sheng, Z., Ni, Q., Chen, M., et al. (2018). A distributed position-based protocol for emergency messages broadcasting in vehicular ad hoc networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 5(2), 1218–1227.
Duarte, Joao M., Braun, Torsten, & Villas, Leandro A. (2018). MobiVNDN: A distributed framework to support mobility in vehicular named-data networking. Ad hoc Networks, 82, 77–90.
Hasan, K. F., Feng, Y., & Tian, Y.-C. (2018). GNSS time synchronization in vehicular ad-hoc networks: Benefits and feasibility. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 99, 1–10.
Chinnasamy, A., Sivakumar, B., & Selvakumari, P. (2018). Minimum connected dominating set based RSU allocation for smartCloud vehicles in VANET. Cluster Computing, 22, 1–10.
Ramakrishnan, B., Selvi, M., & Bhagavath Nishanth, R. (2017). An emergency message broadcasting technique using transmission power based clustering algorithm for vehicular ad hoc network. Wireless Personal Communications, 94(4), 3197–3216.
Viriyasitavat, W., Tonguz, O. K., & Bai, F. (2009). Network connectivity of VANETs in urban areas. In IEEE Secon 2009 proceedings (pp. 646–654).
Das, Debasis, Misra, Rajiv, & Raj, A. (2015). Approximating geographic routing using coverage tree heuristics for wireless network. Wireless Networks, 21(4), 1109–1118.
Zhao, J., & Cao, G. (2006). VADD: Vehicle -assistant data delivery in vehicular ad hoc networks. In Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM (pp. 1–12).
Li, F., & Wang, Y. (2007). Routing in vehicular ad hoc networks: A survey. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2(2), 12–22.
Durresi, M., Durresi, A., & Barolli, L. (2005). Emergency broadcast protocol for inter-vehicle communication. In ICPADS-05 (Vol. 2, pp. 402–406).
Korkmaz, G., Ekici, E., Ozguner, F., & Ozguner, U. (2004). Urban multi-hop broadcast protocol for inter-vehicle communication systems. In ACM VANET-04 (pp. 76–85).
Tonguz, O. K., Wisitpongphan, N., Bai, F., Mudalige, P., & Sadekar, V. (2007). Broadcasting in VANET. In Mobile networking for vehicular environments (pp. 7–12).
Viriyasitavat, W., Tonguz, O. K., & Bai, F. (2011). UV-CAST: An urban vehicular broadcast protocol, topics in automative networking and applications. IEEE Communications Magazine, 49(11), 116–124.
Wisitpongphan, N., Tonguz, O. K., Parikh, J. S., Mudalige, P., Bai, F., & Sadekar, V. (2007). Broadcast storm mitigation techniques in vehicular ad hoc networks. IEEE Wireless Communications, 14(6), 84–94.
Tonguz, O. K., Wisitpongphan, N., & Bai, F. (2010). DV-CAST: A distributed vehicular broadcast protocol for vehicular ad hoc networks. IEEE Wireless Communications, 17(2), 47–57.
Yi, C.-W., Chuang, Y.-T., Yeh, H.-H., Tseng, Y.-C., & Liu, P.-C. (2010). Streetcast: An urban broadcast protocol for vehicular ad-hoc networks. In 71st vehicular technology conference (VTC 2010-Spring) (pp. 1–5). IEEE
Slavik, M., & Mahgoub, I. (2010). Stochastic broadcast for VANET. In IEEE CCNC (pp. 1–5).
Tonguz, O. K., Wisitpongphan, N., Parikht, J. S., Bait, F., Mudaliget, P., & Sadekart, V. K. (2006). On the broadcast storm problem in ad hoc wireless networks. In 3rd International conference on broadband communications, networks and systems 2006, BROADNETS (pp. 1–11).
Gorain, B., & Mandal, P. S. (2014). Approximation algorithm for sweep coverage in wireless sensor networks. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 74, 2699–2707.
Chaqfeh, M., & Laka, A. (2016). A novel approach for scalable multi-hop data dissemination in vehicular ad hoc networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 37, Part 2, 228–239.
Dua, A., Kumar, N., & Bawa, S. (2016). ReIDD: Reliability-aware intelligent data dissemination protocol for broadcast storm problem in vehicular ad hoc networks. Telecommunication Systems, 64, 1018–4864.
Panda, B. S., & Pushparaj Sheety, D. (2013). Strong minimum energy 2-hop rooted topology for hierarchical wireless sensor networks. Journal of Combinatorial Optimization, 30, 1077–1094.
Nossack, J., & Pesch, E. (2014). A branch-and-bound algorithm for the acyclic partitioning problem. Journal of Computers and Operation Research, 41, 174–184.
Ayaida, M., Barhoumi, M., Fouchal, H., Ghamri Doudane, Y., & Afilal, L. (2014). Joint routing and location-based service in VANETs. Journal of of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 74, 2077–2087.
Feldmann, A. E., & Foschini, L. (2013). Balanced partitions of trees and applications. Algorithmica,. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00453-013-9802-3.
Stanton, I., & Kliot G. (2012). Streaming graph partitioning for large distributed graphs. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, ACM KDD (pp. 1222–1230).
Dutta, P., Jaiswal, S., & Rastogi, R. (2007). Routing and channel allocation in rural wireless mesh networks. In 26th IEEE international conference on computer communications. IEEE INFOCOM (pp. 598–606).
Even, G., Naor, J., Rao, Satish B., & Schieber, B. (1999). Fast approximate graph partitioning algorithms. SIAM Journal on Computing, 28(6), 2187–2214.
Brazil, M., Ras, C. J., Swanepoel, K. J., & Thomas, D. A. (2013). Generalised k-Steiner tree problems in normed planes. Algorithmica, 71, 66–86.
Brazil, Marcus, Ras, Charl J., & Thomas, Doreen A. (2012). The bottleneck 2-connected k-Steiner network problem for \(k \le 2\). Discrete Applied Mathematics, 160, 1028–1038.
Aazami, A., Cheriyan, J., & Jampani, K. R. (2012). Approximation algorithms and hardness results for packing element-disjoint Steiner trees in planar graphs. Algorithmica, 63, 425–456.
Calinescu, G., Chekuri, C., & Vondrak, J. (2009). Disjoint bases in a polymatroid. Random Structures and Algorithms, 35(4), 418–430.
Cheriyan, J., & Salavatipour, M. R. (2006). Hardness and approximation results for packing Steiner tree. Algorithmica, 45(1), 21–43.
Cheriyan, J., & Salavatipour, M. R. (2007). Packing element-disjoint Steiner trees. ACM Transactions on Algorithms, 34(4), 47.
West, D. B., & Wu, H. (2012). Packing of Steiner trees and S-connectors in graphs. Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B, 102, 186–205.
Allali, O., Magnien, C., Latapy, M. (2009). Link prediction in bipartite graphs using internal links and weighted projection.
Kriesell, M. (2003). Edge-disjoint trees containing some given vertices in a graph. Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B, 88, 53–65.
Hoshika, D., & Miyano, E. (2014). Approximation algorithms for packing element-disjoint Steiner trees on bounded terminal nodes. In AAIM 2014. LNCS (Vol. 8546, pp. 100–111).
Acknowledgements
This research work is fully supported by Early Career Research Award (ECRA) from Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Dept. of Science and Technology (DST), Govt. of India, Delhi, India (Project \(\#\) : ECRA/2015/000256/Engineering Science).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, D., Misra, R. EASBVN: efficient approximation scheme for broadcasting in vehicular networks. Wireless Netw 27, 339–349 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-020-02455-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-020-02455-4