Abstract
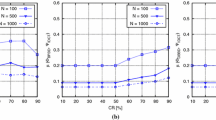
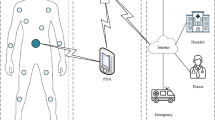
Biomedical sensor networks find wide applications in human health monitoring. In such applications, routing strategies in the sensor nodes play a key role towards energy efficiency of the overall system. In this work, we present a new data routing scheme, which is based on residual energy in a node and equalization (named EEQ) among the neighbours to achieve enhanced average node lifetime under short range monitoring scenario. The scheme was hardware implemented using 12 number of indigenous ATmega328 based static biomedical sensor nodes (BSN) arranged in a grid matrix spread over a floor area of 564 sqm. The objective was to collect short duration electrocardiogram and photoplethysmogram signals from human subjects in a local supervisory computer placed outside the grid. Under simulation platform using 100 BSNs with first order radio model, it was found that the average node lifetime was enhanced by 17% against without EEQ evaluated over 10,000 consecutive data collection sessions. The proposed scheme can be useful for providing low cost solution in healthcare settings in developing nations like India.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang, D., Huo, L., Lv, Z., Song, H., & Qin, W. (2018). A joint multi-criteria utility-based network selection approach for vehicle-to-infrastructure networking. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 19, 3305–3319. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2017.2778939.
Jiang, D., Zhang, P., Lv, Z., & Song, H. (2016). Energy-efficient multi-constraint routing algorithm with load balancing for smart city applications. IEEE Internet Things Journal, 3, 1437–1447. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2016.2613111.
Jiang, D., Wang, Y., Lv, Z., Qi, S., & Singh, S. (2020). Big data analysis based network behavior insight of cellular networks for industry 4.0 applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 16, 1310–1320. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2019.2930226.
Qi, S., Jiang, D., & Huo, L. (2019). A prediction approach to end-to-end traffic in space information networks. Mobile Networks and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-019-01424-2.
Jiang, D., Li, W., & Lv, H. (2017). An energy-efficient cooperative multicast routing in multi-hop wireless networks for smart medical applications. Neurocomputing, 220, 160–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.07.056.
Alemdar, H., & Ersoy, C. (2010). Wireless sensor networks for healthcare: A survey. Computer Networks, 54, 2688–2710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2010.05.003.
Lee, H. J., Lee, S. H., Ha, K. S., Jang, H. C., Chung, W. Y., Kim, J. Y., et al. (2009). Ubiquitous healthcare service using Zigbee and mobile phone for elderly patients. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 78, 193–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2008.07.005.
Xu, X., Wu, M., Ding, C., Sun, B., & Zhang, J. (2010). Outdoor wireless healthcare monitoring system for hospital patients based on ZigBee. In Proceedings of the 2010 5th IEEE conference on industrial electronics and applications, ICIEA 2010. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIEA.2010.5517084.
Sahandi, R., Noroozi, S., Roushan, G., Heaslip, V., & Liu, Y. (2010). Wireless technology in the evolution of patient monitoring on general hospital wards. Journal of Medical Engineering & Technology. https://doi.org/10.3109/03091900903336902.
Fernández-López, H., Macedo, P., Afonso, J. A., Correia, J. H., & Simões, R. (2010). Evaluation of the impact of the topology and hidden nodes in the performance of a ZigBee network. In Lecture notes of the institute for computer sciences, social-informatics and telecommunications engineering (pp. 256–271). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-11528-8_18.
Kim, Y. H., Lim, I. K., Lee, J. P., Lee, J. G., & Lee, J. K. (2013). Study on low-power transmission protocols for ZigBee wireless network-based remote biosignal monitoring systems. In Lecture notes in electrical engineering (pp. 709–716). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5857-5_76.
Fernández-López, H., Correia, J. H., Simões, R., & Afonso, J. A. (2011). Experimental evaluation of IEEE 802.15.4/ZigBee for multi-patient ECG monitoring. In Lecture notes of the institute for computer sciences, social-informatics and telecommunications engineering (pp. 184–191) (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-23635-8_23.
Wu, M., & Xie, Q. (2012). The design of wireless medical monitoring network based on ZigBee. In NCIS 2012: Network computing and information security (pp. 705–713). Berlin: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-35211-9_89.
Wu, M., Zhou, W., & Hou, H. (2012). Design and application of ZiGbee locating and transparent transmission serial port module for tele-health monitoring. Communications in Computer and Information Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-35211-9_90.
Magno, M., Spagnol, C., Benini, L., & Popovici, E. (2014). A low power wireless node for contact and contactless heart monitoring. Microelectronics Journal, 45, 1656–1664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2014.07.002.
Yseboodt, L., De Nil, M., Huisken, J., Berekovic, M., Zhao, Q., Bouwens, F., et al. (2009). Design of 100 μw wireless sensor nodes for biomedical monitoring. Journal of Signal Processing Systems, 57, 107–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-008-0255-x.
Wang, L. H., Chen, T. Y., Lin, K. H., Fang, Q., & Lee, S. Y. (2015). Implementation of a wireless ECG acquisition SoC for IEEE 802.15.4 (ZigBee) applications. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 19, 247–255. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2014.2311232.
Gajjar, S., Sarkar, M., & Dasgupta, K. (2014). Self organized, flexible, latency and energy efficient protocol for wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Wireless Information Networks, 21, 290–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10776-014-0251-y.
Jiang, D., Wang, Y., Zhihan, L., Wang, W., & Wang, H. (2020). An energy-efficient networking approach in cloud services for IIoT networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 38, 928–941. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2020.2980919.
Wang, Y., Jiang, D., Huo, L., & Zhao, Y. (2019). A new traffic prediction algorithm to software defined networking. Mobile Networks and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-019-01423-3.
Zhang, H., & Shen, H. (2010). Energy-efficient beaconless geographic routing in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 21, 881–896. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPDS.2009.98.
Huang, H., Hu, G., Yu, F., & Zhang, Z. (2011). Energy-aware interference-sensitive geographic routing in wireless sensor networks. IET Communications, 5, 2692–2702.
Yuce, M. R., Ng, P. C., & Khan, J. Y. (2008). Monitoring of physiological parameters from multiple patients using wireless sensor network. Journal of Medical Systems, 32, 433–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-008-9149-5.
Abreu, C., Ricardo, M., & Mendes, P. M. (2014). Energy-aware routing for biomedical wireless sensor networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 40, 270–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2013.09.015.
Yadav, S., & Yadav, R. S. (2016). A review on energy efficient protocols in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 22, 335–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-1025-x.
Qin, D., Ji, P., Yang, S., & Berhane, T. M. (2019). An efficient data collection and load balance algorithm in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 25, 3703–3714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-017-1652-5.
Effatparvar, M., Dehghan, M., & Rahmani, A. M. (2016). A comprehensive survey of energy-aware routing protocols in wireless body area sensor networks. Journal of Medical Systems. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-016-0556-8.
Marinković, S. J., Popovici, E. M., Spagnol, C., Faul, S., & Marnane, W. P. (2009). Energy-efficient low duty cycle MAC protocol fo wireless body area networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 13, 915–925. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITB.2009.2033591.
Chen, S. L., Lee, H. Y., Chen, C. A., Huang, H. Y., & Luo, C. H. (2009). Wireless body sensor network with adaptive low-power design for biometrics and healthcare applications. IEEE Systems Journal, 3, 398–409. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2009.2032440.
Bouachir, O., Ben Mnaouer, A., & Touati, F. (2016). PEAM: A polymorphic, energy-aware MAC protocol for WBAN. In 2016 23rd international conference on telecommunications, ICT 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICT.2016.7500491.
Pérez-Solano, J. J., & Felici-Castell, S. (2017). Improving time synchronization in wireless sensor networks using Bayesian inference. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 82, 47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2017.01.007.
Chen, B., & Pompili, D. (2011). Transmission of patient vital signs using wireless body area networks. Mobile Networks and Applications, 16, 663–682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-010-0253-7.
Khan, Z., Aslam, N., Sivakumar, S., & Phillips, W. (2012). Energy-aware peering routing protocol for indoor hospital body area network communication. Procedia Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2012.06.027.
Khan, Z. A., Sivakumar, S., Phillips, W., & Robertson, B. (2013). A QoS-aware routing protocol for reliability sensitive data in hospital body area networks. Procedia Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2013.06.027.
Kulshrestha, J., & Mishra, M. K. (2017). An adaptive energy balanced and energy efficient approach for data gathering in wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 54, 130–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2016.10.013.
Lipare, A., Edla, D. R., & Kuppili, V. (2019). Energy efficient load balancing approach for avoiding energy hole problem in WSN using Grey Wolf Optimizer with novel fitness function. Soft Computer Journal Applications. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105706.
Mohemed, R. E., Saleh, A. I., Abdelrazzak, M., & Samra, A. S. (2017). Energy-efficient routing protocols for solving energy hole problem in wireless sensor networks. Computer Networks, 114, 51–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2016.12.011.
Nilsaz Dezfouli, N., & Barati, H. (2020). A distributed energy-efficient approach for hole repair in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 26, 1839–1855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1867-0.
Qureshi, K. N., Din, S., Jeon, G., & Piccialli, F. (2020). Link quality and energy utilization based preferable next hop selection routing for wireless body area networks. Computer Communications, 149, 382–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2019.10.030.
Gupta, R., Bera, J. N., & Mitra, M. (2012). An intelligent telecardiology system for offline wireless transmission and remote analysis of ECG. Journal of Medical Engineering & Technology, 36, 358–365. https://doi.org/10.3109/03091902.2012.712200.
Chandra, S., Gupta, R., Ghosh, S., & Mondal, S. (2019). An intelligent and power efficient biomedical sensor node for wireless cardiovascular health monitoring. IETE Journal Research. https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2019.1611489.
Ds_Xbee Multipoint Modules Datasheet, https://www.digi.com/pdf/ds_xbeemultipointmodules.pdf.
AD8232 front end. http://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/AD8232.pdf.
Easy Pulse PPG sensor. http://embedded-lab.com/blog/easy-pulse-version-1-1-sensor-overview-part-2/.
Bera, P., & Gupta, R. (2016). Real-time compression of electrocardiogram using dynamic bit allocation strategy. In 2016 IEEE 1st international conference on control, measurement and instrumentation (CMI 2016) (pp. 21–25). https://doi.org/10.1109/CMI.2016.7413703.
Acknowledgements
The work is funded by Department of Higher Education, Science & Technology and Biotechnology (DHESTB), Govt. of West Bengal [sanction No.851(sanc.)/ST/P/S&T/6G-2/2013 dtd: 11/01/2016]. The authors sincerely thank Dr. Arunansu Talukdar, Professor in Medicine Department, Medical College and Hospital, Kolkata for his cooperation in performance testing of the BSNs in the hospital ward. The Authors also thank the SAP DRS-II program (2015-2020) from University Grants Commission (UGC) at Department of Applied Physics, University of Calcutta for the technical support. Soumyak Chandra also acknowledges the Centre of Excellence for Systems Biology & Biomedical Engineering, University of Calcutta for the SRA fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandra, S., Chandra, A. & Gupta, R. An efficient data routing scheme for multi-patient monitoring in a biomedical sensor network through energy equalization strategy. Wireless Netw 27, 635–648 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-020-02472-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-020-02472-3