Abstract
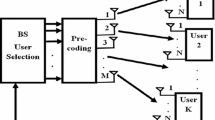
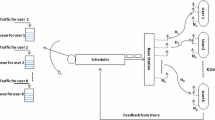
In this paper, we propose a scheduling algorithm that reduces the feedback load with no penalty loss in the spectral efficiency when compared to the optimal selective diversity scheme (Harthi et al. in IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 6(1), 2007). In order to reduce the feedback rate, a two stage probing technique is introduced. In the first stage, the scheduler estimates the threshold level in which the best user is likely to be found. In the second stage, the scheduler permits two users to contend for a mini-slot using only one bit of feedback information per user. After deriving closed-form expressions for the feedback load, we compare the performance of our algorithm with the discrete rate switch-based multiuser diversity (DSMUDiv) scheme (Harthi et al. in IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 6(1), 2007) and the optimal selective diversity scheme. Numerical results show that our scheme further reduces the feedback load, rate and guard time when compared to both the DSMUDiv and the optimal selective diversity schemes under slow Rayleigh fading assumption.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Viswanath P., Tse D. and Laroia R. (2002). Opportunistic beamforming using dumb antennas. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 48: 1277–1294
Catreux S., Erceg V., Gesbert D. and Heath R. (2002). Adaptive modulation and MIMO coding for broadband wireless datanetworks. IEEE Communication Magazine 40(6): 108–115
Gesbert, D., & Slim-Alouini, M. (2004). How much feedback is multi-user diversity really worth? In Proceedings of IEEE international communication conference (ICC’04) (pp. 234–238). Paris, France.
Hassel V., Alouini M.-S., Øien G. and Gesbert D. (2006). Rate-optimal multiuser scheduling with reduced feedback load and analysis of delay effects. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking 2006(26424): 7
Hassel, V., Alouni, M., Gesbert, D., & Øien, G. (2005). Exploiting multi user diversity using multiple feedback thresholds. In IEEE proceedings on wireless communications (Vol. 9, no. 5).
Florén, F., Edfors, O., & Molin, B.-A. (2003). The effect of feedback quantization on the throughput of a multiuser diversity scheme. In Proceedings of IEEE GLOBECOM (Vol. 1, pp. 497–501). San Francisco, CA.
Sanayei, S., & Nosratinia, A. (2005). Exploiting multiuser diversity with 1-bit feedback. In Proceedings of IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC’05) (pp. 978–983). New Orleans, LA.
Xue Y. and Kaiser T. (2007). Exploiting multiuser diversity with imperfect one-bit channel state feedback. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 56(1): 183–193
Al-Harthi Y., Tewfik A. and Alouini M. (2007). Multiuser diversity with quantized feedback. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 6(1): 330–337
Qin, X., & Berry, R. (2004). Opportunistic splitting algorithms for wireless networks with heterogeneous users. In Proceedings of the 38th conference on information sciences and systems (CISS ’04). Princeton, NJ, USA.
Patil S. and Veciana G. (2007). Reducing feedback for opportunistic scheduling in wireless systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 6(12): 4227–4232
Park Y., Park D. and Love D. (2007). On scheduling for multiple-antenna wireless networks using contention-based feedback. IEEE Transactions on Communications 55(6): 1174–1190
Hwang C.-S. and Cioffi J. M. (2008). Achieving multi-user diversity gain using user identity feedback. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 7(8): 2911–2916
Koubaa, H., Hassel, V., & Øien, G. E. (2005). Multiuser diversity gain enhancement by guard time reduction. In IEEE workshop on signal processing advances in wireless communications (SPAWC). New York, NY, USA.
Koubaa, H., Hassel, V., & Øien, G. E. (2005). Contention-less feedback for multi-user diversity scheduling. In Proceedings of IEEE VTC Fall 2005. Dallas, Texas, USA.
IEEE Standards Department. (1999). IEEE Std. 802.11. paert 11: Wireless Lan medium access control(MAC) and physical layer (PHY) specifications. Technical Report, IEEE, NJ.
Hassel, V. (2007). Design issuses and performance analysis for opportunistic scheduling algorithms in wireless networks. PhD. Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eltayeb, M.E., Al-Harthi, Y.S. Multiuser Diversity with Binary Feedback. Wireless Pers Commun 58, 669–680 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-009-9900-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-009-9900-3