Abstract
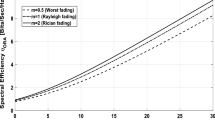
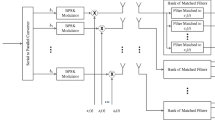
It is well known that power control error (PCE) is a critical issue in CDMA cellular systems. In this paper, the bit error rate (BER) of a direct sequence-code division multiple access (DS-CDMA) receiver with imperfect power control, adaptive beamforming, and voice activity is derived in frequency-selective Nakagami fading channels. We discuss the effects of PCE, Nakagami-m fading parameter, and channel’s multipath intensity profile as average signal strength and rate of average power decay and their effects on the BER performance of DS-CDMA cellular systems. In this paper, the RAKE receiver consists of three stages. In the first stage, with conjugate gradient adaptive beamforming algorithm, the desired users’ signal in an arbitrary path is passed and the inter-path interference is canceled in other paths in each RAKE finger. Also in this stage, the multiple access interference (MAI) from other users is reduced. Thus, the matched filter (MF) can be used for the MAI reduction in each RAKE finger in the second stage. In the third stage, the output signals from the MFs are combined according to the conventional maximal ratio combining principle and then are fed into the decision circuit for the desired user. How the Nakagami fading parameters, power control imperfections, or the number of resolvable paths affect the reverse link capacity of the system is discussed in detail. Analytical and simulation results are also given for systems with different processing gains and number of BSs in the cell-selection process with various Nakagami fading parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gejji R. R. (1992) Forward-link-power control in CDMA cellular systems. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 41(4): 532–536
Abrardo A., Sennati D. (2000) On the analytical evaluation of closed-loop power-control error statistics in DS-CDMA cellular systems. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 49(6): 2071–2080
Carrasco L., Femenias G. (2008) Reverse link performance of a DS-CDMA system with both fast and slow power controlled users. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 7(4): 1255–1263
Femenias G., Carrasco L. (2006) Effect of slow power control error on the reverse link of OSTBC DS-CDMA in a cellular system with Nakagami frequency-selective MIMO fading. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 55(6): 1927–1934
Qian L., Gajic Z. (2006) Variance minimization stochastic power control in CDMA system. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 5(1): 193–202
Rintamaki M., Koivo H., Hartimo I. (2004) Adaptive closed-loop power control algorithms for CDMA cellular communication systems. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 53(6): 1756–1768
Wang J., Yu A. (2001) Open-loop power control error in cellular CDMA overlay systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 19(7): 1246–1254
Tam W.-M., Lau F. C. M. (1999) Analysis of power control and its imperfections in CDMA cellular systems. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 48(5): 1706–1717
Newson P., Heath M. R. (1994) The capacity of a spread spectrum CDMA system for cellular mobile radio with consideration of system imperfections. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 12(4): 673–684
Romero-Jerez J. M., Tellez-Labao C., Diaz-Estrella A. (2004) Effect of power control imperfections on the reverse link of cellular CDMA networks under multipath fading. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 53(1): 61–71
Jansen M. G., Prasad R. (1995) Capacity, throughput, and delay analysis of a cellular DS CDMA system with imperfect power control and imperfect sectorization. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 44(1): 67–74
Wang J. T. (2009) Admission control with distributed joint diversity and power control for wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 58(1): 409–419
Kumatani K., McDonough J., Rauch B., Klakow D., Garner P. N., Li W. (2009) Beamforming with a maximum negentropy criterion. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing 17(5): 994–1008
Zhang R., Chai C. C., Liang Y. (2009) Joint beamforming and power control for multiantenna relay broadcast channel with QoS constraints. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 57(2): 726–737
Chang J., Tassiulas L., Rashid-Farrokhi F. (2002) Joint transmitter receiver diversity for efficient space division multiaccess. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 1(1): 16–27
Abrardo A. (2003) Noncoherent MLSE in DS-CDMA wireless systems with antenna arrays. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 52(6): 1435–1446
Yang L.-L., Fang W. (2009) Performance of distributed-antenna DS-CDMA systems over composite lognormal shadowing and Nakagami-m-fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 58(6): 2872–2883
Cai Y., de Lamare R. C. (2009) Space-time adaptive MMSE multiuser decision feedback detectors with multiple-feedback interference cancellation for CDMA systems. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 58(8): 4129–4140
Abdel-Samad A., Davidson T. N., Gershman A. B. (2006) Robust transmit eigen beamforming based on imperfect channel state information. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 54(5): 1596–1609
Wang J., Payaro M. (2010) On the robustness of transmit beamforming. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 58(11): 5933–5938
Nai S. E., Ser W., Yu Z. L., Rahardja S. (2009) A robust adaptive beamforming framework with beampattern shaping constraints. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 57(7): 2198–2203
El-Keyi A., Champagne B. (2010) Adaptive linearly constrained minimum variance beamforming for multiuser cooperative relaying using kalman filter. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 9(2): 641–651
Lorenz R. G., Boyd S. P. (2005) Robust minimum variance beamforming. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 53(5): 1684–1696
Lawrence D. E. (2010) Low probability of intercept antenna array beamforming. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 58(9): 2858–2865
Park S.-H., Lee H., Lee S.-R., Lee I. (2009) A new beamforming structure based on transmit-MRC for closed-loop MIMO systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications 57(6): 1847–1856
Dosaranian-Moghadam, M., Bakhshi, H., & Dadashzadeh, G. (2011). Reverse link performance of DS-CDMA cellular systems through closed-loop power control, base station, and antenna arrays in 2D urban environment. Wireless Personal Communications. doi:10.1007/s11277-011-0250-6.
Efthymoglou G. P., Aalo V. A., Helmken H. (1997) Performance analysis of coherent DS-CDMA systems in a Nakagami fading channel with arbitrary parameters. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 46(2): 289–297
Rashid-Farrokhi F., Ray-Liu K. J., Tassiulas L. (1998) Transmit beamforming and power control for cellular systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 16(8): 1437–1450
Mohamed N. A., Dunham J. G. (2002) A low-complexity combined antenna array and interference cancellation DS-CDMA receiver in multipath fading channels. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 20(2): 248–256
Mohamed, N. A., & Dunham, J. G. (1999). Adaptive beamforming for DS-CDMA using conjugate gradient algorithm in a multipath fading channel. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE emerging technologies symposium, Dallas, TX (pp. 859–863)
Dosaranian-Moghadam, M., Bakhshi, H., & Dadashzadeh, G. (2010). Interference management for DS-CDMA receiver through base station assignment in multipath fading channels. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE international conference on wireless communications, networking and information security, Beijing, China (pp. 257–263). June 2010.
Dosaranian-Moghadam, M., Bakhshi, H., & Dadashzadeh, G., (2010). Adaptive beamforming method based on closed-loop power control for DS-CDMA receiver in multipath fading channel. In 21st annual IEEE international symposium on personal, indoor, and mobile radio communications, Istanbul, Turkey (pp. 2087–2092). 26–30 September, 2010.
Litva J., Kwok-Yeung T. (1996) Digital beamforming in wireless communications. Artech House, Boston, London
Gradshteyn I. S., Ryzhik I. M. (1996) Table of integrals, series, and products. Academic, San Diego, CA
Alouini M.-S., Abdi A., Kaveh M. (2001) Sum of gamma variates and performance of wireless communication systems over Nakagami-fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 50(6): 1471–1480
Lei X., Fan P. (2010) On the error performance of M-ary modulation schemes on Rician-Nakagami fading channels. Wireless Personal Communications 53(4): 591–602
Chen J.I.-Z. (2005) Performance evaluation of multiple-cell DS-CDMA systems over correlated Nakagami-m fading environments. Wireless Personal Communications 33(1): 21–34
Oh S. W., Li K. H. (2001) Performance evaluation for forward-link cellular DS-CDMA over frequency-selective Nakagami multipath fading channels. Wireless Personal Communications 18(3): 275–287
Peterson R. L., Ziemer R. E., Borth D. E. (1995) Spread-spectrum communications. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Kong N., Milstein L. B. (1999) Average SNR of a generalized diversity selection combining scheme. IEEE Communications Letters 3(3): 57–59
Holtzman J. M. (1992) A simple, accurate method to calculate spread-spectrum multiple-access error probabilities. IEEE Transactions on Communications 40(3): 461–464
Dosaranian-Moghadam M., Bakhshi H., Dadashzadeh G. (2010) Interference management for DS-CDMA systems through closed-loop power control, base station assignment, and beamforming. Journal of Wireless Sensor Network 2(6): 472–482
Dosaranian-Moghadam, M., Bakhshi, H., Dadashzadeh, G., & Godarzvand-Chegini, M. (2010). Joint base station assignment, power control error, and adaptive beamforming for DS-CDMA cellular systems in multipath fading channels. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE global mobile congress, Shanghai, China (pp. 1–7). 18–19 October, 2010.
Dosaranian-Moghadam, M., Bakhshi, H., & Dadashzadeh, G. (2010). Joint constrained LMS algorithm and base station assignment for DS-CDMA receiver in multipath fading channels. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE wireless communications, networking and mobile computing, Chengdu, China (pp. 1–7). 23–25 September, 2010.
Liberti J. C., Rappaport T. S. (1999) Smart antennas for wireless communications IS-95 and third generation CDMA applications. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Sun, X. Y., Lian, X. H., & Zhou, J. J. (2008). Robust adaptive beamforming based on maximum likelihood estimation. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE international conference on microwave and millimeter wave technology, Nanjing, China (Vol. 3, pp. 1137–1140). 21–24 April, 2008.
Dosaranian-Moghadam, M., Bakhshi, H., Dadashzadeh, G., & Rahmati, P. (2009). Adaptive beamforming method based on constrained LMS algorithm for tracking mobile user. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE global mobile congress, Shanghai, China (pp. 1–6). October 2009.
Gotsis K. A., Siakavara K., Sahalos J. N. (2009) On the direction of arrival (DoA) estimation for a switched-beam antenna system using neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 57(5): 1399–1411
Dosaranian-Moghadam M., Bakhshi H., Dadashzadeh G. (2010) Joint centralized power control and cell sectoring for interference management in CDMA cellular systems in a 2D urban environment. Journal of Wireless Sensor Network 2(8): 599–605
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dosaranian-Moghadam, M., Bakhshi, H. & Dadashzadeh, G. Effects of Nakagami-Fading Parameters and Power Control Error on Performance of DS-CDMA Cellular Systems with Adaptive Beamforming. Wireless Pers Commun 68, 1197–1223 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0504-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0504-y