Abstract
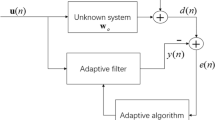
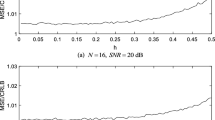
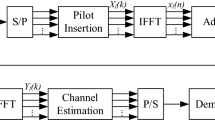
Frequency-domain equalization (FDE) is an effective technique that exhibits the property of relatively low complexity which grows with increasing the number of symbols of dispersion in multipath propagation environments for broadband wireless communications compared with the conventional time-domain equalization. However, in practical broadband wireless communications, there exists not only multipath but also narrowband interference (NBI). The conventional FDE methods do not consider NBI and their performance degrades obviously in such case. In this paper, we propose a new optimization criterion which can effectively suppress NBI to obtain the maximum decision signal-to-noise ratio. The proposed scheme employs a conventional adaptive algorithm such as least-mean-square or recursive-least-square and operates in the spatial-frequency domain, which is concerned with the use of FDE and space diversity within block transmission schemes jointly. The simulation results show that the proposed schemes have better error-rate performance with low complexity and can be used even in the presence of strong NBI, compared to other existing adaptive FDE algorithms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wc J. Jr. (1974) Microwave mobile communications. Wiley, New York
Proakis J. G. (1983) Digital communications. McGraw-Hill, New York
Falconer D., Ariyavisitakul S. L., Benyamin-Seeyar A., Eidson B. (2002) Frequency domain equalization for single-carrier broadband wireless systems. IEEE Communications Magazine 40: 58–66
Clark M. V. (1998) Adaptive frequency-domain equalization and diversity combining for broadband wireless communications. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 16: 1385–1395
Gusmao A., Dinis R., Esteves N. (2003) On frequency-domain equalization and diversity combining for broadband wireless communications. IEEE Transactions on Communications 51: 1029–1033
Benvenuto N., Dinis R., Falconer D., Tomasin S. (2010) Single carrier modulation with nonlinear frequency domain equalization: An idea whose time has come-again. Proceedings of the IEEE 98: 69–96
Liang L., Yong Liang G., Guoan B., Dingrong S. (2011) Effect of carrier frequency offset on single-carrier CDMA with frequency-domain equalization. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 60: 174–184
Chao Z., Zhaocheng W., Changyong P., Sheng C., Hanzo L. (2011) Low-complexity iterative frequency domain decision feedback equalization. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 60: 1295–1301
Chan-Ho C., Gi-Hong I. (2010) Bit-interleaved coded multilevel modulation for single-carrier frequency-domain equalization. IEEE Communications Letters 14: 193–195
Sari, H., Karam, G., & Jeanclaud, I. (1994). Frequency-domain equalization of mobile radio and terrestrial broadcast channels. In Global telecommunications conference, 1994. GLOBECOM ’94. ’Communications: The global bridge’, IEEE, (Vol. 1, pp. 1–5).
Czylwik, A. (1997). Comparison between adaptive OFDM and single carrier modulation with frequency domain equalization. In IEEE 47th Vehicular technology conference, 1997, (Vol. 2, pp. 865–869).
Kadel, G. (1997). Diversity and equalization in frequency domain a robust and flexible receiver technology for broadband mobile communication systems. In IEEE 47th Vehicular technology conference, 1997, (Vol. 2, pp. 894–898).
Morelli M., Sanguinetti L., Mengali U. (2005) Channel estimation for adaptive frequency-domain equalization. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 4: 2508–2518
Poor H. V. (2001) Active interference suppression in CDMA overlay systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 19: 4–20
Haykin S. (1988) Digital communications. Wiley, New York, NY, USA
Jiangzhou W., Wong Tat T. (2006) Narrowband interference suppression in time-hopping impulse radio ultra-wideband communications. IEEE Transactions on Communications 54: 1057–1067
Yu Z., Letaief K. B. (2006) Single carrier frequency domain equalization with time domain noise prediction for wideband wireless communications. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 5: 3548–3557
Qureshi S. U. H. (1985) Adaptive equalization. Proceedings of the IEEE 73: 1349–1387
Clark M. V., Greenstein L. J., Kennedy W. K., Shafi M. (1994) Optimum linear diversity receivers for mobile communications. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 43: 47–56
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, N., Wang, H. & Lin, X. Adaptive Frequency-Domain Equalization with Narrowband Interference Suppression. Wireless Pers Commun 70, 267–281 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0693-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0693-4