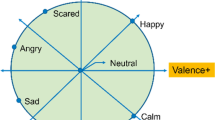
Abstract
Recently user quality of experience (QoE) is employed in evaluating end user satisfaction in communications systems. Generally, current approaches for QoE assessment are obtrusive, laboratory based and offline. Estimation of user satisfaction in static manner based on mean opinion score is not directly related to instantaneous individual end user contentment. In this paper, based on correlations between user’s physiological signals and her/his feelings about the service quality, a non-intrusive and user centric QoE assessment system for voice communications is developed. The findings of this study indicate that the emotional patterns in response to the changes in channel quality can be adapted to estimate the level of satisfaction in a QoE assessment system in a live manner. Based on experimental results, two categories of users are identified: sensitive and insensitive towards quality degradations. The results indicate that for the sensitive users, our non-intrusive subjective quality assessment method outperforms ITU-T P.563 standard with respect to root mean square error; while, the results are much better among the insensitive users.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Survey, A. G. C. (2012). Are your consumers on the speedway or stuck in the slow lane? Accenture global consumer survey report. Accenture.
Schatz, R., Hoßfeld, T., Janowski, L., & Egger, S. (2013). From packets to people: Quality of experience as a new measurement challenge. In Data traffic monitoring and analysis. Springer, Berlin (pp. 219–263).
Chikkerur, S., Sundaram, V., Reisslein, M., & Karam, L. J. (2011). Objective video quality assessment methods: A classification, review, and performance comparison. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 57(2), 165–182.
Brooks, P., & Hestnes, B. (2010). User measures of quality of experience: Why being objective and quantitative is important. Network, IEEE, 24(2), 8–13.
Fiedler, M., Hossfeld, T., & Phuoc, T.-G. (2010). A generic quantitative relationship between quality of experience and quality of service. Network, IEEE, 24(2), 36–41.
Moller, S., Engelbrecht, K. P., Kuhnel, C., Wechsung, I., & Weiss, B. (2009). A taxonomy of quality of service and quality of experience of multimodal human-machine interaction. In Quality of multimedia experience, 2009. QoMEx 2009. International workshop on, 29–31 July 2009 (pp. 7–12).
Agboma, F., & Liotta, A. (2008). QoE-aware QoS management. In Proceedings of the 6th international conference on advances in mobile computing and multimedia, 2008 (pp. 111–116). ACM, New York
Stankiewicz, R., & Jajszczyk, A. (2011). A survey of QoE assurance in converged networks. Computer Networks, 55(7), 1459–1473.
Song, W., Tjondronegoro, D. W., & Docherty, M. (2012). Understanding user experience of mobile video: Framework, measurement, and optimization. In D. W. Tjondronegoro (Ed.), Mobile Multimedia: User and Technology Perspectives (pp. 3–30). InTech Open Access Publisher.
De Pessemier, T., De Moor, K., Joseph, W., De Marez, L., & Martens, L. (2013). Quantifying the influence of rebuffering interruptions on the user’s quality of experience during mobile video watching. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 59(1), 47–61. doi:10.1109/tbc.2012.2220231.
Kuan-Ta, C., Cheng-Chun, T., & Wei-Cheng, X. (2009). OneClick: A framework for measuring network quality of experience. In INFOCOM 2009, IEEE, 19–25 April 2009 (pp. 702–710).
Recommendation, I. (1994). E. 800: Terms and definitions related to quality of service and network performance including dependability. ITU-T August 1994.
ITU-T (2008). Recommendation ITU-T P.10/G.100, Amendment 2, “New definitions for inclusion in Recommendation ITU-T P.10/G.100”. International Telecommunication Union.
Le Callet, P., Möller, S., & Perkis, A. (2012). Qualinet white paper on definitions of quality of experience (2012). European network on quality of experience in multimedia systems and services (COST Action IC 1003),(Version 1.1) Published online by COST Action IC 2003.
ITU-T (2006). Recommendation P.10/G.100, “Vocabulary for performance and quality of service”. International Telecommunication Union.
ITU-T (1996). Recommendation P.800, methods for subjective determination of transmission quality. International Telecommunication Union-Telecommunication Standardisation Sector (ITU-T).
Quan, H.-T., Garcia, M. N., Speranza, F., Corriveau, P., & Raake, A. (2011). Study of rating scales for subjective quality assessment of high-definition video. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 57(1), 1–14.
Tominaga, T., Hayashi, T., Okamoto, J., & Takahashi, A. (2010). Performance comparisons of subjective quality assessment methods for mobile video. In Quality of multimedia experience (QoMEX), 2010 second international workshop on, 21–23 June 2010 (pp. 82–87).
Dai, Q. (2011). A survey of quality of experience. In R. Lehnert (Ed.), Energy-Aware Communications (Vol. 6955, pp. 146–156, Lecture Notes in Computer Science). Berlin: Springer.
Hoßfeld, T., Tran-Gia, P., & Fiedler, M. (2007). Quantification of quality of experience for edge-based applications. Paper presented at the proceedings of the 20th international teletraffic conference on managing traffic performance in converged networks, Ottawa, Canada.
Takahashi, A., Hands, D., & Barriac, V. (2008). Standardization activities in the ITU for a QoE assessment of IPTV. IEEE Communications Magazine, 46(2), 78–84.
ITU-T (2004). Recommendation P.563: Single ended method for objective speech quality assessment in narrow-band telephony applications. International Telecommunication Union.
Mrvová, M., & Pocta, P. (2013). Quality estimation of synthesized speech transmitted over IP channel using genetic programming approach. In Digital technologies (DT), 2013 international conference on, 2013 (pp. 39–43): IEEE.
Zegarra Rodríguez, D., Lopes Rosa, R., & Bressan, G. (2013). Predicting the quality level of a VoIP communication through intelligent learning techniques. In ICDS 2013, the seventh international conference on digital society, 2013 (pp. 42–47).
Mitra, K., Zaslavsky, A., & Åhlund, C. (2011). Dynamic Bayesian networks for sequential quality of experience modelling and measurement. Smart Spaces and Next Generation Wired/Wireless Networking, pp. 135–146.
Menkovski, V., Exarchakos, G., Liotta, A., & Cuadra-Sánchez, A. (2011). A quality of experience management module. International Journal on Advances in Intelligent Systems, 4(1 and 2), 13–19.
Sun, L., Mkwawa, I.-H., Jammeh, E., & Ifeachor, E. (2013). VoIP quality of experience (QoE). In Guide to voice and video over IP Springer, Berlin (pp. 123–162).
Staelens, N., Moens, S., Van den Broeck, W., Marien, I., Vermeulen, B., Lambert, P., et al. (2010). Assessing quality of experience of IPTV and video on demand services in real-life environments. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 56(4), 458–466.
Jingjing, Z., & Ansari, N. (2011). On assuring end-to-end QoE in next generation networks: Challenges and a possible solution. IEEE Communications Magazine, 49(7), 185–191.
Rodrigues, C., Lima, S. R., Álvarez Sabucedo, L. M., & Carvalho, P. (2012). An ontology for managing network services quality. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(9), 7938–7946, doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2012.01.106
McNamara, N., & Kirakowski, J. (2011). Measuring user-satisfaction with electronic consumer products: The consumer products questionnaire. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 69(6), 375–386.
Dubey, R. K., & Kumar, A. (2013). Non-intrusive speech quality assessment using several combinations of auditory features. International Journal of Speech Technology, 16(1), 89–101.
Narwaria, M., Lin, W., McLoughlin, I. V., Emmanuel, S., & Chia, L.-T. (2012). Nonintrusive quality assessment of noise suppressed speech with mel-filtered energies and support vector regression. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 20(4), 1217–1232.
Assem, H., Malone, D., Dunne, J., & O’Sullivan, P. (2013). Monitoring VoIP call quality using improved simplified E-model. In Computing, networking and communications (ICNC), 2013 international conference on, 2013 (pp. 927–931): IEEE.
Kuan-Ta, C., Chi-Jui, C., Chen-Chi, W., Yu-Chun, C., & Chin-Laung, L. (2010). Quadrant of euphoria: A crowdsourcing platform for QoE assessment. Network, IEEE, 24(2), 28–35.
Wu, W., Arefin, A., Rivas, R., Nahrstedt, K., Sheppard, R., & Yang, Z. (2009). Quality of experience in distributed interactive multimedia environments: Toward a theoretical framework. Paper presented at the proceedings of the 17th ACM international conference on Multimedia, Beijing, China.
Reichl, P., Stiller, B., & Tuffin, B. (2009). Network economics for next generation networks. In 6th international workshop on internet charging and QoS technologies, ICQT 2009, Aachen, Germany, May 11–15, 2009, proceedings, 2009 (vol. 5539) Springer, New York.
Ries, M., Fröhlich, P., & Schatz, R. (2011). OptiBand: Optimization of bandwdith fo IPTV video srteaming. D2.1: Criteria specification for the QoE research.
Karatepe, O. M. (2011). Service quality, customer satisfaction and loyalty: The moderating role of gender. Journal of Business Economics and Management, 12(2), 278–300.
Picard, R. W. (2003). Affective computing: Challenges. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 59(1–2), 55–64. doi:10.1016/s1071-5819(03)00052-1.
Picard, R. W. (2000). Affective computing. sl. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Bradley, M. M., & Lang, P. J. (2007). Emotion and motivation. Handbook of Psychophysiology, 3, 587–589.
Russell, J. A., & Mehrabian, A. (1977). Evidence for a three-factor theory of emotions. Journal of Research in Personality, 11(3), 273–294. doi:10.1016/0092-6566(77)90037-x.
Knapp, R. B., Kim, J., & André, E. (2011). Physiological signals and their use in augmenting emotion recognition for human-machine interaction. In Emotion-oriented systems Springer, Berlin, pp. 133–159.
Reiter, U., & De Moor, K. (2015) Content categorization based on implicit and explicit user feedback: Combining self-reports with EEG emotional state analysis. In Quality of multimedia experience (QoMEX), 2012 fourth international workshop on, 2012 (pp. 266–271): IEEE.
Gunes, H., & Pantic, M. (2010). Automatic, dimensional and continuous emotion recognition. International Journal of Synthetic Emotions (IJSE), 1(1), 68–99.
Huang, Y.-P., & Huang, K.-N. (2013). Monitoring of breathing rate by a piezofilm sensor using pyroelectric effect. In Orange technologies (ICOT), 2013 international conference on, 2013 (pp. 99–102): IEEE.
Wu, D., Liu, G.-Z., Wong, M., & Zhang, Y.-T. (2010). The accuracy of respiratory rate estimation using electrocardiography and photoplethysmography. In Information technology and applications in biomedicine (ITAB), 2010 10th IEEE international conference on, 2010 (pp. 1–3): IEEE.
Wu, D., Yang, P., Liu, G.-Z., & Zhang, Y.-T. (2012). Automatic estimation of respiratory rate from pulse transit time in normal subjects at rest. In Biomedical and health informatics (BHI), 2012 IEEE-EMBS international conference on, 2012 (pp. 779–781): IEEE.
ITU-T, R. P. (1996). 920, Interactive test methods for audiovisual communications. International Telecommunications Union Radiocommunication Assembly.
Raake, A. (2007). Speech quality of VoIP: Assessment and prediction. Wiley. com.
Kim, K. H., Bang, S., & Kim, S. (2004). Emotion recognition system using short-term monitoring of physiological signals. Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing, 42(3), 419–427.
Žliobaitė, I., Bifet, A., Pfahringer, B., & Holmes, G. (2013). Active learning with drifting streaming data. Neural Networks and Learning Systems, IEEE Transactions on, (99), 1–1, doi:10.1109/tnnls.2012.2236570.
Domingos, P., & Hulten, G. (2000). Mining high-speed data streams. In Proceedings of the sixth ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining (pp. 71–80) ACM.
Broek, E. L. (2011). Affective signal processing (ASP): Unraveling the mystery of emotions.
Chen-Chi, W., Kuan-Ta, C., Yu-Chun, C., & Chin-Laung, L. (2013). Crowdsourcing multimedia QoE evaluation: A trusted framework. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 15(5), 1121–1137. doi:10.1109/tmm.2013.2241043.
Keimel, C., Habigt, J., Horch, C., & Diepold, K. (2012). QualityCrowd: A framework for crowd-based quality evaluation. In Picture coding symposium (PCS), 2012 (pp. 245–248): IEEE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afshari, S., Movahhedinia, N. Non-Intrusive Online Quality of Experience Assessment for Voice Communications. Wireless Pers Commun 79, 2155–2170 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-1978-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-1978-6