Abstract
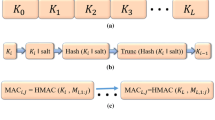
This paper introduces a new scheme that confronts one of the critical flaws of conditional access (CA) systems employed in satellite pay-TV, the long or infinite cryptoperiod of a master key (MK). Through the new scheme, which is based on Shamir’s secret sharing and Simmons’ prepositioned shared secret scheme, the administrator of the CA system is able to refresh the MKs of all the users by simply broadcasting a common message of 256 bits. As a result, the vulnerabilities introduced by the long or infinite cryptoperiod of MKs are alleviated. Newton interpolation (NI) is utilized to accomplish the refreshment of the MK, and its scalability is fully exploited. Therefore, as it is verified by the implementation of NI on ATmega128, the MK can be refreshed in \(<\)0.05 s, depending on the desired security level. Moreover, the increase in the security that the new scheme provides is analyzed. A security comparison with the CA systems presented in the literature proves the superiority of the proposed scheme. Finally, the bandwidth overhead of the new scheme is estimated by comparing it to the bandwidth that is assigned to several modern CA systems of the pay-TV market, and it is proven to be negligible.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
EBU Project Group BKA. (1995). Functional model of a conditional access system. In EBU technical review (pp. 64–77). Winter.
ETR 289. (1996). Digital video broadcasting (DVB); Support for use of scrambling and conditional access (CA) within digital broadcasting systems.
Tews, E., Walde, J., & Weiner, M. (2011). Breaking DVB-CSA. In Western European workshop on research in cryptology (WEWoRC’11).
Wirt, K. (2005). Fault attack on the DVB common scrambling algorithm. In ICCSA 2005. LNCS (Vol. 3481, pp. 577–584). Heidelberg: Springer.
Oechslin, P. (2003). Making a faster cryptanalytic time-memory trade-off. In Advances in cryptology, CRYPTO 2003. Lecture notes in computer science (Vol. 2729. pp. 617–630). Berlin: Springer.
Li, W., & Gu, D. (2007). Security analysis of DVB common scrambling algorithm. In Data, privacy, and E-Commerce, ISDPE 2007, the first international symposium on (pp. 271–273).
ETSI EN 300 468 v. 1.5.1. (2003). Digital video broadcasting (DVB); Specification for service information (SI) in DVB systems.
Lee, W. (1996). Key Distribution and management for conditional access system on DBS. In Proceedings of international conference on cryptology and information security (pp. 82–86).
Tu, F. K., Laih, C. S., & Tung, H. H. (1999). On key distribution management for conditional access system on pay-TV system. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 45, 151–158.
Naor, D., Naor, M., & Lotspiech, J. (2001). Revocation and tracing schemes for stateless receivers. In J. Killian (Ed.), Advances in cryptology: Proceedings of the Crypto 01 (pp. 41–62).
Halevy, D., & Shamir, A. (2002). The LSD broadcast encryption scheme. In Proceedings of the Crypto 2002, volume 2442 of LNCS (pp. 47–60). Berlin: Springer.
Song, R., & Korba, L. (2003). Pay-TV system with strong privacy and non-repudiation protection. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 49, 408–413.
Sun, H. M., Chen, C. M., & Shieh, C. Z. (2008). Flexible-pay-per-channel: A new model for content access control in pay-TV broadcasting systems. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 10, 1109–1120.
Liu, B., Zhang, W., & Jiang, T. (2004). A scalable key distribution scheme for conditional access system in digital pay-TV system. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 50, 632–637.
Jiang, T., Zheng, S., & Liu, B. (2004). Key distribution based on hierarchical access control for conditional access system in DTV broadcast. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 50(1), 225–230.
Huang, Y.-L., Shieh, S., Ho, F.-S., & Wang, J.-C. (2004). Efficient key distributions schemes for secure media delivery in pay-TV systems. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 6(5), 760–769.
Wong, C. K., Gouda, M., & Lam, S. S. (2000). Secure group communications using key graphs. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 8(1), 16–30.
Barker, E., Barker, W., Burr, W., Polk, W., & Smid, M. (2007). Recommendation for key management—Part 1: General (Revised). NIST Special Publication 800-57.
Biham, E., & Shamir, A. (1993). Differential cryptanalysis of the data encryption standard. Berlin: Springer.
Matsui, M. (1994). Linear cryptanalysis method for DES cipher. In Advances in cryptology: Proceedings of the EUROCRYPT ’93, LNCS 765 (pp. 386–397). Berlin: Springer.
Biryukov, A., & Wagner, D. (1999). Slide attacks fast software encryption. In FSE’99, LNCS 1636 (pp. 245–259).
Biham, E., Dunkelman, O., & Keller, N. (2001). The rectangle attack—Rectangling the serpent. In Advances in cryptology: EUROCRYPT’01, LNCS 2045 (pp. 340–357). Berlin: Springer.
Kocher, P. (1996). Timing attack on implementation of Diffie–Hellman, RSA, DSS and other systems. In Advances in cryptology: Proceedings of the CRYPTO ’96 (pp. 104–113). Berlin: Springer.
Kocher, P., Jaffe, J., & Jun, B. (1999). Differential power analysis. In: Proceedings of the CRYPTO (pp. 388–397).
Gandolfi, K., Mourtel, C., & Olivier, F. (2001). Electromagnetic attacks: Concrete results. In Proceedings of CHES (pp. 252–261).
Quisquater, J., & Samyde, D. (2001). Electromagnetic analysis (EMA): Measures and countermeasures for smart cards. In Proceedings e-Smart (pp. 200–210).
Rao, J. R., & Rohatgi, P. (2001). EMpowering side-channel attacks. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive, 2001, 37.
Shamir, A. (1979). How to share a secret. Communications of the ACM, 22(11), 612–613.
Simmons, G. J. (1990). Prepositioned shared secret and/or shared control schemes. In Lecture notes in computer science (Vol. 434, pp. 436–467). Berlin: Springer.
Spaliaras, I., & Dokouzyannis, S. (2013). A novel key refreshment scheme increasing the security of conditional access systems in digital satellite pay-TV. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 59(3), 571–577.
Skorobogatov, S. (2005). Semi-invasive attacks—A new approach to hardware security analysis. Technical report. University of Cambridge, Computer Laboratory.
Kömmerling, O., & Kuhn, M. (1999). Design principles for tamper-resistant smartcard processors. In Proceedings of the USENIX workshop on smartcard technology on USENIX workshop on smartcard technology. USENIX Association.
Boneh, D., DeMillo, R., & Lipton, R. (1997). On the importance of checking cryptographic protocols for faults. In W. Fumy (Ed.), Advances in cryptology—EUROCRYPT ’97, volume 1233 of lecture notes in computer science (pp. 37–51). Berlin: Springer.
Boneh, D., DeMillo, R., & Lipton, R. (2001). On the importance of checking cryptographic protocols for faults. Journal of Cryptology, 14(2), 101–119.
Blömer, J., & Seifert, J.-P. (2003). Fault based cryptanalysis of the advanced encryption standard (AES). In R. N. Wright (Ed.), Financial cryptography—FC 2003, volume 2742 of lecture notes in computer science (pp. 162–181). Berlin: Springer.
Amiel, F., Clavier, C., & Tunstall, M. (2006). Collision fault analysis of DPA-resistant algorithms. In L. Breveglieri, I. Koren, D. Naccache, & J.-P. Seifert (Eds.), Fault diagnosis and tolerance in cryptography 2006—FDTC 06, volume 4236 of lecture notes in computer science (pp. 223–236). Berlin: Springer.
Bar-El, H., Choukri, H., Naccache, D., Tunstall, M., & Whelan, C. (2006). The sorcerer’s apprentice guide to fault attacks. Proceedings of the IEEE, 94(2), 370–382.
Samyde, D., Skorobogatov, S. P., Anderson, R. J., & Quisquater, J.-J. (2002). On a new way to read data from memory. In Proceedings of the first international IEEE security in storage workshop (pp. 65–69).
Chang, H. (2004). International data encryption algorithm. In CS-627-1 Fall.
Rivest, R., & Ronald, L. (1995). The RC5 encryption algorithm. In Fast software encryption (pp. 86–96). Berlin: Springer.
Miyaguchi, S., Shiraishi, A., & Shimizu, A. (1988). Fast data encryption algorithm FEAL-8. Review of Electrical Communications laboratories, 36(4), 433–437.
Tunstall, M., Mukhopadhyay, D., & Ali, S. (2011). Differential fault analysis of the advanced encryption standard using a single fault. In Information security theory and practice, security and privacy of mobile devices in wireless communication (pp. 224–233). Berlin: Springer.
Kogan, N., & Tassa, T. (2006). Improved efficiency for revocation schemes via Newton interpolation. ACM Transactions on Information and System Security, 9(4), 461–486.
Asharov, G., & Lindell, Y. (2011). A full proof of the BGW protocol for perfectly-secure multiparty computation. In Electronic colloquium on computational complexity (ECCC) (Vol. 18, p. 36), http://dblp.uni-trier.de
Atmel, 8 bit AVR Microcontroller ATmega128(L) Manual, v. 2467M-AVR-11/04, November 2004.
Seroussi, G. (1998). Table of low-weight binary irreducible polynomials. HP Labs Technical Report HPL-98-135. Computer Systems Laboratory.
Hinkelmann, H., Zipf, P., Li, J., Liu, G., & Glesner, M. (2009). On the design of reconfigurable multipliers for integer and Galois field multiplication. Microprocessors and Microsystems, 33(1), 2–12.
Rodrıguez-Henrıquez, F., Saqib, N. A., & Dıaz-Pérez, A. (2004). A fast parallel implementation of elliptic curve point multiplication over GF(2m). Microprocessors and Microsystems, 28(5–6), 329–339.
Loi, K. C., & Ko, S.-B. (2013). High performance scalable elliptic curve cryptosystem processor for Koblitz curves. Microprocessors and Microsystems, 37(4–5), 394–406.
Järvinen, K., & Skyttä, J. (2009). Fast point multiplication on Koblitz curves: Parallelization method and implementations. Microprocessors and Microsystems, 33(2), 106–116.
Zhang, Y., Chen, D., Choi, Y., Chen, L., & Ko, S.-B. (2010). A high performance ECC hardware implementation with instruction-level parallelism over GF(2\(^{163}\)). Microprocessors and Microsystems, 34(6), 228–236.
Gura, N., Patel, A., Wander, A., Eberle, H., & Shantz, S. C. (2004). Comparing elliptic curve cryptography and RSA on 8-bit CPUs. In M. Joye & J.-J. Quisquater (Eds.), Workshop on cryptographic hardware and embedded systems (CHES’04), LNCS (Vol. 3156, pp. 119–132). Berlin: Springer.
Hutter, M., & Wenger, E. (2011). Fast multi-precision multiplication for public-key cryptography on embedded microprocessors. In B. Preneel & T. Takagi (Eds.), Cryptographic hardware and embedded systems—CHES 2011, LNCS (Vol. 6917, pp. 459–474). Berlin: Springer.
Comba, P. (1990). Exponentiation cryptosystems on the IBM PC. IBM Systems Journal, 29(4), 526–538.
Scott, M., & Szczechowiak P. (2007). Optimizing multiprecision multiplication for Public Key Cryptography. Cryptology ePrint Archive, Report 2007/299.
López, J., & Dahab, R. (2000). High-speed software multiplication in GF(2m). In B. K. Roy & E. Okamoto (Eds.), First international conference in cryptology in India (INDOCRYPT’00), LNCS (Vol. 1977, pp. 203–212). Berlin: Springer.
Szczechowiak, P., Kargl, A., Scott, M., & Collier, M. (2009). On the application of pairing based cryptography to wireless sensor networks. In D. A. Basin, S. Capkun, & W. Lee (Eds.), Second ACM conference on wireless network security (WISEC’09) (pp. 1–12). ACM Press.
Lim, C. H., & Lee, P. J. (1994) More flexible exponentiation with precomputation. In Y. G. Desmedt (Ed.), Advances in cryptology—CRYPTO ’94. LNCS 839 (pp. 95–107).
Rodrıguez-Henrıquez, F., & Koç, Ç. K. (2003). on fully parallel karatsuba multipliers for GF(2m). In International conference on computer science and technology (CST 2003), Cancun, Mexico.
Schroeppel, R., Orman, H., O’Malley, S., & Spatscheck, O. (1995). Fast key exchange with elliptic curve systems. In Advances in cryptology—CRYPTO ’95. Lecture notes in computer science (Vol. 963, pp. 43–56).
Fong, K., Hankerson, D., López, J., & Menezes, A. (2004). Field inversion and point halving revisited. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 53(8), 1047–1059.
Shantz, S. C. (2001). From Euclid’s GCD to montgomery multiplication to the great divide. SML Technical Report SMLI TR-2001-95, Sun Microsystems Laboratories.
Schroeppel, R. (2002). Automatically solving equations in finite fields. US Patent Application No. 09/834,363, filed 12 April 2001, publication number US 2002/0055962 A1.
Goodman, J., & Chandrakasan, A. (2000). An energy efficient reconfigurable public-key cryptography processor architecture. In Cryptographic hardware and embedded systems—CHES 2000, lecture notes in computer science 1965 (pp. 175–190).
Eskicioglu, A. M., & Delp, E. (2002). A key transport protocol based on secret sharing applications to information security. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 48(4), 816–824.
ETSI EN 302 307. (2006). Digital video broadcasting (DVB); Second generation framing structure, channel coding and modulation systems for broadcasting, interactive services news gathering and other broadband satellite applications.
EN 300 421. (2008). Digital video broadcasting (DVB); Framing structure, channel coding and modulation for 11/12 GHz satellite services.
ISO/IEC 13818-1. (2000). Information technology generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information: Systems.
ISO/IEC-14496-1. (2004). Generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio system.
TS 101 197-1. (1997). Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB); Technical specification of SimulCrypt in DVB systems.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spaliaras, I., Dokouzyannis, S. Design and Evaluation of a New Scheme Based on Secret Sharing Mechanisms that Increases the Security of Conditional Access Systems in Satellite Pay-TV. Wireless Pers Commun 82, 1461–1481 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2293-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2293-6