Abstract
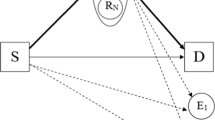
A two-hop relaying system for secrecy cooperative communication in the presence of an eavesdropper is investigated, where each relay node is equipped with a unitary matrix and cooperates to transmit the received signals, which can partly mitigate the deep channel fade. Gaussian distributed artificial noise (AN) is added in the null space of the intended receiver to ensure the secrecy of communication and achieve a better secrecy capacity while only the wiretap channel is degraded. The secrecy capacity and the optimal power distribution are studied in two scenarios, AN added by the transmitter and AN added by the cooperative relay nodes. Also, a sub-optimal power distribution strategy independent of the channel state information of eavesdropper is proposed to alleviate the computational overhead. The analytical results are confirmed by simulations that it is better to distribute more power to the available signals if the main channel is better, while more power to AN if the wire-tap channel is better. The sub-optimal power distribution can attain close performance compared with the optimal power distribution strategy but with substantially reduced computational complexity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wyner, A. D. (1975). The wire-tap channel. Bell System Technical Journal, 54(8), 1355–1387.
Leung-Yan-Cheong, S. K., & Hellman, M. E. (1978). The Gaussian wire-tap channel. IEEE Transaction on Information Theory, 24(4), 451–456.
Liang, Y., & Poor, H. V. (2008). Generalized multiple access channels with confidential messages. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 54(3), 976–1002.
Liu, R., Maric, I., Yates, R. D., & Spasojevic, P. (2006). The discrete memoryless multiple access channel with confidential messages. In IEEE international symposium on information theory (pp. 957–961).
Sendonaris, A., Erkip, E., & Aazhang, B. (2003). User cooperation diversity-Part I: System description. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 51(11), 1927–1938.
Sendonaris, A., Erkip, E., & Aazhang, B. (2003). User cooperation diversity-Part II: Implementation aspects and performance analysis. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 51(11), 1939–1948.
Yang, B., Wang, W., & Yao, B. (2013). Destination assisted secret wireless communication with cooperative helpers. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 20(11), 1032–1035.
Zheng, G., Krikidis, I., & Li, J. (2013). Improving physical layer secrecy using full-duplex jamming receivers. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 61(20), 4962–4974.
Jin, H., Shin, W.-Y., & Jung, B. C. (2013). On the multi-user diversity with secrecy in uplink wiretap networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 17(9), 1778–1781.
Yang, N., Yeoh, P. L., & Elkashlan, M. (2013). MIMO wiretap channels: Secure transmission using transmit antenna selection and receive generalized selection combining. IEEE Communications Letters, 17(9), 1754–1757.
Jemin, L., Andrea, C., & Alberto, R. (2013). Distributed network secrecy. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 31(9), 1889–1990.
Negi, R., & Goel, S. (2005). Secret communication using artificial noise. In IEEE vehicular technology conference (Vol. 3, pp. 1906–1910).
Zhu, J. G., Mo, J. H., & Tao, M. X. (2010). Cooperative secret communication with artificial noise in symmetric interference channel. IEEE Communications Letters, 14(10), 885–887.
Goeckel, D., Vasudevan, S., Towsley, D., et al. (2011). Artificial noise generation from cooperative relays for everlasting secrecy in two-hop wireless networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 29(10), 2067–2076.
Li, Q., & Ma, W.-K. (2011). A robust artificial noise aided transmit design for MISO secrecy. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 3436–3439).
Ding, Z., Peng, M., & Chen, H.-H. (2012). A general relaying transmission protocol for MIMO secrecy communications. IEEE Transactions on Wireless communications, 60(11), 3461–3471.
Yang, Y.-C., Zhao, H., Sun, C., et al. (2013). Joint power allocation and relay selection for decode-and-forward cooperative relay in secure communication. The Journal of China Universities of Posts and Telecommunications, 20(2), 79–85.
Lin, P.-H., Lai, S.-H., & Lin, S.-C. (2013). On secrecy rate of the generalized artificial noise assisted secure beamforming for wiretap channels. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 31(9), 1728–1740.
Muralidharan, V. T., & Rajan, B. S. (2012). Distributed space time coding for wireless two-way relaying. In IEEE global communications conference (GLOBECOM) (pp. 2455–2461).
Dong, L., Han, Z., Petropulu, P. A., et al. (2010). Improving wireless physical layer security via cooperating relays. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 58(3), 1875–1888.
Parada, P., & Blahut, R. (2005). The secrecy capacity of SIMO and slow fading channels. In International symposium on information theory, 2005. ISIT 2005. Proceedings (pp. 2152–2155).
Gerbracht, S., Scheunert, C., & Jorswieck, E. A. (2012). Secrecy outrage in MISO systems with partial channel information. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 7(2), 704–716.
Li, J., & Pertropulu, A. P. (2011). On ergodic secrecy rate for Gaussian MISO wiretap channels. IEEE Transactions on Wireless communications, 10(4), 1176–1187.
Zhou, N., Chen, X., Li, C., & Xue, Z. (2013). Secrecy rate of two-hop AF relaying networks with an untrusted relay. Wireless Personal Communications, 75, 119–129.
Shafiee, S., & Ulukus, S. (2007). Achievable rates in Gaussian MISO channels with secrecy constraints. In IEEE international symposium on information theory (pp. 2466–2470).
Acknowledgments
The work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61371115 and 61262084), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, China (Grant Nos. 20114BAB201018 and 20132BAB201019), the Foundation for Young Scientists of Jiangxi Province (Jinggang Star) (Grant No. 20122BCB23002), the Research Foundation of the Education Department of Jiangxi Province (Grant No. GJJ14133), and the Opening Project of Shanghai Key Laboratory of Integrate Administration Technologies for Information Security (Grant No. AGK2014004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, N.R., Kang, Z.J. & Liang, X.R. Secure Cooperative Communication via Artificial Noise for Wireless Two-Hop Relaying Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 82, 1759–1771 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2311-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2311-8