Abstract
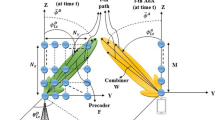
This paper addresses the problem of two-dimensional (2D) direction of arrival (DOA) estimation for monostatic multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radar equipped with arbitrary arrays manifold. A low-complexity multi-way compressive sensing (MCS) 2D DOA estimation algorithm is derived in this paper. To ease the computational burden, the received data are first arranged into a trilinear model, and then three random compression matrixes are individually applied to reduce each tensor to a much smaller tensor. Finally, the 2D DOA estimation problem then links to the low-dimensional trilinear model. The proposed algorithm has estimation performance close to that of the trilinear decomposition algorithm while it is more appealing form the perspective of storage capacity. Compared with other estimation algorithms, such as multiple signal classification, our MCS algorithm requires neither eigenvalue decomposition of the received signal covariance matrix nor spectral peak searching. It also doesn’t require array interpolation of the array geometry, therefore the proposed algorithm has much less computational load, which indicates the proposed algorithm will have wide application in the future for Massive MIMO systems.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fishler, E., Haimovich, A., Blum, R., Chizhik, D., Cimini, L., Valenzuela, R. (2004). MIMO radar: An idea whose time has come. In Proceedings of the IEEE radar conference (pp. 71–78).
Haimovich, A. M., Blum, R. S., & Cimini, L. J. (2008). MIMO radar with widely separated antennas. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 25(1), 116–129.
Zhang, X., Huang, Y., Chen, C., Li, J., & Xu, D. (2012). Reduced-complexity Capon for direction of arrival estimation in a monostatic multiple-input multiple-output radar. IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 6(8), 796–801.
Yan, H., Li, J., & Liao, G. (2008). Multitarget identification and localization using bistatic MIMO radar systems. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2008, 48.
Duofang, C., Baixiao, C., & Guodong, Q. (2008). Angle estimation using ESPRIT in MIMO radar. Electronics Letters, 44(12), 770–771.
Zhang, X., Xu, Z., Xu, L., & Xu, D. (2011). Trilinear decomposition-based transmit angle and receive angle estimation for multiple-input multiple-output radar. IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 5(6), 626–631.
Kruskal, J. B. (1977). Three-way arrays: rank and uniqueness of trilinear decompositions, with application to arithmetic complexity and statistics. Linear Algebra and its Applications, 18(2), 95–138.
Jon, A.B. (2002). Genetic algorithms as a tool for opportunistic phased array radar design. California Naval Postgraduate School.
Cao, Y., Zhang, Z., Dai, F., & Xie, R. (2011). Fast DOA estimation for monostatic MIMO radar with arbitrary array configurations. IEEE Radar Conference, 1, 959–962.
Cao, Y., Zhang, Z., Dai, F., & Xie, R. (2012). Direction of arrival estimation for monostatic multiple-input multiple-output radar with arbitrary array structures. IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 6(7), 679–686.
Chen, C., & Zhang, X. (2013). A low-complexity joint 2D-DOD and 2D-DOA estimation algorithm for MIMO radar with arbitrary arrays. International Journal of Electronics, 100(10), 1455–1469.
Friedlander, B. (1993). The root-MUSIC algorithm for direction finding with interpolated arrays. IEEE Transaction on Signal Processing, 30(1), 15–19.
Belloni, F., Richter, A., & Koivunen, V. (2007). DoA estimation via manifold separation for arbitrary array structures. IEEE Transaction on Signal Processing, 55(10), 4800–4810.
Rusek, F., Persson, D., Lau, B. K., Larsson, E. G., Marzetta, T. L., Edfors, O., & Tufvesson, F. (2013). Scaling up MIMO: Opportunities and challenges with very large arrays. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 30(1), 40–60.
Larsson, E., Edfors, O., Tufvesson, F., & Marzetta, T. (2014). Massive MIMO for next generation wireless systems. IEEE Communications Magazine, 52(2), 186–195.
Donoho, D. L. (2006). Compressed sensing. IEEE Transaction Information Theory, 52(4), 1289–1306.
Yao, Yu., Petropulu, A. P., & Poor, H. V. (2011). Measurement matrix design for compressive sensing-based MIMO radar. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 59(11), 5338–5352.
Jindong, Z., Daiyin, Z., & Gong, Z. (2013). Adaptive compressed sensing radar oriented toward cognitive detection in dynamic sparse target scene. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 60(4), 1718–1729.
Sidiropoulos, N. D., & Kyrillidis, A. (2012). Multi-way compressed sensing for sparse low-rank tensors. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 19(11), 757–760.
Renzheng, C., Xiaofei, Z., & Weiyang, C. (2014). Compressed sensing parallel factor analysis-based joint angle and Doppler frequency estimation for monostatic multiple-input–multiple-output radar. IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation, IET Radar Sonar Navigation, 8(6), 597–606.
Jiang, T., & Sidiropoulos, N. D. (2004). Kruskal’s permutation lemma and the identification of CANDECOMP/PARAFAC and bilinear models with constant modulus constraints. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 52(9), 2625–2636.
Stoica, P., & Nehorai, A. (1990). Performance study of conditional and unconditional direction-of-arrival estimation. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 38(10), 1783–1795.
Arias-Castro, E., & Eldar, Y. C. (2011). Noise folding in compressed sensing. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 18(8), 478–481.
Rossi, M., Haimovich, A. M., & Eldar, Y. C. (2014). Spatial compressive sensing for MIMO radar. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 62(2), 419–430.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by China NSF Grants (61071163, 61271327 and 61471191), Funding for Outstanding Doctoral Dissertation in NUAA (BCXJ14-08), Funding of Jiangsu Innovation Program for Graduate Education (KYLX_0277), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (3082015NP2015504), and partly funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PADA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, FQ., Zhang, G. Multi-way Compressive Sensing Based 2D DOA Estimation Algorithm for Monostatic MIMO Radar with Arbitrary Arrays. Wireless Pers Commun 85, 2393–2406 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2911-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2911-3