Abstract
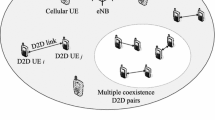
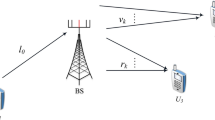
The introduction of device-to-device (D2D) communication may provide higher energy efficiency and spectrum efficiency to the traditional cellular network. One important question coming out of this introduction is how to select the transmission mode for user equipment (UE). In this work, we investigate the mode selection problem in a distributed way which gives a rule for determining the transmitter to use cellular transmission or D2D transmission. Firstly, the link performances are analyzed for UE under cellular transmission mode and D2D transmission mode, respectively, and closed-form expressions are presented. Then the optimum mode selection metric is derived to maximize the successful transmission probability for the transmission link. Lastly, a distributed mode selection scheme is proposed which can determine the transmission mode by UE itself without frequent information exchanges. In addition, the link performance can be optimized by using this scheme. Simulation results show that the link performance is dependent on many wireless environment factors such as numbers of existing D2D links and cellular links, channel quality, decoding threshold at the receiver and power control. However, the optimum link performance can be achieved by the proposed scheme under these different deployment conditions and wireless environments. Compared with the random mode selection methods, the proposed scheme can at most improve the link performance by seven times .









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doppler, K., Rinne, M. P., Janis, P., Ribeiro, C., & Hugl, K. (2009). Device-to-device communications; functional prospects for LTE-advanced networks. In 2009 IEEE international conference on communications workshops (ICC) (pp. 1–6).
Fodor, G., Dahlman, E., Mildh, G., & Parkvall, S. (2012). Design aspects of network assisted device-to-device communications. IEEE Communications Magazine, 50(3), 170–177.
Baccelli, F., Khude, N., Laroia, R., Li, J., Richardson, T., Shakkottai, S., et al. (2012). On the design of device-to-device autonomous discovery. In 2012 Fourth international conference on communication systems and networks (COMSNETS) (pp. 1–9).
Tang, H., Ding, Z., & Levy, B. C. (2014). Enabling D2D communications through neighbor discovery in LTE cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 62(19), 5157–5170.
Choi, K. W., & Han, Z. (2015). Device-to-device discovery for proximity-based service in LTE-advanced system. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 33(1), 55–66.
Gu, J., Bae, S. J., Choi, B.-G., & Chung, M. Y. (2011). Dynamic power control mechanism for interference coordination of device-to-device communication in cellular networks. In Proceedings of 3rd international conference ubiquitous future networks (pp. 71–75).
Wang, D., & Wang, X. (2014). Effective interference cancellation schemes for device-to-device multicast uplink period underlaying cellular networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 75(4), 2201–2216.
Yu, C.-H., Tirkkonen, O., Doppler, K., & Ribeiro, C. (2009). On the performance of device-to-device underlay communication with simple power control. In 2009 IEEE 69th vehicular technology conference (VTC) (pp. 1–5).
Kaufman, J. L., & Aazhang, B. (2013). Spectrum sharing scheme between cellular users and ad-hoc device-to-device users. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(3), 1038–1049.
Pei, Y., & Liang, Y.-C. (2013). Resource allocation for device-to-device communications overlaying two-way cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(7), 3611–3621.
Tsolkas, E. L., Passas, N., & Merakos, L. (2012). A graph-coloring secondary resource allocation for D2D communications in LTE networks. In 2012 IEEE 17th international workshop on computer aided modeling and design of communication links and networks (CAMAD) (pp. 56–60).
Xu, Y., Liu, Y., Yang, K., Li, D., & Luo, Q. (2013). Interference mitigation scheme for device-to-device communication with QoS constraint. In IEEE 24th international symposium on personal indoor and mobile radio communications (PIMRC) (pp. 1784–1788).
Min, S. H., Seo, W., Lee, J., Park, S., & Hong, D. (2011). Reliability improvement using receive mode selection in the device-to-device uplink period underlaying cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(2), 413–418.
Ma, C., Wu, W., Cui, Y., & Wang, X. (2015). On the performance of successive interference cancellation in D2D-enabled cellular networks. In IEEE INFOCOM (pp. 1–9).
ElSawy, H., Hossain, E., & Alouini, M.-S. (2014). Analytical modeling of mode selection and power control for underlay D2D communication in cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 62(11), 4147–4161.
Xiao, X., Tao, X., & Lu, J. (2011). A qos-aware power optimization scheme in ofdma systems with integrated device-to-device (D2D) communications. In Proceedings of IEEE vehicular technology conference (pp. 1–5).
Xingqin, L. T. X., & Andrews, J. G. (2013). Optimal spectrum partition and mode selection in device-to-device overlaid cellular networks. In 2013 IEEE global communications conference (GLOBECOM) (pp. 1837–1842).
Doppler, K., Yu, C.-H., Ribeiro, C. B., & Janis, P. (2010). Mode selection for device-to-device communication underlaying an LTE-advanced network. In 2010 IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC) (pp. 1–6).
Hakola, S., Chen, T., Lehtomaki, J., & Koskela, T. (2010). Device-to-device (D2D) communication in cellular network—Performance analysis of optimum and practical communication mode selection. In 2010 IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC) (pp. 1–6).
Andrews, J. G., Claussen, H., Dohler, M., Rangan, S., & Reed, M. C. (2012). Femtocells: Past, present, and future. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 30(3), 497–508.
Stoyan, D., Kendall, W. S., Mecke, J., & Hoboken. (1995). Stochastic geometry and its applications (2nd ed.). Hoboken: Wiley.
Jeffrey, A., & Zwillinger, D. (2007). Table of integrals, series, and products (7th ed.). Waltham: Academic Press.
3GPP Technical Report 36.843. Technical report, 3GPP WG RAN1 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y. A Distributed Mode Selection Scheme for Device-to-Device Communications. Wireless Pers Commun 90, 639–655 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-3141-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-3141-4