Abstract
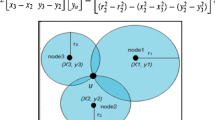
It is a crucial factor to determine the locations of the sensor nodes accurately and promptly. It affects the stability of connections among sensors significantly since the routes between signal source and its destination can be established within a minimum time when they are required. To this end it can be achieved through the measurement of the bi-directional channel qualities among the nodes after the locations of the sensor nodes are temporarily placed. For the 1st stage the piconet-type sensor networks are considered to measure the channel qualities between a specific node and the cluster node of the master node. After completing the 1st stage measurement the nodes needing the relay nodes are selected and the measurement action enters into the 2nd stage. In the 2nd stage the measurement between a candidate relay node and the node with a relay node is initiated. After the 2nd stage the relay nodes connecting to the cluster node are determined and the information delivery paths between a node and the cluster head are established. The feasibility of the proposed scheme has been checked by gathering and analyzing the measurement results in the realistic environment to show that the measurement procedure can be applied in the wireless indoor shipboard networks. The indoor propagation characteristics measurement and location determination scheme based on signature sequences can be reliably applied to the shipboard indoor sensor networks.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao, X., Tufvesson, F., Edfors, O., & Rusek, F. (2012). Measured propagation characteristics for very-large MIMO at 2.6 GHz. In 2012 Conference record of the 46th Asilomar conference on signals, systems and computers (ASILOMAR) (pp. 295–299).
Hoydis, J., Hoek, C., Wild, T., & Brink, S. (2012). Channel behavior for very-large MIMO systems—initial characterization. Bristol: COST IC1004.
Pu, D., & Wyglinski, A. M. (2013). Digital communication systems engineering with Software-Defined radio, Artech House.
Goldsmith, A. (2005). Wireless communications. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Tarokh, V., Seshadri, N., & Calderbank, A. R. (1998). Space time codes for high data rate wireless communications: Performance criterion and code construction. IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 44, 744–765.
Proakis, J. (1995). Digital communications (3rd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2014R1A1A2053294).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heo, S.W., Kim, JH. Measurements Data-Based Location Determination for Characterizing Indoor Signal Propagations of the Shipboard Sensor Nodes. Wireless Pers Commun 90, 1405–1412 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3400-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3400-z