Abstract
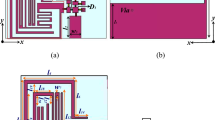
This paper presents a novel beamforming antenna array that combines pattern and polarization diversity for indoor cognitive radio systems. This combination is set to meet two goals. In order to reduce interference between users in cognitive radio networks by using pattern diversity, and to mitigate multipath fading in indoor environments by employing polarization diversity, so as to enhance the capacity and the reliability of communication link. The proposed structure is simulated, optimized, and its performance is verified by experiments. Measured results show that the proposed structure achieves an impedance bandwidth from 2.2 to 3.2 GHz, which covers the IEEE 802.11 b/g/n and WiMAX bands. By switching the input port, the antenna system can produce four beams at \(\pm 15^\circ\) and \(\pm 45^\circ\) that have circular polarization diversity; two of them have left-hand circular polarization and the other two beams have right-hand circular polarization. Moreover, radiation patterns with low cross-polarization level, good axial ratio around the center frequency, and low envelope correlation coefficient across the operating band are obtained. The measured gain at 2.4 and 2.6 GHz are 5.3 and 6.6 dBi, respectively. All these proprieties make the proposed antenna system very suitable for future cognitive radio applications, particularly in dense urban and indoor environments, where the challenge of interference and multipath fading are a major concern.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Federal Communications Commission Spectrum Policy Task Force. (2002). Report of the Spectrum Efficiency Working Group. https://transition.fcc.gov/sptf/files/SEWGFinalReport_1
Mitola, J., & Maguire, G. Q, Jr. (1999). Cognitive radio: Making software radios more personal. IEEE Personal Communication, 6(4), 13–18.
Stavroulakis, P. (2003). Interference analysis and reduction for wireless systems. Boston: Artech House.
Otmani, M., & Lecours, M. (1996). Indoor radio measurements and simulations with polarization diversity. Wireless Personal Communications, 3(3), 243–256.
Yang, J. (2004). Spatial channel characterization for cognitive radios. MS Thesis, UC Berkeley.
Balanis, C. A., & Ioannides, P. I. (2007). Introduction to smart antennas. San Rafael: Morgan & Claypool.
Rotman, W., & Turner, R. (1963). Wide-angle microwave lens for line source applications. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 11(6), 623–632.
Ruze, J. (1950). Wide-angle metal-plate optics. In Proceedings of the IRE, 38, 852–855.
Hansen, R. (2009). Phased array antennas (2nd ed.). Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley.
Butler, J. (1965). Digital, matrix and intermediate-frequency scanning. IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation Society, 3, 66–70.
Nachouane, H., Najid, A., Tribak, A., & Riouch, F. (2014). Broadband \(4\times 4\) Butler matrix using wideband \(90^\circ\) hybrid couplers and crossovers for beamforming networks. In International conference on multimedia computing and systems, 1444–1448.
Hiranandani, M. A., & Kishk, A. A. (2005). Widening Butler matrix bandwidth within the X-band. IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation Society, 4A, 321–324.
Abdelghani, L., Denidni, T. A., & Nedil, M. (2012). Design of a new ultra-wideband \(4\times 4\) Butler matrix for beamforming antenna applications. IEEE international symposium on antennas and propagation society, pp. 2–3.
He, J., Wang, B.-Z., He, Q.-Q., Xing, Y.-X., & Yin, Z.-L. (2007). Wideband X-band microstrip Butler matrix. Progress In Electromagnetics Research, 74, 131–140.
Kumar, S., Tannous, C., & Danshin, T. (1995). Multisection broadband impedance transforming branch-line hybrid. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 43(11), 2517–2523.
Wang, J., Lv, Z., & Li, X. (2014). Analysis of MIMO diversity improvement using circular polarized antenna. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2014(1), 1–9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/570923.
Dietrich, C. B., Dietze, K., Nealy, J. R., & Stutzman, W. L. (2001). Spatial, polarization, and pattern diversity for wireless handheld terminals. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 49(9), 1271–1281.
Cox, D. (1983). Antenna diversity performance in mitigating the effects of portable radiotelephone orientation and multipath propagation. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 31(5), 620–628.
Yang, F., & Rahmat, S. (2002). A reconfigurable patch antenna using switchable slots for circular polarization diversity. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 12(3), 96–98.
Han, J. H., & Myung, N. H. (2014). Novel feed network for circular polarization antenna diversity. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 13, 979–982.
Kim, Y. J., Kim, J. K., Kim, J. H., & Lee, H. M. (2007). Reconfigurable annular ring slot antenna with circular polarization diversity. In Asia-Pacific microwavce conference proceedings.
Khaleghi, A., & Kamyab, M. (2009). Reconfigurable single port antenna with circular polarization diversity. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 57(2), 555–559.
Chen, A., Yang, C., Chen, Z., Zhang, Y., & He, Y. (2012). Design of multilevel sequential rotation feeding networks used for circularly polarized microstrip antenna arrays. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2012(1), 1–10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/304816.
Sun, L., Ou, G., Lu, Y., & Tan, S. (2008). Axial ratio bandwidth of a circularly polarized microstrip antenna. In Ahmed Kishk (Ed.), Advancement in microstrip antennas with recent applications. In Tech. doi:10.5772/54664.
Bhowmik, W., Srivastava, S., & Prasad, L. (2014). Design of a low cost \(4\times 4\) Butler matrix fed antenna array partially loaded with substrate integrated waveguide (SIW). International Journal of Microwave and Optical Technology, 9(3), 227–236.
Tseng, C.-H., Chen, C.-J., & Chu, T.-H. (2008). A low-cost 60-GHz switched-beam patch antenna array with Butler matrix network. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 7, 432–435.
Abdelghani, M. L. (2012). Conception et ralisation d’un systme rseau d’antennes ultra large bande formation de faisceaux bas sur la matrice de Butler. M.S. thesis, Institut national de la recherche scientifique, Universit du Qubec.
Denidni, T. A., & Libar, T. E. (2003). Wide band four-port butler matrix for switched multibeam antenna arrays. 14th IEEE Proceedings on Personal Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, 3, 2461–2464.
Khan, O. U. (2006). Design of X-band \(4\times 4\) Butler matrix for microstrip patch antenna array. In IEEE region 10 conference TECOM, pp. 1–4.
Prieto, S. (2009). Diseo De Acopladores Direccionales De Microondas Para Matrices De Butler. M.S. thesis, Escuela Politecnica Superior, Universidad Autonoma De Madrid.
Wu, L. (2007). Planar multi-beam antenna for W-LAN. PhD thesis, Germany: University of Duisburg-Essen.
El-Tager, A. M. & Eleiwa, M. A. (2009). Design and implementation of a smart antenna using Butler matrix for ISM-band. In Progress in electromagnetics research symposium, Beijing, China, March 23–27.
Gao, S. S., Luo, Q., & Zhu, F. (2014). Circularly polarized antennas. West Sussex: Wiley.
Balanis, C. A. (2012). Antenna theory: Analysis and design. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley.
IEEE Standard Test Procedures for Antennas. IEEE Std 149-1965. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, AP-13, 437 (1965). Revised IEEE Std 149–1979.
Blanch, S., Romeu, J., & Corbella, I. (2003). Exact representation of antenna system diversity performance from input parameter description. Electronics Letters, 39(53), 705–707.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Departamento de Ingenieria de Comunicaciones (DICOM), University of Cantabria (UNICAN), Spain, for support with regard to simulation software and facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nachouane, H., Najid, A., Tribak, A. et al. Beamforming Antenna Array Combining Pattern and Polarization Diversity for Cognitive Radio Applications. Wireless Pers Commun 91, 957–973 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3507-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3507-2