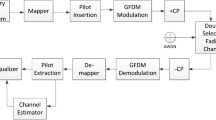
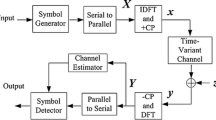
Abstract
This paper investigates the channel estimation in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing system under a fast-varying channel, by exploiting a frequency shifted complex exponential basis expansion models (CE-BEM). The conventional CE-BEM model suffers from power leakage and consequential modelling error floor, especially at the channel boundaries. The proposed BEM model reduces the leakage power efficiently by exploiting a fractional frequency on the coefficients of CE-BEM matrix. Numerical results show that the performance of the proposed channel modeling and coefficients estimation method are robust against various normalized Doppler frequency. The modeling error at the channel boundaries can be reduced substantially.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai, B., Shen, Y., Zhong, Z.-D., et al. (2011). Enhanced sampling clock offset correction based on time domain estimation scheme. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 57(2), 696–704.
Ai, B., Yang, Z.-X., Pan, C.-Y., et al. (2006). On the synchronization techniques for wireless OFDM system. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 52(2), 236–244.
Hrycak, T., Das, S., Matz, G., & Feichtinger, H. (2011). Practical estimation of rapid varying channels for DFDM system. IEEE Transactions on Communication, 59(11), 3040–3048.
Zhang, R., Ai, B., Yang, L., et al. (2014). A precoding and detection scheme for OFDM based wireless communication system in high speed environment. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 60(4), 558–566.
Ma, X., & Giannakis, G. B. (2003). Maximum-diversity transmission over doubly selective wireless channel. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 49(7), 1832–1840.
Shin, C., Andrews, J. G., & Power, E. J. (2007). An efficient design of doubly selective channel estimation for OFDM system. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 6(10), 3790–3802.
Schniter, P. (2004). Low-complexity equalization of OFDM in doubly selective channels. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 52(4), 1002–1011.
Ma, X., Giannakis, G. B., & Ohno, S. (2003). Optimal training for block transmissions over double-selective fading channel. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 51(5), 1351–1366.
Hijazi, H., & Ros, L. (2009). Polynomial estimation of time-varying multipath gains with interference mitigation in OFDM system. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 58(1), 140–151.
Tomasin, S., Grorkhov, A., Yang, H., & Linnartz, J. P. (2005). Iterative interference cancellation and channel estimation for OFDM. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 52(1), 238–245.
Hrycak, T., Das, S., Matz, G., & Feichtinger, H. (2010). Low complexity equalization for doubly selective channel modeled by basis expansion. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 58(11), 5706–5719.
Zemen, T., & Mecklenbrauker, C. F. (2005). Time variant channel estimation using discrete prolate spheroidal sequences. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 33(9), 3597–3607.
Tugnait, J. K., He, S., & Kim, H. (2010). Double selective channel estimation using exponential basis models and subblock tracking. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 58(3), 1275–1289.
Song, L., & Tugnait, J. K. (2009). Doubly-selective fading channel equalization: A comparison of the Kalman filter approach with the basis expansion model-based equalizers. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(1), 60–65.
Giannakis, G. B., & Tepedelenlioglu, C. (2002). Basis expansion models and diversity techniques for blind identification and equalization over time-varying channel. Proceedings of the IEEE, 86(10), 1969–1986.
Thoen, S., Perre, L. V., & Engles, M. (2002). Modeling the channel time variance for fixed wireless communication. IEEE Communications Letters, 6(8), 331–333.
Tang, Z., Cannizzaro, R. C., Leus, G., & Banelli, P. (2007). Pilot-assisted time-varying channel estimation for OFDM system. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 55(5), 2226–2238.
Ma, Y., & Tafazolli, R. (2007). Channel estimation for OFDMA uplink: A hybrid of linear and BEM interpolation approach. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 55(4), 1568–1573.
Barhumi, I., Leus, G., & Moonen, M. (2005). Time-varying FIR equalization for douby selective channel. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 4(1), 202–214.
Wang, G., Gao, F., Chen, W., & Tellambura, C. (2011). Channel estimation and training design for two-way relay network in time-selective fading enviroments. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(8), 2681–2691.
Rabbi, M. F., Hou, S., & Ko, C. C. (2010). High mobility OFDMA channel estimation using basis expansion model. IET Communications, 4, 353–367.
Leus, G. (2004). On the estimation of rapid time-varying channels. In Proceedings of the European signal processing conference (pp. 2227–2233).
Cui, T., Tellambura, C., & Wu, Y. (2005). Low-complexity pilot-aided channel estimation for OFDM system over doubly-selective channels. In Proceedings of the IEEE ICC (Vol. 3, pp. 1980–1984).
Barhumi, I., & Moonen, M. (2009). MLSE and MAP equalization for transmission over doubly selective channels. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 58(8), 4120–4128.
Carvalho, E., & Slock, D. (1997). Cramer-Rao Bounds for semi-blind, blind and training sequence based channel estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE signal processing workshop on signal processing advances in wireless communications (pp. 129–132).
Yong, D. J., & Beaulieu, N. C. (2000). The generation of correlated Rayleigh random variants by inverse discrete Fourier transform. IEEE Communications Magazine, 48(7), 1114–1127.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61222105, the National Key Technology R&D Program of China 2014ZX03001011-002, the Project of State Key Lab under Grant RCS2014ZT11, the Key Project of Chinese Ministry of Education under Grant 313006 and the NSFC under Grant U1334202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Ai, B. A Channel Estimation Method for OFDM Based Wireless Communication System in High Speed Environment. Wireless Pers Commun 94, 909–926 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3657-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3657-2